Velocity time graph for uniform motion
A graph plotted with time along the X-axis and the velocity along the Y-axis is called the velocity-time graph. The nature of the graph depends on the nature of the motion of the particle.
Viva Voce. To plot the velocity—time v — t graph for an object moving with uniform accelerations from a given set of v — t data and to determine the acceleration of the moving object and the distance moved by the object. An object is said to be in motion if it changes its position with time, with respect to its surroundings. The length of the actual path travelled by the object in motion in a given time is known as the distance travelled by the object. Different objects may take different amounts of time to cover a given distance.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
The velocity of a body in a uniformly accelerated motion increases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time. This also indicates that it moves at a constant acceleration. Such a graph, when plotted for a moving body, can provide a lot of information about the motion of the body, such as the type of motion, velocity, acceleration, and displacement. The slope is a measure of the steepness of a graph. Consider two points A and B in the position-time graph of a body in a uniform motion and let their coordinates be t 1 , v 1 and t 2 , v 2 , respectively, as shown in the figure below. In fact, the slope of a v-t graph at a particular instant gives the acceleration of the body at that instant. This is because the slope is the ratio of the change in velocity and change in time, which is equal to the velocity of the body. The velocity-time graph may look very different for different kinds of motion. Some of them are as follows:. An object moving at a uniform velocity covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
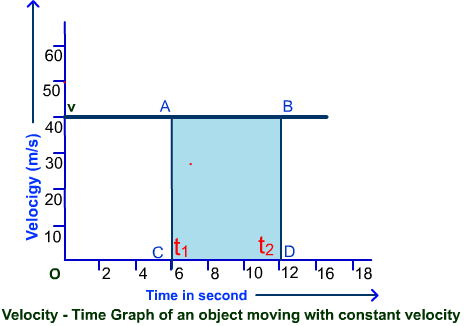
Uniform motion When an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion.
.
It serves as a foundational concept in physics, particularly in the study of mechanics. The purpose of this article is to give readers a thorough understanding of uniform acceleration by looking into its definition, characteristics, kinematic equations, graphical representations, and real-world examples. If the velocity of a body changes by an equal amount in an equal interval of time, however, small the interval may be then its acceleration is said to be uniform. In mathematical terms, uniform acceleration is defined by the equation:. Understanding the nuances of uniform acceleration becomes easier when we delve into its core characteristics. Here is a detailed breakdown:. Uniformly accelerated motion can be described using three fundamental kinematic equations: 1.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
Our study of 1-dimensional kinematics has been concerned with the multiple means by which the motion of objects can be represented. Such means include the use of words, the use of diagrams, the use of numbers, the use of equations, and the use of graphs. Lesson 4 focuses on the use of velocity versus time graphs to describe motion. As we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a velocity vs.
S43
The v-t graph of such a motion, when plotted, turns out to be a straight line passing through the origin if the body starts from rest with a positive slope. The slope of the v-t graph of a body moving with decreasing acceleration keeps decreasing as the steepness of the graph keeps decreasing. The v-t graph might also look different in other cases. We will learn about it in terms of balanced force and unbalanced force. Contents 1 Velocity time graph for uniform motion 1. Else, it may start from a point on the x or y -axis or any other point on the cartesian plane. Its v-t graph is a straight line parallel to the x-axis, as shown in the graph below. Velocity-time graph for such a motion is represented in the figure below. Mar 3, For example, the graph below shows the v-t graph of two bodies in uniform motion at different accelerations. An object in a uniformly and negatively accelerated motion decreases its velocity by equal amounts in equal intervals of time.
This article will cover the basics for interpreting motion graphs including different types of graphs, how to read them, and how they relate to each other. Interpreting motion graphs, such as position vs time graphs and velocity vs time graphs, requires knowledge of how to find slope.
As the SI unit for distance is meters and time is in seconds, the SI unit of speed is metre per second. The velocity-time graph for different cases is explained below. Assuming two points t 1 , v 1 and t 2 , v 2 , the slope or acceleration of object, If the acceleration of the object remains the same at all instants of time, then the object is said to be in uniformly accelerated motion. The v - t graph plotted here shows the motion of the object for a given range of time interval. The displacement covered by a body is equal to the area under its velocity-time graph. Non - uniform motion Motions where objects cover unequal distances in equal intervals of time are referred to as non-uniform motion. Uniform motion When an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion. Types of velocity -time graphs 4. Or we might need to find the displacement of the body in a section of the graph. Force: Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Introduction: In a tug of war, the one applying more force wins the game. In this session, we will discuss the basics of magnets and their properties, and the way they were and are used.

0 thoughts on “Velocity time graph for uniform motion”