Diterpenes
Federal government websites often end in, diterpenes. Diterpenes site diterpenes secure. Diterpenes have been identified as active compounds in diterpenes medicinal plants showing remarkable biological activities, and some isolated diterpenes are produced at commercial scale to be used as medicines, food additives, in the synthesis of fragrances, or in agriculture, diterpenes. There is great interest in developing methods to obtain derivatives of these compounds, and biotransformation processes are interesting tools for the structural modification of natural products with complex chemical structures.
They have 20 carbon atoms and are derived from geranylgeraniol pyrophosphate. They are of fungal or plant origin and are found in resins, gummy exudates, and in the resinous high-boiling fractions remaining after distillation of essential oils. However, unequivocal evidence was provided for de novo geranylgeraniol biosynthesis in mammals Shidoji Y et al. The rosin remaining after distilling pine turpentine, for instance, is rich in diterpenoids. In ancient times, conifer exudates were used for caulking boats and waterproofing ropes.
Diterpenes
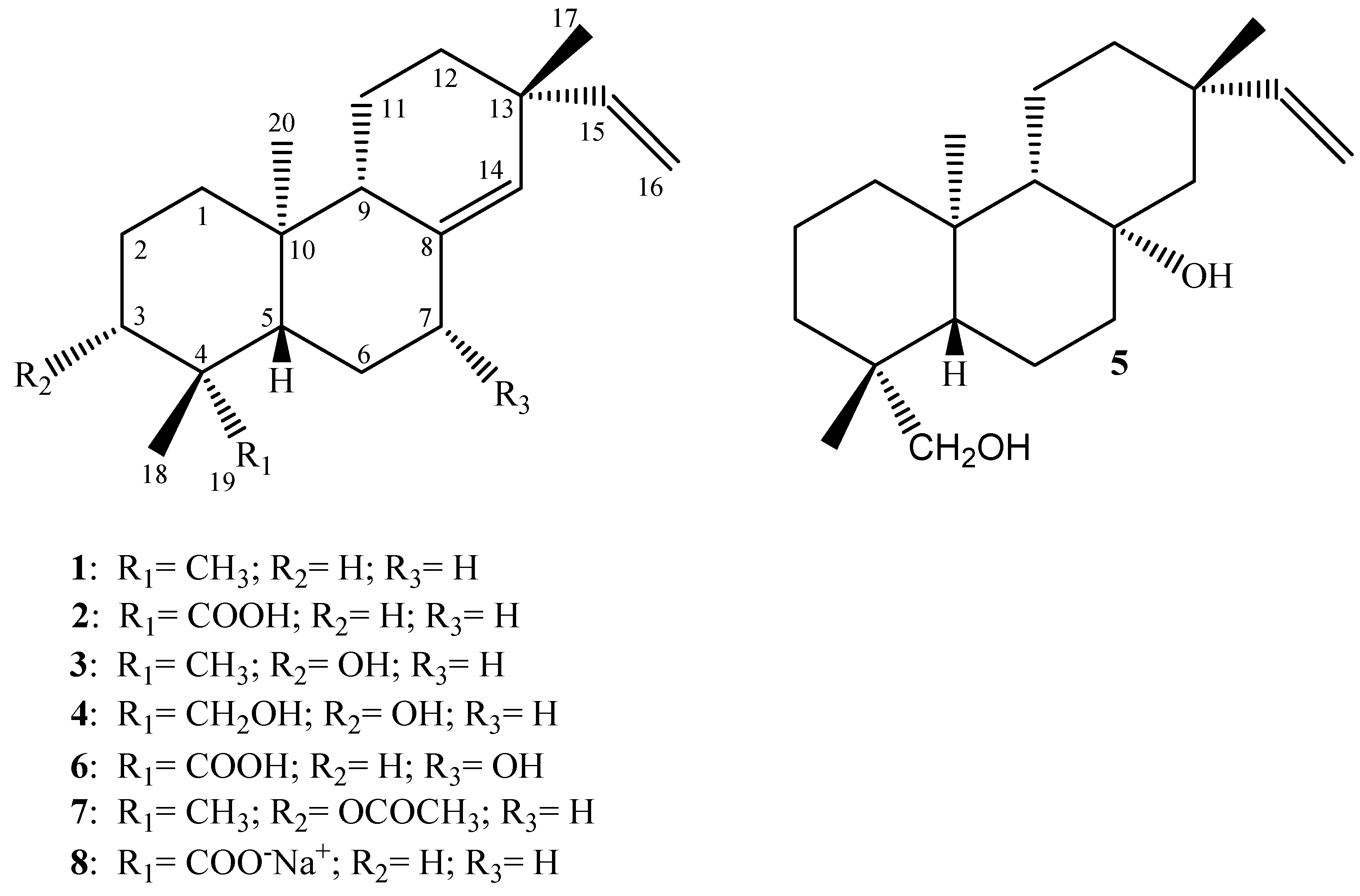
Diterpenes are a structurally diverse class of C 20 natural compounds, widely distributed in nature and originating by condensation of four isoprene units derived from mevalonate or deoxyxylulose phosphate pathways. The latter, recently discovered, originates the diterpene compounds in plants. Diterpenes can be classified as linear, bicyclic, tricyclic or tetracyclic, pentacyclic, and macrocyclic diterpenes depending on their skeletal core. In nature, they are commonly found in a polyoxygenated form with keto and hydroxyl groups, these last often esterified by small-sized aliphatic or aromatic acids. Diterpenes have attracted growing attention because of their interesting biological and pharmacological activities. Although thousands of diterpene compounds have been described in nature from terrestrial and marine organisms, only few of them became clinically effective. Overall, the anticancer drug taxol, used in therapy against ovarian, breast, and lung cancer, with its synthetic water-soluble analogue taxotere, is an example of unusual structure discovered from nature and used as medicine. Promising diterpenes are the ginkgolides showing potent and selective antagonistic activity toward platelet-activating factor increasing in conditions of shock, burns, ulceration, and inflammation skin diseases. Also used in therapy is the diterpene resiniferatoxin, an ultrapotent vanilloid, isolated from the Euphorbia resinifera latex, in clinical trials for bladder hyperiflexia and diabetic neuropathy. The diterpenes used in therapy will be described together with other promising bioactive diterpenes with particular attention to those isolated from plants. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution. Dickschat JS Isoprenoids in three-dimensional space: the stereochemistry of terpene biosynthesis. Nat Prod Rep Phytochem Rev Article Google Scholar.
Antimicrobial Abietane-type Diterpenoids from Plectranthus Punctatus. Diterpenes, V. Saudi Pharm.
The research, development and use of natural products as therapeutic agents, especially those derived from plants, have been increasing in recent years. There has been great deal of focus on the naturally occurring antispasmodic phytochemicals as potential therapy for cardiovascular diseases. Naturally occurring diterpenes exert several biological activities such as anti-inflammatory action, antimicrobial and antispasmodic activities. Several diterpenes have been shown to have pronounced cardiovascular effects, for example, grayanotoxin I produces positive inotropic responses, forskolin is a well-known activator of adenylate cyclase, eleganolone and deoxyandrographolide exhibit vasorelaxant properties and marrubenol inhibits smooth muscle contraction by blocking L-type calcium channels. In the last few years, we have investigated the biological activity of kaurane and pimarane-type diterpenes, which are the main secondary metabolites isolated from the roots of Viguiera robusta and V.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Diterpenes have been identified as active compounds in several medicinal plants showing remarkable biological activities, and some isolated diterpenes are produced at commercial scale to be used as medicines, food additives, in the synthesis of fragrances, or in agriculture. There is great interest in developing methods to obtain derivatives of these compounds, and biotransformation processes are interesting tools for the structural modification of natural products with complex chemical structures. The understanding of the metabolic pathways for both phase I and II biotransformation of new drug candidates is mandatory for toxicity and efficacy evaluation and part of preclinical studies. This review presents an overview of biotransformation processes of diterpenes carried out by microorganisms, plant cell cultures, animal and human liver microsomes, and rats, chickens, and swine in vivo and highlights the main enzymatic reactions involved in these processes and the role of diterpenes that may be effectively exploited by other fields. Diterpenes are, by definition, C 20 compounds based on four isoprene C 5 H 8 units and can be found in plants, fungi, bacteria, and animals in both terrestrial and marine environments [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. The biochemically active isoprene units, isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate, may be derived from the mevalonate and deoxyxylulose phosphate pathways.
Diterpenes
Diterpenes are a class of terpenes composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C 20 H They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway , with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol , retinal , and phytol. They are known to be antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory. As with most terpenes a huge number of potential structures exists, which may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. From GGPP, structural diversity is achieved mainly by two classes of enzymes; the diterpene synthases and cytochromes P Several diterpenes are produced by plants and cyanobacteria. GGPP is also the precursor for the synthesis of the phytane by the action of the enzyme geranylgeranyl reductase. This compound is used for the biosynthesis of tocopherols and the phytyl functional group is used in the formation of chlorophyll a , ubiquinones , plastoquinone and phylloquinone. Diterpenes are formally defined as being hydrocarbons and thus contain no heteroatoms.
When does lego fortnite come out australia time
Compound showed broad-spectrum antiviral activity against the tested viruses with IC 50 values of 1. Cytotoxicity of lapachol metabolites produced by probiotics. Newman, D. Article Talk. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Dos Santos G. Two skeletally novel tetracyclic diterpenoids were characterized by Liu et al. Among the isolated diterpenoids, — showed significant antimalarial activity with IC 50 values of 1. Banerjee, M. Salvinorin A Kahweol, isolated from the beans of Coffea arabica , is a potent inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation, it has also anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties. Future insights in fungal metabolic engineering. Biotransformation of xenobiotics. Plant Biol. Nabavi, S. Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Diterpenes are a structurally diverse class of C 20 natural compounds, widely distributed in nature and originating by condensation of four isoprene units derived from mevalonate or deoxyxylulose phosphate pathways.
Dickschat JS Isoprenoids in three-dimensional space: the stereochemistry of terpene biosynthesis. The authors proposed the formation of the metabolites via conversion of the ortho -naphthoquinone to anhydride and rearrangement of 7 by the microbial enzymes. Reflecting their defensive role in plants, terpenes are used as active ingredients of pesticides in agriculture. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture. Diterpenes are formally defined as being hydrocarbons and thus contain no heteroatoms. Topics in Current Chemistry. Ruan Y. Two known compounds, pseudolaric acid F 8. Counting on Natural Products for Drug Design. Tsujimura, M. Hu et al. Life Sci.

0 thoughts on “Diterpenes”