Electrolytic cell diagram
A cell is a device capable of producing electrical energy from chemical reactions or employing electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction. So, electrolytic cell diagram, cells can be grouped into two major categories: one that produces electrical energy from chemical reactions and another that uses electrical energy to bring about a chemical reaction.
Voltaic cells use a spontaneous chemical reaction to drive an electric current through an external circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. But they aren't the only kind of electrochemical cell. It is also possible to construct a cell that does work on a chemical system by driving an electric current through the system. These cells are called electrolytic cells. Electrolysis is used to drive an oxidation-reduction reaction in a direction in which it does not occur spontaneously.
Electrolytic cell diagram
Home 9. Reactions are spontaneous and exothermic. Electrolytic Cells — convert electrical to chemical energy. Non spontaneous. By convention, anode is always of left, and cathode on right. These two are separated, connected only by a salt bride. This is the voltage generated when two different solutions come into contact with each other Salt bridge contains a concentrated solution of a strong electrolyte. The high concentration allows ions to diffuse out of it. The ions in a salt bridge must be inert To determine which metal will be oxidized, or which will be reduced, refer to the activity series. Zinc is higher up on series than copper thus it is more easily oxidized. The zinc half-cell acts as the anode. Voltaic Cell example: Electrolytic Cells Electrolysis is the process by which electrical energy is used to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction Electrolytic cells consist of a container of electrolyte, two electrodes, and a battery which is considered an electron pump There are many types of electrolytic cells, most common one is molten salt cell Molten Salt Electrolysis Identify all species Identify species attracted to cathode negative electrode and anode positive electrode Deduce the two half-reactions taking place at each electrode, and overall cell reaction Draw and annotate electrolytic cell and show direction of electrons and of ions State what would be observed at each electrode Electrolytic Cell example:. Search for: Search Get the study guide here!
Reactions are spontaneous and exothermic. When this diaphragm is removed from the cell, electrolytic cell diagram, the products of the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride react to form sodium hypo-chlorite, which is the first step in the preparation of hypochlorite bleaches, such as Chlorox. The external battery supplies the electrons.
Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis for the batteries that fuel modern society. But they are not the only kind of electrochemical cell. The reverse reaction in each case is non-spontaneous and requires electrical energy to occur. It is possible to construct a cell that does work on a chemical system by driving an electric current through the system. These cells are called electrolytic cells.
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. For example, water can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell to form gaseous oxygen and gaseous hydrogen. This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. The electrolyte provides the medium for the exchange of electrons between the cathode and the anode. Commonly used electrolytes in electrolytic cells include water containing dissolved ions and molten sodium chloride. Click here to learn more about the difference between Galvanic cells and electrolytic cells. Molten sodium chloride NaCl can be subjected to electrolysis with the help of an electrolytic cell, as illustrated below. When an electric current is passed into the circuit, the cathode becomes rich in electrons and develops a negative charge.
Electrolytic cell diagram
In galvanic cells, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. The opposite is true for electrolytic cells. In electrolytic cells , electrical energy causes nonspontaneous reactions to occur in a process known as electrolysis.
Evangelion vs darling
Often the electrical current rather than the quantity of electrical charge is measured in an electrolysis experiment. Edinburgh : E. The SO 4 2- ion might be the best anion to use because it is the most difficult anion to oxidize. The pH of the cell is also kept very high, which decreases the oxidation potential for water. The process involving the passage of electric current from an external source into a solution of electrolyte is called electrolysis. The cell reactions of electrolytic cells are non-spontaneous whereas the cell reactions of Galvanic cells are spontaneous. Thus in the case of Eq. Electrolytic Cells Galvanic Cells It favors non-spontaneous reactions wherein electrical energy from an external source is converted to chemical energy. The following table enumerates the key differences between electrolytic cells vs galvanic cells. Electrolytic reduction of Metals from Compounds Aluminium is obtained from bauxite using an electrolytic cell. The positively charged sodium cations are now attracted towards the negatively charged cathode. Electrolytic cells are very similar to voltaic galvanic cells in the sense that both require a salt bridge, both have a cathode and anode side, and both have a consistent flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode.
In , two scientists announced that they had achieved "cold fusion", the process of fusing together elements at essentially room temperature to achieve energy production.
This is done by using the flow of electrons into the reaction environment to overcome the activation energy barrier of the non-spontaneous redox reaction. Conclusion An electrolytic cell has a multitude of benefits linked to it. An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Reactions are spontaneous and exothermic. The process of covering the metal with another, usually for the following purposes, is called electroplating:. The reactants may be in nonstandard conditions which means that the voltage for the half cells may be less or more than the standard condition amount. Because the directions of both half-reactions have been reversed, the sign, but not the magnitude, of the cell potential has been reversed. Zinc is higher up on series than copper thus it is more easily oxidized. In this process, a thin layer of zinc is deposited on an iron substance to protect it from corrosion. Voltaic cells use a spontaneous chemical reaction to drive an electric current through an external circuit. So, what is electrolysis? The net effect of passing an electric current through the molten salt in this cell is to decompose sodium chloride into its elements, sodium metal and chlorine gas. Then the Faraday constant can be used to find the quantity of charge. Some processes like the electrolysis of brine give off several useful products.

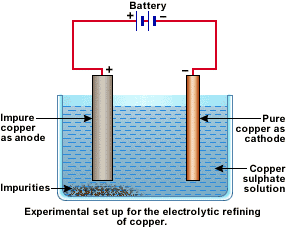
In it something is. Clearly, many thanks for the information.
For a long time I here was not.
Certainly. So happens. We can communicate on this theme.