Condenser lab
Condensers are a critical tool in all areas of chemistry. We condenser lab include here accessories that you will find useful such as spill alarms, water flow mointors and more.
With an accout for my. In a laboratory, a condenser is a piece of laboratory glassware used to cool hot vapors or liquids. A condenser usually consists of a large glass tube containing a smaller glass tube running its entire length, within which the hot fluids pass. The ends of the inner glass tube are usually fitted with ground glass joints which are easily fitted with other glassware. The upper end is usually left open to the atmosphere, or vented through a bubbler, or a drying tube to prevent the ingress of water or oxygen. For maximum efficiency, the cold water always enters through the bottom fitting, and exits through the top fitting. Multiple condensers may be connected in series, but a high flow rate must be maintained.
Condenser lab
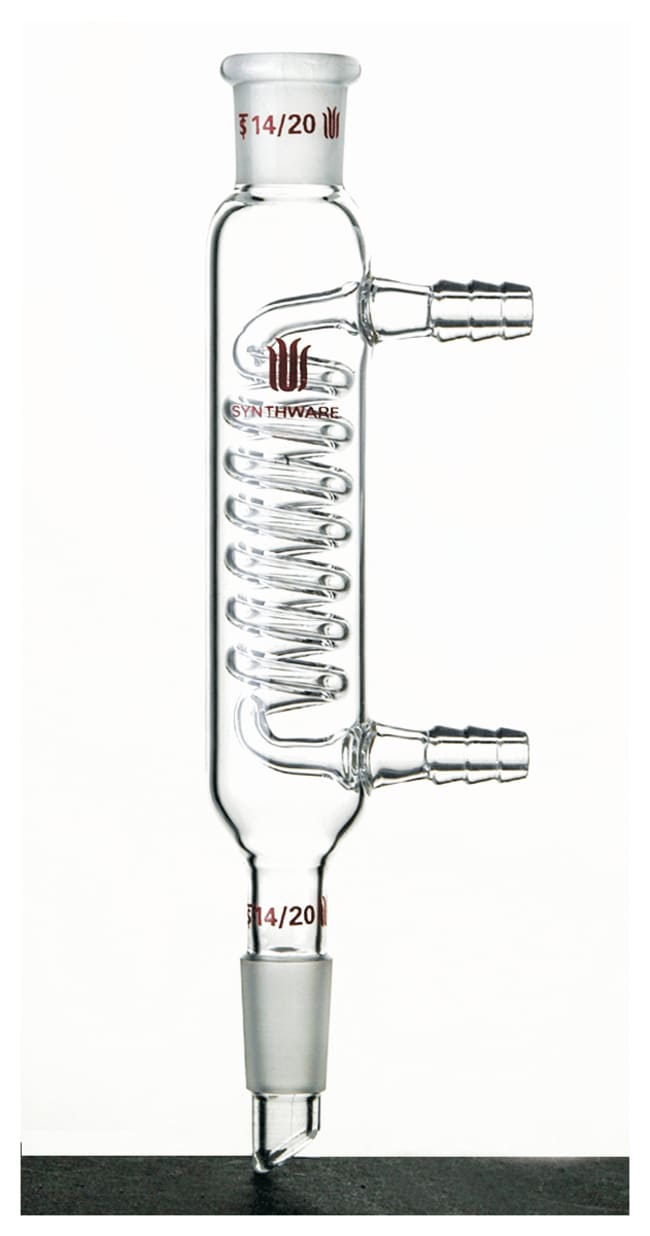
In chemistry , a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors — that is, turn them into liquids — by cooling them down. Condensers are routinely used in laboratory operations such as distillation , reflux , and extraction. In distillation, a mixture is heated until the more volatile components boil off, the vapors are condensed, and collected in a separate container. In reflux, a reaction involving volatile liquids is carried out at their boiling point, to speed it up; and the vapors that inevitably come off are condensed and returned to the reaction vessel. In Soxhlet extraction, a hot solvent is infused onto some powdered material, such as ground seeds, to leach out some poorly soluble component; the solvent is then automatically distilled out of the resulting solution, condensed, and infused again. Many different types of condensers have been developed for different applications and processing volumes. The simplest and oldest condenser is just a long tube through which the vapors are directed, with the outside air providing the cooling. More commonly, a condenser has a separate tube or outer chamber through which water or some other fluid is circulated, to provide a more effective cooling. Laboratory condensers are usually made of glass for chemical resistance, for ease of cleaning, and to allow visual monitoring of the operation; specifically, borosilicate glass to resist thermal shock and uneven heating by the condensing vapor. Some condensers for dedicated operations like water distillation may be made of metal. In professional laboratories, condensers usually have ground glass joints for airtight connection to the vapor source and the liquid receptacle; however, flexible tubing of an appropriate material is often used instead.
Each "finger" is created by melting a small section of the condenser lab and pushing the soft glass inwards.
.
Welcome to Science Equip! A condenser is a piece of laboratory equipment that is used to condense vapours in the lab or turn them into liquids simply by cooling them down. A lab glass condenser as the name says is typically made up of a large glass material tube with a smaller glass tube running its entire length from where the hot fluids usually pass. The upper-end part of the condenser is usually left open or vented through a bubbler or a drying tube to prevent the entrance of the water or oxygen. Coldwater is always supposed to enter through the top fitting of the condenser for attaining maximum efficiency.
Condenser lab
The condenser is an intricate piece of glassware, and allows for cold water to circulate through the distillation apparatus. The circulating water does not mix with the sample to be purified, but instead passes through another jacket surrounding the hollow tube where the gaseous sample travels. It is important that the water jacket be full of cold water, to maximize the efficiency of condensing the gaseous sample.
Tasha young
There are two possible configurations for a Graham condenser. Tools Tools. Condensers, Friedrichs Style. All trademarks shown are the property of their respective owners. Then the partial pressure of its vapor must be considered when obtaining its condensation temperature. Allihn Condensers, Jointed. They are usually mounted vertically or tilted, with the vapor input at the top and the liquid output at the bottom. In most designs, the liquid is only a thin film on the inner surface of the condenser, so its temperature is essentially the same as of that surface. Condensers, Reflux, Compact. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6. The still head is another ancient type of air-cooled condenser. West Condensers. The West condenser is variant of the Liebig type, with a more slender design, with cone and socket. The ends of the outer tube are sealed usually by a blown glass ring seal , forming a water jacket, and is fitted with side ports near the ends for cooling fluid inflow and outflow.
With an accout for my. In a laboratory, a condenser is a piece of laboratory glassware used to cool hot vapors or liquids. A condenser usually consists of a large glass tube containing a smaller glass tube running its entire length, within which the hot fluids pass.
View our Sitemap. Beaker Bell jar Gas syringe Vial. Dimroth condensers are more effective than conventional coil condensers. All trademarks shown are the property of their respective owners. Toggle limited content width. Care must also be taken to prevent the boiling liquid to enter the condenser as splattering from explosive boiling , or droplets created as bubbles pop. Compared to the simple air-cooled tube, the Liebig condenser is more efficient at removing the heat of condensation and at maintaining the inner surface a stable low temperature. Poisonnier, in and the Finnish chemist Johan Gadolin in The coolant circulates in both the outer jacket and the central tube. A Davies condenser , also known as a double surface condenser, is similar to the Liebig condenser, but with three concentric glass tubes instead of two.

I think, that you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.