When an object undergoes acceleration
Use app Login. When an object undergoes acceleration Its speed always increases Magnitude of velocity may remain constant It always falls towards the earth A force always acts on it.
The correct answer is Option 1. Key Points. Additional Information. Last updated on Mar 31, More than vacancies are expected to be released.
When an object undergoes acceleration
Courses for Kids. Free study material. Offline Centres. Talk to our experts When an object undergoes acceleration then which one of the following is true? Last updated date: 08th Mar Study Material. Important Questions. Chapter Pages. Revision Notes. Difference Between. Preparation Tips. Exam Info. Important Dates.
Maths Mock Test. Admit Card.
.
The Learning Objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:. In addition, the High School Physics Laboratory Manual addresses content in this section in the lab titled: Position and Speed of an Object , as well as the following standards:. Ask for examples of both. Explain that deceleration is not used in physics because acceleration is either positive or negative. Lead students to their topics of interest, such as motor vehicles or sports. Explain that the capital Greek letter delta always means final minus initial and that the net change may be zero, positive, or negative. What does a vector arrow represent? Ask them to name some quantities that are vectors and some that are scalars. Throughout this chapter we will use the following terms: time , displacement , velocity , and acceleration. Recall that each of these terms has a designated variable and SI unit of measurement as follows:.
When an object undergoes acceleration
In everyday conversation, to accelerate means to speed up. The accelerator in a car can in fact cause it to speed up. The greater the acceleration , the greater the change in velocity over a given time. The formal definition of acceleration is consistent with these notions, but more inclusive. Recall that velocity is a vector—it has both magnitude and direction. This means that a change in velocity can be a change in magnitude or speed , but it can also be a change in direction. For example, if a car turns a corner at constant speed, it is accelerating because its direction is changing. The quicker you turn, the greater the acceleration. So there is an acceleration when velocity changes either in magnitude an increase or decrease in speed or in direction, or both.
Push pull worksheet
For this trajectory. Chemistry Mock Test. Study Material. JEE Main Cutoff. So, option A is incorrect. Negative Acceleration Deceleration : Slowing down or moving in the opposite direction. Velocity is a vector quantity , meaning it has both magnitude speed and direction. JEE Main Result. Physics Mock Test. More Physical Sciences Questions Q1. The ratio of the frequencies of the normal modes is.
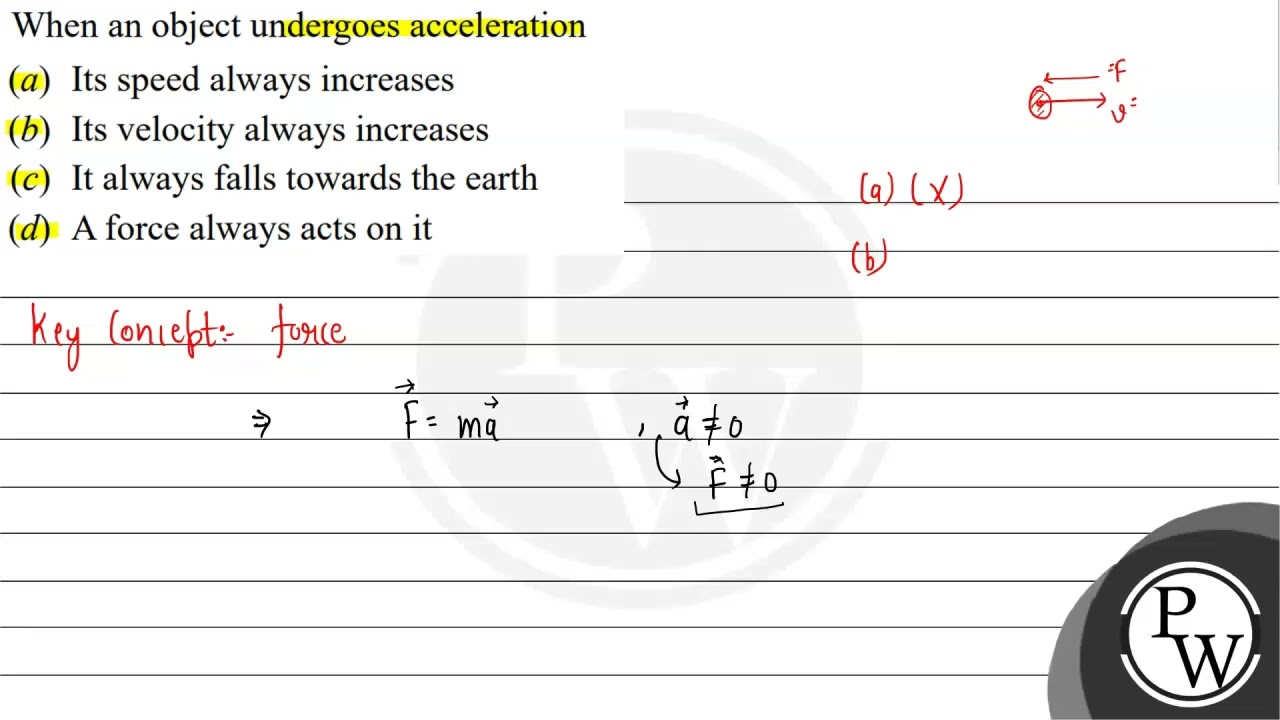
It mathematically gives the cause-and-effect relationship between force and changes in motion.
Hence, option B is correct. When the speed is decreasing, we call it deceleration. Let vr and ar denote the velocity and acceleration, respectively, in the radial direction. Physics Mock Test. In order to get a lower cut-off frequency of Hz and an upper cut-off frequency of 10 kHz, the appropriate values of C1 and C2 respectively are. Preparation Tips. Therefore, B is the correct option. Eligibility Criteria. Application Form. For a p-type semiconductor in which the mobility of holes is less than that of electrons, which of the following graphs best describes the variation of the Hall coefficient with temperature? Acceleration can be positive or negative: Positive Acceleration : Speeding up in the positive direction. More Physical Sciences Questions Q1. When an object undergoes acceleration Its speed always increases Magnitude of velocity may remain constant It always falls towards the earth A force always acts on it. Objects falling towards the earth is one example of acceleration because a gravitational force is experienced by the object due to its mass when it falls towards the earth.

Very useful idea
Certainly. I join told all above.