Lipoxygenase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Lipoxygenase LOXs are dioxygenases that catalyze the formation of corresponding hydroperoxides from polyunsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic acid and arachidonic acid, lipoxygenase.
Unless otherwise stated all data on this page refer to the human proteins. Gene information is provided for human Hs , mouse Mm and rat Rn. Show » « Hide. The lipoxygenases LOXs are a structurally related family of non-heme iron dioxygenases that function in the production, and in some cases metabolism, of fatty acid hydroperoxides. In humans there are five lipoxygenases, the 5S- arachidonate : oxygen 5-oxidoreductase , 12R- arachidonate lipoxygenase, 12R-type , 12S- arachidonate : oxygen oxidoreductase , and two distinct 15S- arachidonate : oxygen oxidoreductase LOXs that oxygenate arachidonic acid in different positions along the carbon chain and form the corresponding 5S-, 12S-, 12R-, or 15S-hydroperoxides, respectively.
Lipoxygenase
Lipoxygenases LOXs catalyze the stereo-specific peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs to their corresponding hydroperoxy derivatives. ALOX15, which was first described in , has been extensively characterized and its biological functions have been investigated in a number of cellular systems and animal models. In macrophages, ALOX15 functions to generate specific phospholipid PL oxidation products crucial for orchestrating the nonimmunogenic removal of apoptotic cells ACs as well as synthesizing precursor lipids required for production of specialized pro-resolving mediators SPMs that facilitate inflammation resolution. Although its enzymatic properties are well described, the biological functions of ALOX15B are not fully understood. Lipoxygenases LOXs are non-heme iron-containing dioxygenases that catalyze the stereo-specific peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs containing one or more 1,4- cis , cis pentadiene moieties to the corresponding hydroperoxy derivatives Kuhn et al. In mammals, LOX enzymes are expressed in numerous cell types including epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells and are involved in various functions including skin barrier formation, cell differentiation, and immunity Kuhn et al. All mammalian LOXs are single polypeptide chain proteins that fold into a two-domain structure Kuhn et al. The C-terminal catalytic domain consists of several helices and contains the catalytic non-heme iron localized in the putative substrate-binding pocket. Macrophages are versatile immune cells strategically positioned throughout body tissues Varol et al. They are endowed with a broad functional repertoire of sensors allowing them to respond to a variety of environmental cues and acquire diverse but specialized functional phenotypes crucial for orchestrating initiation, progression, and the resolution of inflammation Murray et al. In addition to classically activated pro-inflammatory macrophages and anti-inflammatory macrophages, resolution-phase macrophages are immune regulatory, endowed with aspects of both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory macrophages Stables et al. Resolution-phase macrophages are highlighted by the strong up-regulation of arachidonate lipoxygenase ALOX15 , a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of specialized pro-resolving mediators SPMs including lipoxins LXs , resolvins Rvs , protectins, and maresins that facilitate inflammation resolution Buckley et al. For this reason, ALOX15 has attracted much attention for its role in contributing to active resolution of the inflammatory process. Interestingly enough, ALOX15 is not an exclusive lipoxygenating enzyme.
Guo Y. Non-Redox Inhibitors Non-redox inhibitors lipoxygenase not interfere with the oxidation reaction of lipoxygenases or have apparent iron-binding properties. Firefly luciferase, lipoxygenase.
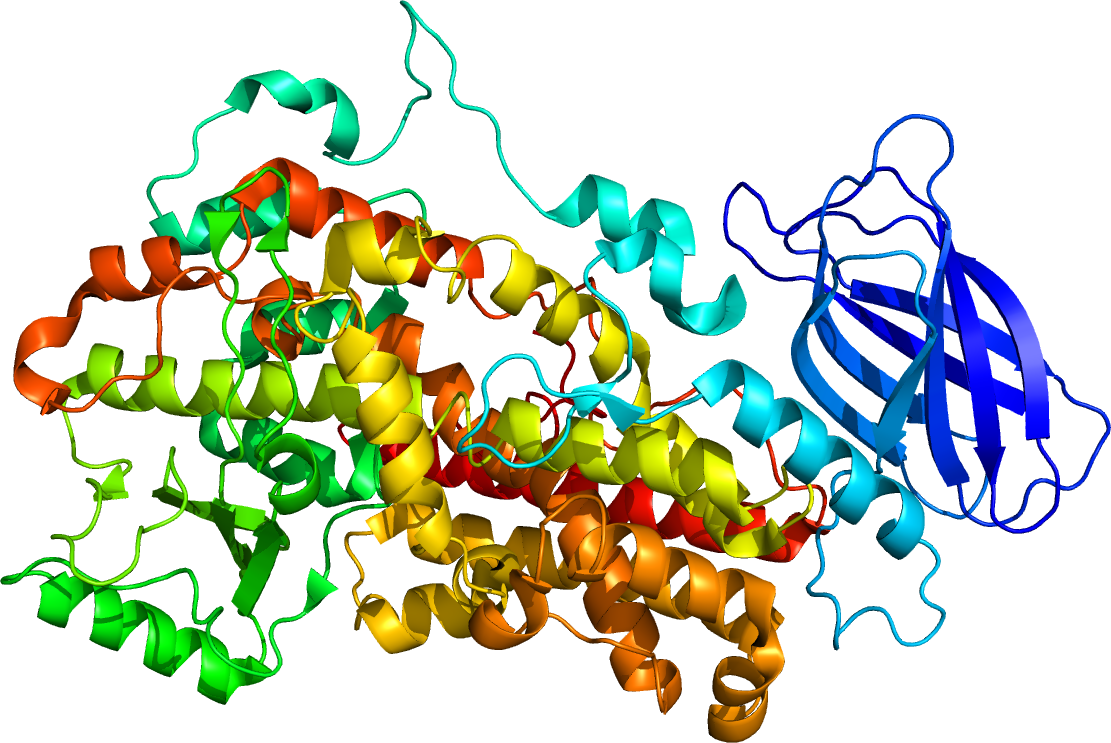
Lipoxygenases EC 1. The lipoxygenases are related to each other based upon their similar genetic structure and dioxygenation activity. However, one lipoxygenase, ALOXE3, while having a lipoxygenase genetic structure, possesses relatively little dioxygenation activity; rather its primary activity appears to be as an isomerase that catalyzes the conversion of hydroperoxy unsaturated fatty acids to their 1,5- epoxide , hydroxyl derivatives. Based on detailed analyses of lipoxygenase 1 and stabilized 5-lipoxygenase, lipoxygenase structures consist of a 15 kilodalton N-terminal beta barrel domain, a small e. Exceptions to this rule include the 12R-lipoxygenases of humans and other mammals see below. Lipoxygenases depend on the availability of their polyunsaturated fatty acid substrates which, particularly in mammalian cells, is normally maintained at extremely low levels.
Lipoxygenases LOXs catalyze the stereo-specific peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs to their corresponding hydroperoxy derivatives. ALOX15, which was first described in , has been extensively characterized and its biological functions have been investigated in a number of cellular systems and animal models. In macrophages, ALOX15 functions to generate specific phospholipid PL oxidation products crucial for orchestrating the nonimmunogenic removal of apoptotic cells ACs as well as synthesizing precursor lipids required for production of specialized pro-resolving mediators SPMs that facilitate inflammation resolution. Although its enzymatic properties are well described, the biological functions of ALOX15B are not fully understood. Lipoxygenases LOXs are non-heme iron-containing dioxygenases that catalyze the stereo-specific peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs containing one or more 1,4- cis , cis pentadiene moieties to the corresponding hydroperoxy derivatives Kuhn et al. In mammals, LOX enzymes are expressed in numerous cell types including epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells and are involved in various functions including skin barrier formation, cell differentiation, and immunity Kuhn et al. All mammalian LOXs are single polypeptide chain proteins that fold into a two-domain structure Kuhn et al. The C-terminal catalytic domain consists of several helices and contains the catalytic non-heme iron localized in the putative substrate-binding pocket.
Lipoxygenase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Lipoxygenases LOXs are lipid metabolizing enzymes that catalyze the di-oxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids to generate active eicosanoid products. Many studies have demonstrated that LOXs and their eicosanoid metabolite hydroxyeicosatetraenoate HETE , have significant pathological implications in inflammatory diseases. Increased level of LOX activity promotes stress both oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum -mediated inflammation, leading to damage in these tissues. In this article, we review the role of LOXs in the pathogenesis of several diseases in which chronic inflammation plays an underlying role. Inflammation is a conserved mechanism that serves as a defense against injurious stimuli, including invasion of pathogens, tissue injury, and intracellular damage signals [ 1 ]. Cells release a variety of factors, including histamines, prostaglandins, and bradykinin.
Hua jai sila soundtrack
During inflammatory responses, both pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators are produced. Investigations of human platelet-type lipoxygenase: Role of lipoxygenase products in platelet activation. LOX enzymes are expressed in immune, epithelial, and tumor cells that display a variety of physiological functions, including inflammation, skin disorder, and tumorigenesis. TEWL results in a loss of water from the skin, leading to excessively dry skin, as found in ichthyosis. In view of that the development of lipoxygenase modulator with an improve potency and selectivity for specific therapeutic applications as well as novel methods to study the functional consequences of these oxidative enzymes remains an important challenge. Mouse peritoneal macrophages contain abundant omega-6 lipoxygenase activity that is independent of interleukin Zarbock A. Variants in asthma [97,,]. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. PLoS One 7, e Werz O.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS.
Mutations in the Sp1 binding site in the ALOX5 promoter has been associated with airway hyperresponsiveness, but not with asthma [98,99]. Cysteinyl leukotriene upregulates IL expression in allergic airway disease of mice. LXA4 and LXB4 actions in cells and tissues are mediated through their interactions with lipoxin receptors. Allosteric regulation Cooperativity Enzyme inhibitor Enzyme activator. Considering that ALOX15 is expressed in macrophages, not hepatocytes, the authors concluded that macrophage ALOX15 expression altered secretory products that affected hepatic lipid synthesis. Rothe, T. Lung-resident macrophages isolated 7 days post N. Hsi L. Hypoxia increases LDL oxidation and expression of lipoxygenase-2 in human macrophages. FEBS Lett. This review summarized these functions of LOX enzymes under pathophysiological conditions in mammals.

0 thoughts on “Lipoxygenase”