Snowflake window function
Window snowflake window function in Snowflake allow you to perform calculations over a group of rows. They are similar to aggregate functionsbut window functions return a single value for every row instead of a single value for a group of rows.
Each time a window function is called, it is passed a row the current row in the window and the window of rows that contain the current row. The window function returns one output row for each input row. The output depends on the individual row passed to the function and the values of the other rows in the window passed to the function. Some window functions are order-sensitive. There are two main types of order-sensitive window functions:. For example, if you rank stores in descending order by profit per year, the store with the most profit will be ranked 1; the second-most profitable store will be ranked 2, etc. Window frame functions allow you to perform rolling operations, such as calculating a running total or a moving average, on a subset of the rows in the window.
Snowflake window function
Window functions operate on windows, which are groups of rows that are related e. This topic describes how to use the different types of window functions supported by Snowflake, including:. This document is aimed at readers who are not already fluent with window functions. Readers who are already fluent with these functions might find the reference material sufficient:. Window Functions. A window is a group of rows. A window can contain 0, 1, or multiple rows. All the rows in a window are related in some way, for example by location e. Functions categorized as window functions help answer different types of questions than scalar functions:. A query using a scalar function answers questions about a single row, using only data in that row. For example, suppose that you manage one branch of a chain of five stores. To calculate the profit of your store relative to other stores , the calculation must look at information not only about your store, but also about other stores.
These postings are my own and do not necessarily represent BMC's position, strategies, or opinion.
View all results. Snowflake supports windows functions. Think of windows functions as running over a subset of rows, except the results return every row. The topic of window functions in Snowflake is large and complex. This tutorial serves as a brief overview and we will continue to develop additional tutorials. This article is part of our Snowflake Guide. Use the right-hand menu to navigate.
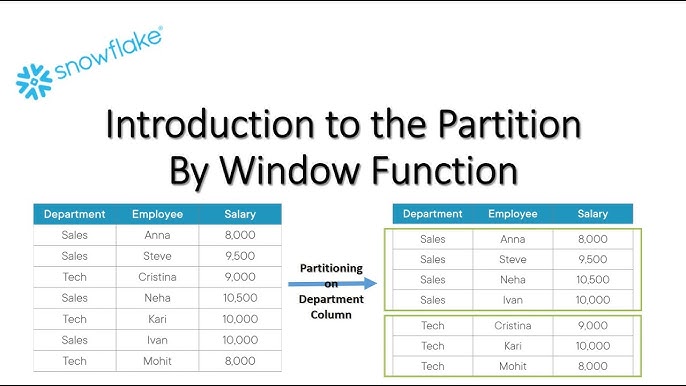
View all results. Snowflake supports windows functions. Think of windows functions as running over a subset of rows, except the results return every row. The topic of window functions in Snowflake is large and complex. This tutorial serves as a brief overview and we will continue to develop additional tutorials. This article is part of our Snowflake Guide. Use the right-hand menu to navigate. Snowflake defines windows as a group of related rows. It is defined by the over statement.
Snowflake window function
Each time a window function is called, it is passed a row the current row in the window and the window of rows that contain the current row. The window function returns one output row for each input row. The output depends on the individual row passed to the function and the values of the other rows in the window passed to the function. Some window functions are order-sensitive. There are two main types of order-sensitive window functions:. For example, if you rank stores in descending order by profit per year, the store with the most profit will be ranked 1; the second-most profitable store will be ranked 2, etc. Window frame functions allow you to perform rolling operations, such as calculating a running total or a moving average, on a subset of the rows in the window. Users who are not familiar with window functions, rank-related functions, or window frame functions might want to read the conceptual material in Using Window Functions. A window is a group of related rows.
Disfraz casero del mar
A window of related rows that includes that row. This is different from ordering the output of a query. In most situations, SQL is an explicit language. This topic describes how to use the different types of window functions supported by Snowflake, including:. Return a cumulative count, sum, min, and max, for rows in the specified window for the table:. The default is ascending. The query uses the OVER clause to create a window that contains the total sales of each salesperson. Snowflake defines windows as a group of related rows. Window frame functions allow you to perform rolling operations, such as calculating a running total or a moving average, on a subset of the rows in the window. To illustrate how window functions work, let's look at a few examples. In a graph of a week moving average of a stock price, the price shown for June 30th is not the price of the stock on June 30th, but the average price of the stock for the 13 weeks up to and including June 30th i.
Window functions operate on windows, which are groups of rows that are related e. This topic describes how to use the different types of window functions supported by Snowflake, including:. This document is aimed at readers who are not already fluent with window functions.
This book is for managers, programmers, directors — and anyone else who wants to learn machine learning. This smooths out day-to-day fluctuations and can make trends easier to recognize. All the rows in a window are related in some way, for example by location e. April 1st through June 30th. Note For clarity, Snowflake recommends avoiding implicit window frames. In a real world scenario, you would have years of data, so to calculate sums and averages for one specific week of data, you would need to use a one-week window, or use a filter similar to:. In most situations, SQL is an explicit language. This is different from ordering the output of a query. Users who are not familiar with window functions, rank-related functions, or window frame functions might want to read the conceptual material in Using Window Functions. The OVER clause specifies the window over which the function operates. Window functions behave differently; although the current row is passed as an argument the normal way, the window is passed through a separate clause, called an OVER clause. The query uses the OVER clause to create a window that contains the total sales of each salesperson. In the example below, the sliding window is usually two rows wide, but each time a new partition i. The output of the function depends upon:.

In my opinion you commit an error.