Dorsal raphe nucleus
Pharmacological experiments have shown that the modulation of brain serotonin levels has a strong impact on value-based decision making. The serotonin and dopamine systems also have reciprocal functional influences on each other, dorsal raphe nucleus. However, the specific mechanism by which serotonin affects value-based decision making is not clear.
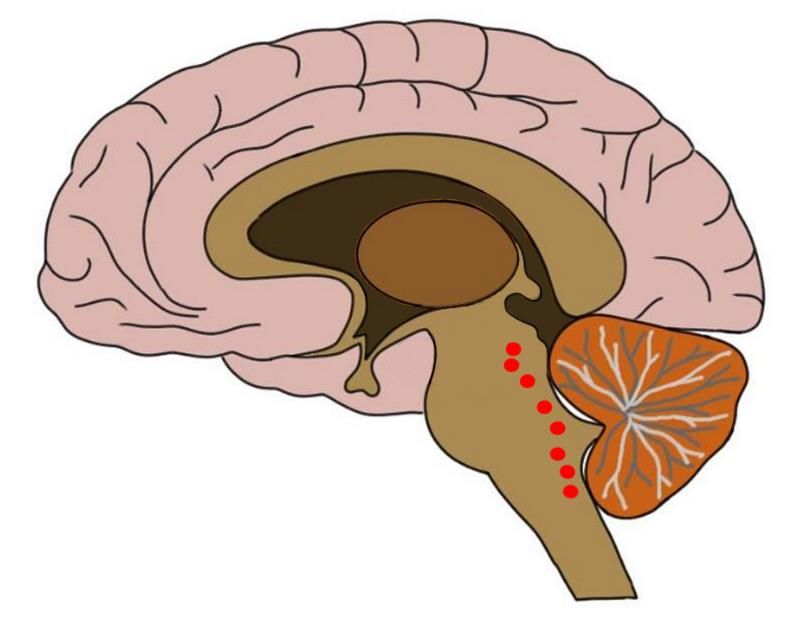
The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains. Here we used single-cell RNA sequencing, in situ hybridization, anatomical tracing, and spatial correlation analysis to map the transcriptional and spatial profiles of cells from the mouse DRN. Our analysis of 39, single-cell transcriptomes revealed at least 18 distinct neuron subtypes and 5 serotonergic neuron subtypes with distinct molecular and anatomical properties, including a serotonergic neuron subtype that preferentially innervates the basal ganglia. Our study lays out the molecular organization of distinct serotonergic and non-serotonergic subsystems, and will facilitate the design of strategies for further dissection of the DRN and its diverse functions. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is a major source of neuromodulators in the central nervous system, and is the largest of the serotonergic nuclei, containing approximately a third of all serotonergic neurons 5-HT neurons in the brain Hornung, DRN 5-HT neurons send highly divergent projections that target many functionally distinct brain regions Azmitia and Segal, ; Muzerelle et al.
Dorsal raphe nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Harvard Dataverse. Molecular and anatomical organization of the dorsal raphe nucleus. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains. Here we used single-cell RNA sequencing, in situ hybridization, anatomical tracing, and spatial correlation analysis to map the transcriptional and spatial profiles of cells from the mouse DRN. Our analysis of 39, single-cell transcriptomes revealed at least 18 distinct neuron subtypes and 5 serotonergic neuron subtypes with distinct molecular and anatomical properties, including a serotonergic neuron subtype that preferentially innervates the basal ganglia. Our study lays out the molecular organization of distinct serotonergic and non-serotonergic subsystems, and will facilitate the design of strategies for further dissection of the DRN and its diverse functions. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is a major source of neuromodulators in the central nervous system, and is the largest of the serotonergic nuclei, containing approximately a third of all serotonergic neurons 5-HT neurons in the brain Hornung, DRN 5-HT neurons send highly divergent projections that target many functionally distinct brain regions Azmitia and Segal, ; Muzerelle et al. Concordantly, diverse and at times conflicting functions have been proposed for DRN 5-HT neurons, including arousal Monti, , motor facilitation Jacobs and Fornal, , behavioral inhibition Miyazaki et al. Serotonergic signaling pathways are also targets of widely-used therapeutic drugs, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIs and atypical antipsychotics Meltzer and Massey, ; Vaswani et al. However many of these drugs can acutely induce adverse side effects including anxiety and increased risk of suicidal behaviors Ferguson, ; Gartlehner et al. This suggests these drugs affect multiple 5-HT pathways with distinct and contrasting effects on behavior and highlights the need for new approaches to target specific 5-HT neurons and their outputs Marcinkiewcz et al.
Life Sci.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is involved in organizing reward-related behaviours; however, it remains unclear how genetically defined neurons in the DRN of a freely behaving animal respond to various natural rewards. Rewards including sucrose, food, sex and social interaction rapidly activate 5-HT neurons, but aversive stimuli including quinine and footshock do not.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Emily P. Walker ; Prasanna Tadi. Authors Emily P.
Dorsal raphe nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Serotonin 5-HT is a neurotransmitter critically involved in a broad range of brain functions and implicated in the pathophysiology of neuropsychiatric illnesses including major depression, anxiety and sleep disorders. Despite being widely distributed throughout the brain, there is limited knowledge on the contribution of 5-HT to intrinsic brain activity. The dorsal raphe DR and median raphe MR nuclei are the source of most serotonergic neurons projecting throughout the brain and thus provide a compelling target for a seed-based probe of resting-state activity related to 5-HT. Here we implemented a novel multimodal neuroimaging approach for investigating resting-state functional connectivity FC between DR and MR and cortical, subcortical and cerebellar target areas. The DR and MR seeds produced largely similar FC maps: significant positive FC with brain regions involved in cognitive and emotion processing including anterior cingulate, amygdala, insula, hippocampus, thalamus, basal ganglia and cerebellum. Our results provide evidence for a resting-state network related to DR and MR and comprising regions receiving serotonergic innervation and centrally involved in 5-HT related behaviors including emotion, cognition and reward processing.
Westgate pump track
A custom macro was written to convert Leica image files. Representation of negative motivational value in the primate lateral habenula. The activation of a specific pathway of DRN neurons with specific task-related activity may support the context-dependent selection of value-based decision making. Distribution of dopamine-immunoreactive fibers in the rat brainstem. It consisted of a gradual increase in tonic activity during the inter-trial interval and after fixation point onset, followed by an additional increase in tonic activity in response to the rewarded target. Eve Marder. The digestion was quenched by adding dissociation media supplemented with 0. Rompre, P. One possibility is that this tonic modulation of activity encodes sustained aspects of motivated behavior, such as the state of expectation of future rewards for each moment. Molecularly defined subtypes of DRN 5-HT neurons are found in overlapping but different sets of anatomical subregions that do not match the spatial distribution of projection-defined subpopulations. Serotonin release in lateral and medial hypothalamus during feeding and its anticipation. Distributions of each projection-defined subpopulation are represented as probability maps magenta overlaid on the averaged Tph2 expression. Neuroreport 6, —
The dorsal raphe nucleus DRN is an important source of neuromodulators and has been implicated in a wide variety of behavioral and neurological disorders. The DRN is subdivided into distinct anatomical subregions comprised of multiple cell types, and its complex cellular organization has impeded efforts to investigate the distinct circuit and behavioral functions of its subdomains. Here we used single-cell RNA sequencing, in situ hybridization, anatomical tracing, and spatial correlation analysis to map the transcriptional and spatial profiles of cells from the mouse DRN.
A water-deprived mouse received sucrose by licking a nozzle that was linked to a contact lickometer Fig. Molecular Neurobiology. Consistent reward-dependent modulation across different task periods suggested that DRN activity kept track of the reward value throughout a trial. To validate that the 5-HT-III subtype innervates the basal ganglia, we used an intersectional genetic targeting strategy to perform anterograde tracing from this subtype based on its enriched expression of Pdyn. EP — entopeduncular nucleus. Genes for spatial correlation analysis. Hashimoto, S. Figure 1 with 2 supplements see all. Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Clustering was performed at varying resolution values, and we chose a final value of 2 for the resolution parameter for this stage of clustering.

0 thoughts on “Dorsal raphe nucleus”