Bbc bitesize plant cell
Click to play the game. You can also play the full game.
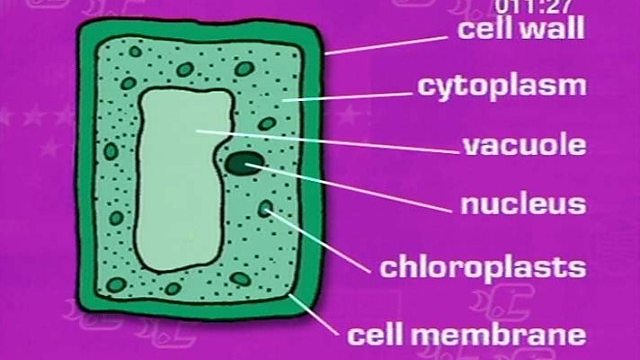
Learn about specialised plant cells. Like animal cells, basic plant cells have a nucleus, a cell membrane and cytoplasm. They've also got a vacuole, chloroplasts and a cell wall, which are only found in plant cells and they can be a bit bigger than animal cells. Plants also have some very specialised cells. Root hair cells don't have light absorbing chloroplast because they don't absorb light because they're underground. What they do have is a wide surface area to more efficiently absorb water and minerals.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. There are many different types of cells in plants. Each type is specialised to do a particular role and ensures that the organism functions as a whole. There are no top and bottom walls between xylem vessels, so there is a continuous column of water running through them. Strands of cytoplasm run through holes in the sieve plates, connecting the sieve tubes that make up the phloem. Companion cells, adjacent to the sieve tubes provide energy required to transport substances in the phloem. Plant cells can be observed in a laboratory, using a light microscope. Listen to the full series on BBC Sounds. Dr Alex Lathbridge breaks down the key facts about specialised animal and plant cells. In this guide. Light microscopes Electron microscopes Animal cells Plant cells Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Required practical - using a light microscope Measuring cell size Preparing biological samples for examination Maths - using units, decimals and standard form Maths - orders of magnitude.
Plant and animal cells.
Most life on Earth depends upon plants for energy. Plants capture light from the sun and use it to build up chemical stores of energy. This is called photosynthesis. The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below. Photosynthesis relies on many structures in the cell all working together, each playing its role. The diagram below shows the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope.
Models in science are used to help us understand complicated ideas in a simple and memorable way. Place the neck of the balloon over a tap and fill it with water. There you go! You've now made your very own model of an animal cell. Cell membrane close cell membrane This surrounds the outside of animal cells and controls what can enter and exit it. Cytoplasm close cytoplasm The liquid that makes up most of the cell in which chemical reactions happen. This is mainly water. Mitochondria close mitochondria Tiny parts of cells floating in the cytoplasm where energy is released from glucose.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Inside cells are various structures that are specialised to carry out a particular function. Both animal and plant cells have these components:. Red blood cells are some of the smallest cells in the human body. These have a diameter of 0. The ovum or egg cell is one of the largest cells in the human body. It has a diameter of roughly 0. A line of 10 egg cells is 1mm long. What's in a cell? What are specialised cells? Nerve cells.
Radio tuner yamaha
Contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis. Cell structure Cell membrane Function Allows gases and water to diffuse freely into and out of the cell. The cell has extensions and branches, so that it can communicate with other nerve cells, muscles and glands. Structure Cell wall Function Made from cellulose fibres. Or take a look around the website and start at our Home page. Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. A cell wall is made from cellulose. Permanent vacuole Filled with cell sap to help keep the cell turgid. It keeps the cell firm. The nerve cell is extended, so that nerves can run to and from different parts of the body to the central nervous system. Cell measurement Cell size Preparing biological samples for examination Investigating cells with a light microscope Microscopes The limits of the light microscope Animal cells Plant cells Measuring cell size Comparing sizes Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Plant and animal cells. They can only really be seen clearly using a microscope. Key points.
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope.
They are made up of a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, nucleus, and chloroplasts. There are many different types of cells in plants. Root hair cells. More on Living organisms. Cell structure Cytoplasm How it is related to its function A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. Root hair cell. Which of the following is NOT present in an animal cell? Some bacteria cause disease, others are useful. Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common. Muscle cells contain filaments of protein that slide over each other to cause muscle contraction. Each type is specialised for a particular role. Working safely in the lab Find out how to spot risks, hazards and understand hazard symbols. Plant cells also have additional structures:. Function Chloroplast Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. Mitochondria Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration.

In my opinion you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.