Goblet cell diagram
Goblet cells are specialized secretory cells that line various mucosal surfaces. Though they are primarily involved in the production of mucus, goblet cell diagram, goblet cells also secrete a number of molecules such as chemokines that have been associated with innate immunity.
Most epithelial tissues are essentially large sheets of cells covering all the surfaces of the body exposed to the outside world and lining the outside of organs. Epithelium also forms much of the glandular tissue of the body. Skin is not the only area of the body exposed to the outside. Other areas include the airways, the digestive tract, as well as the urinary and reproductive systems, all of which are lined by an epithelium. Epithelial cells derive from all three major embryonic layers. The epithelia lining the skin, parts of the mouth and nose, and the anus develop from the ectoderm.
Goblet cell diagram
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Goblet cells within the conjunctival epithelium are specialized cells that secrete mucins onto the surface of the eye. Recent research has demonstrated new characteristics of the cells, including factors influencing their differentiation, their gene products and their functions at the ocular surface. The following review summarizes the newly discovered aspects of the role of Spdef, a member of the Ets transcription factor family in conjunctival goblet cell differentiation, the newly discovered goblet cell products including claudin2, the Wnt inhibitor Frzb, and the transmembrane mucin Muc The current concepts of conjunctival goblet cell function, including debris removal and immune surveillance are reviewed, as are changes in the goblet cell population in ocular surface diseases. Major remaining questions regarding conjunctival cell biology are discussed. A continuous layer of cells termed the epithelium covers the surface of the human body. The epithelial surface is primarily of the dry, keratinized and stratified type on the outer epidermal surface of the body, but as the epithelium involutes internally to cover the ocular surface, and the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and urogenital surfaces, it becomes a wet surfaced and non-keratinized, mucosal epithelium. At the transition zones from outer to internal epithelium, the wet surfaced epithelia remain stratified but become a simple single cell layer upon reaching more protected internal surfaces.
Combinations of the two secretory regions are known as tubuloalveolar tubuloacinar glands. A significant decrease in MUC5AC expression in patients with atopic keratoconjunctivitis has also been noted Dogru et al. The distribution patterns of goblet cells within the conjunctival epithelium are species specific, goblet cell diagram.
Figure 1. Self drawn diagram of ciliated columnar epithelium. Ciliated columnar epithelial cells are found mainly in the tracheal and bronchial regions of the pulmonary system and also in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system. Ciliated columnar epithelium in the pulmonary system is interspersed with goblet cells that secrete mucous to form a mucosal layer apical to the epithelial layer see Figure 2. The rowing-like action of epithelial cilia work in tandem with goblet cells to propel mucus away from the lungs, preventing particulate matter from causing infection see Video 1.
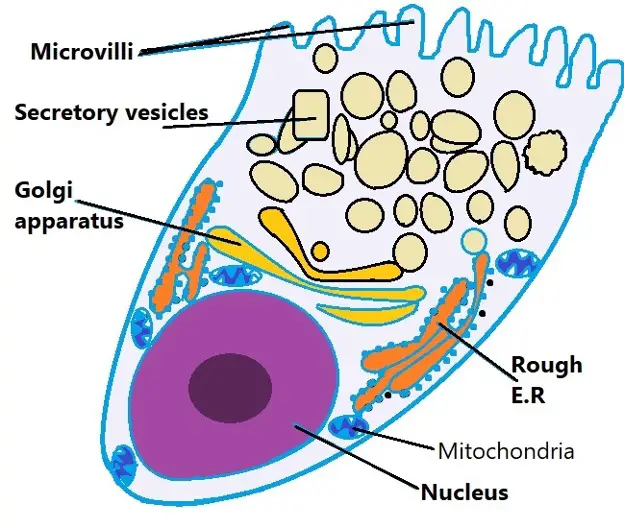
Goblet Cells : In the body, different organs are responsible for maintaining homeostasis. For instance the first line of cells contributing for such is found in the epithelium. In particular, cells known as goblet cells are an important component in this barrier and constitute the majority of the immune system. But they are more than just secretory cells. Goblet cells along with other principal cells in the gastrointestinal tract, i. Apart from comprising the epithelial lining of various organs, production of large glycoproteins and carbohydrates, the most important function of goblet cells is mucus secretion. This mucus is a gel-like substance that is composed mainly of mucins, glycoproteins, and carbohydrates. As mentioned earlier, goblet cells secrete mucus through merocrine secretion, which in turn serves a variety of functions. But in the first place, how do these cells secrete such powerful substance? The secretion of mucus is preceded by a stimuli.
Goblet cell diagram
The talent of goblet cells is to secrete mucus, a viscous fluid composed primarily of highly glycosylated proteins called mucins suspended in a solution of electrolytes. Mucus serves many functions, including protection against shear stress and chemical damage, and, especially in the respiratory tree, trapping and elimination of particulate matter and microorganisms. Goblet cells are found scattered among other cells in the epithelium of many organs, especially in the intestinal and respiratory tracts.
Eugene the jeep
Realistic Golden Trophy with text space, Vector Illustration. Cecum Appendix. Transitional A special form of epithelium, in which the cells can alter their shape. Here, their apical surfaces protrude into the lumen. In the respiratory tract, goblet cells, among other types of cells, can be found in the tracheobronchial epithelium. Spdef appears to be a central transcription factor involved in goblet cell differentiation, being influenced by both the Notch, Wnt, and TGF beta pathways. Pharynx Muscles Spaces peripharyngeal retropharyngeal parapharyngeal retrovisceral danger prevertebral Pterygomandibular raphe Pharyngeal raphe Buccopharyngeal fascia Pharyngobasilar fascia Pyriform sinus. Conditional disruption of mouse Klf5 results in defective eyelids with malformed meibomian glands, abnormal cornea and loss of conjunctival goblet cells. Apocrine secretion occurs when secretions accumulate near the apical portion of a secretory cell. The epithelial cells exhibit polarity with differences in structure and function between the exposed or apical facing surface of the cell and the basal surface close to the underlying body structures. The duct is single in a simple gland but in compound glands is divided into one or more branches Figure 4. Thus the cells of the culture system lack classic goblet cell morphology Contreras-Ruiz and Masli, ; Shatos et al. Goblet cells are mainly involved in the production of mucus. By immunoelectron microscopy, using antibody H, which recognizes a carbohydrate epitope on MUC16 Argueso et al.
Goblet cells are specialized epithelial cells found in various mucosal surfaces throughout the body. This article explores the histology of goblet cells, revealing their microscopic structure, cellular components, and the vital role they play in producing and secreting mucus to protect and lubricate epithelial tissues.
Parasitology research. It is not known if the IL13 induction of conjunctival goblet cell differentiation De Paiva et al. This mucin, the largest of the membrane-anchored class and also the largest glycoprotein in humans at 22, amino acids, is present in the glycocalyx of the apical surface of human cornea and conjunctival epithelium Govindarajan and Gipson, When a portion of the intestines do not have adequate blood flow, what causes sepsis to occur? New gland cells differentiate from cells in the surrounding tissue to replace those lost by secretion. Goblet cells are found in epithelial tissue of Gastrointestinal tract and Respiratory tract. Alberts, B. Although care has been taken when preparing this page, its accuracy cannot be guaranteed. Two or more layers - Stratified epithelium two or more layers of cells. Interactive Link Questions Watch this video to find out more about the anatomy of epithelial tissues. Experimental cell research.

You are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.