Coagulase negative staphylococcus
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Coagulase negative staphylococci. Copy Editor: Gus Mitchell, coagulase negative staphylococcus.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Coagulase-negative staphylococci CoNS are among the most frequently recovered bacteria in routine clinical care. Their incidence has steadily increased over the past decades in parallel to the advancement in medicine, especially in regard to the utilization of foreign body devices. Many new species have been described within the past years, while clinical information to most of those species is still sparse.
Coagulase negative staphylococcus
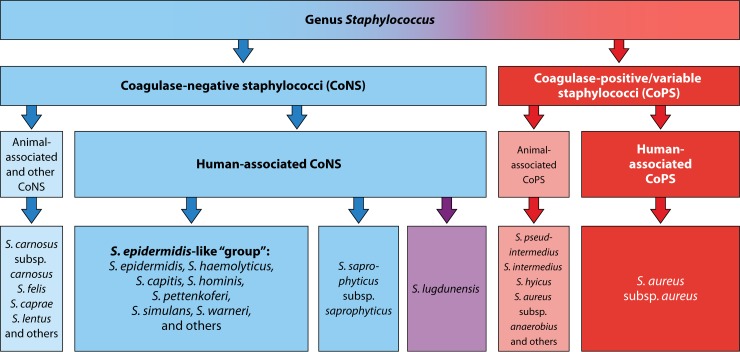
The epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis of CoNS will be reviewed here. Issues related to clinical manifestations and treatment of CoNS infections are discussed separately. See "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Clinical manifestations" and "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Treatment". Patients at particular risk for CoNS infection include those with prosthetic devices eg, pacemakers, intravascular catheters, prosthetic heart valves, orthopedic implants and immunocompromised hosts. Species — There are currently 47 species recognized in the genus Staphylococcus [ 2 ]. Staphylococci are aerobic and facultatively anaerobic gram-positive cocci that produce catalase and have a tendency to form irregular clusters. CoNS are not motile, and they do not form spores. Staphylococcus aureus and the several members of the Staphylococcus hyicus — intermedius group comprise the coagulase-positive staphylococcal species, while all remaining staphylococcal species are classified as coagulase negative. Occasional cases of CoNS infections are identified to be due to S. Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis.
Some S. Crystal structures are available for the catalytically active AM domain and the repeat R2 domain, unraveling their enzymatic mechanism coagulase negative staphylococcus substrate- and ligand-binding properties, respectively ,
Distinguishing true infection from contamination can be difficult; this is discussed separately. See "Infection due to coagulase-negative staphylococci: Epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis", section on 'Distinguishing infection from contamination'. General issues related to antimicrobial resistance and treatment of CoNS infections will be reviewed here. Issues related to treatment of Staphylococcus lugdunensis are discussed separately. See "Staphylococcus lugdunensis". The epidemiology, microbiology, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations of CoNS are discussed separately.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Bacterial small colony variants represent an important aspect of bacterial variability. They are naturally occurring microbial subpopulations with distinctive phenotypic and pathogenic traits, reported for many clinically important bacteria. In clinical terms, SCVs tend to be associated with persistence in host cells and tissues and are less susceptible to antibiotics than their wild-type WT counterparts. The increased tendency of SCVs to reside intracellularly where they are protected against the host immune responses and antimicrobial drugs is one of the crucial aspects linking SCVs to recurrent or chronic infections, which are difficult to treat. An important aspect of the SCV ability to persist in the host is the quiescent metabolic state, reduced immune response and expression a changed pattern of virulence factors, including a reduced expression of exotoxins and an increased expression of adhesins facilitating host cell uptake.
Coagulase negative staphylococcus
DermNet provides Google Translate, a free machine translation service. Note that this may not provide an exact translation in all languages. Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Coagulase negative staphylococci. Copy Editor: Gus Mitchell. October
Skirt sketch with name
Up until now, this strain has only been isolated from an aquatic environment, precisely from the river, Argen, in Southern Germany. Species distribution of CoNS b in animal- and food-derived samples in recent studies published since Site-specific recommendations. Aldman M. More recently, the presence of the bap gene was also demonstrated in nosocomial human isolates of S. Bacterial flora of the normal human skin. Consequently, CoNS have become a major nosocomial pathogen. Conditions underlying the infection of wounds. In the third phase, the biofilm grows and matures into a thick, structured layer. Moreover, in some instances, CoNS seem to be capable of attaching directly to the host tissue, i. A staph infection in your nose can be painful and potentially serious. The distinct phases of biofilm formation by CoNS and the respective underlying molecular mechanisms have been analyzed thoroughly in past years. J Am Coll Cardiol, 21 , pp. Some PSMs also exhibit moderately cytolytic activity see below.
There's more to see -- the rest of this topic is available only to subscribers.
While strains isolated from humans are usually unpigmented and their colonies have gray and gray-white rings, strains isolated from nonhuman primates are i usually pigmented with brilliantly colored colonies, with alternating yellow-orange, gray, gray-white, orange, and gray rings or bands; or ii show colonies with a yellow-green tint and only a subtle ring pattern. Preincubation of either fibronectin-coated surfaces or bacteria with teichoic acid enhanced the attachment of S. Staphylococcus auricularis sp. Up until now, this strain has only been isolated from an aquatic environment, precisely from the river, Argen, in Southern Germany. With descriptions of many novel CoNS species in the past 2 decades and improvements in diagnostic differentiation approaches, further organisms of this group have become apparent. Agents Chemother. All rights reserved. View Topic. Besides highly pathogenic S. Zong Z. CoNS-generated biofilms show significant resistance to antibiotics, caused by impaired penetration of the antibiotics and changes in bacterial metabolism and behavior. GehD seems to be surface associated, at least in part, and mediates binding of bacteria to collagen Beekmann and colleagues proposed that in order to prevent misclassification of CoNS as a cause of infection, at least two independent blood cultures must be positive for CoNS within 5 days. Clonal analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates carrying or lacking biofilm-mediating genes by multilocus sequence typing.

0 thoughts on “Coagulase negative staphylococcus”