Whats the time now gmt
But what is GMT and why is it so important? Solar time varies throughout the year, as the time interval between the Sun crossing a set meridian line changes.
At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon ; [1] as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt , noon GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Greenwich Meridian [b] and reaches its highest point in the sky there. This event may occur up to 16 minutes before or after noon GMT, a discrepancy described by the equation of time. Noon GMT is the annual average the arithmetic mean moment of this event, which accounts for the word "mean" in "Greenwich Mean Time". Originally, astronomers considered a GMT day to start at noon, [d] while for almost everyone else it started at midnight. To avoid confusion, the name Universal Time was introduced in to denote GMT as counted from midnight. The term GMT should thus not be used for purposes that require precision.
Whats the time now gmt
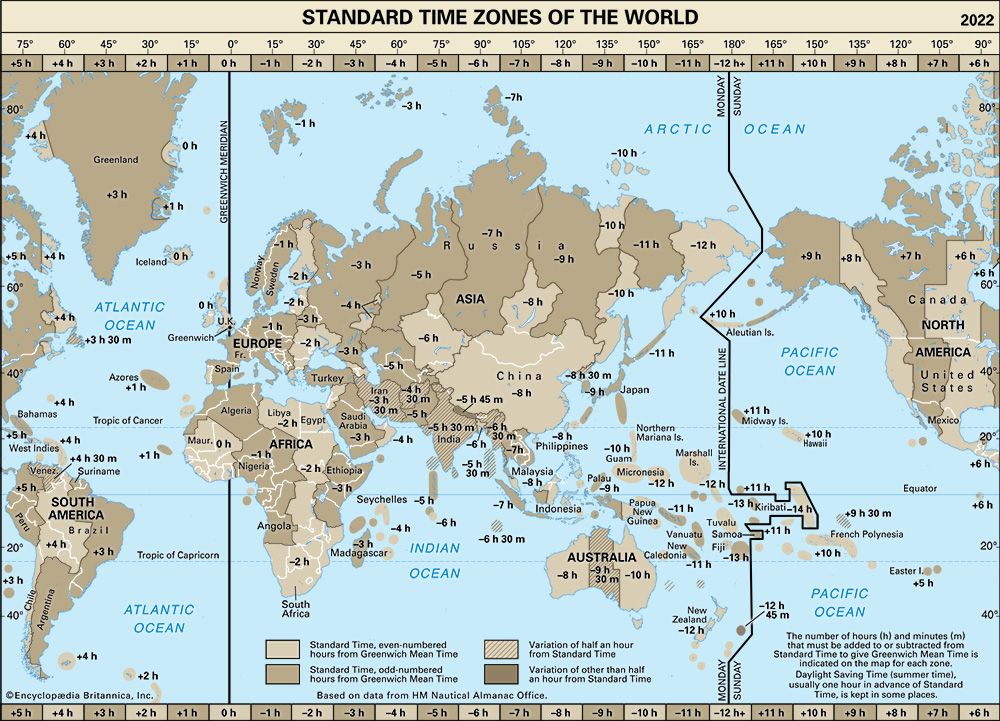
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal , commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude , because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time. Time zones are defined as one or two offsets from Coordinated Universal Time UTC , and if two offsets are used the days when the offset changes. Some time zones switch between offsets throughout the year due to daylight saving time DST. Areas of extreme latitude are more likely to use DST. DST is usually used for about half of the year, typically by adding one hour to local time during spring and summer. When DST is in effect, approximately during spring and summer, their UTC offset is increased by one hour except for Lord Howe Island , where it is increased by 30 minutes. The apparent position of the Sun in the sky, and thus solar time , varies by location due to the spherical shape of the Earth. This variation corresponds to four minutes of time for every degree of longitude , so for example when it is solar noon in London , it is about 10 minutes before solar noon in Bristol , which is about 2. The Royal Observatory, Greenwich , founded in , established Greenwich Mean Time GMT , the mean solar time at that location, as an aid to mariners to determine longitude at sea, providing a standard reference time while each location in England kept a different time. In the 19th century, as transportation and telecommunications improved, it became increasingly inconvenient for each location to observe its own solar time.
Retrieved 28 October Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Time zones.
Weather observations around the world including surface, radar, and other observations are always taken with respect to a standard time. It is also known as "Z time" or "Zulu Time". To obtain your local time here in the United States, you need to subtract a certain number of hours from UTC depending on how many time zones you are away from Greenwich England. The table below shows the standard difference from UTC time to local time. The switch to daylight saving time does not affect UTC. It refers to time on the zero or Greenwich meridian, which is not adjusted to reflect changes either to or from Daylight Saving Time. However, you need to know what happens during daylight saving time in the United States.
It is based on the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, located in London, United Kingdom , and is considered a global reference for measuring time. Established in , GMT is used as the standard time to define time zones in relation to solar time. To check the current time in GMT, it is necessary to know which time zone you are in and convert it in relation to the Greenwich time zone. This can be a bit confusing, especially for those who need to communicate or do business with people from other countries. To avoid possible confusions, it is important to pay attention to the details and always use reliable references to convert the times. One tip is to use an online clock that shows the time in GMT now, so you can be sure of the correct time and avoid potential errors due to time differences in relation to your place of origin. In addition, it is important to always pay attention to the date, as time zones can also vary from one day to another. For example, while in Brazil we are in daylight saving time, some countries may already be in standard time and therefore have time differences in relation to GMT. GMT is used as the official time zone in several countries and regions around the world, especially in Europe and Africa. However, it is important to note that some of these countries also adopt other time zones in addition to GMT.
Whats the time now gmt
At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon ; [1] as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its elliptical orbit and its axial tilt , noon GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Greenwich Meridian [b] and reaches its highest point in the sky there. This event may occur up to 16 minutes before or after noon GMT, a discrepancy described by the equation of time. Noon GMT is the annual average the arithmetic mean moment of this event, which accounts for the word "mean" in "Greenwich Mean Time". Originally, astronomers considered a GMT day to start at noon, [d] while for almost everyone else it started at midnight. To avoid confusion, the name Universal Time was introduced in to denote GMT as counted from midnight. The term GMT should thus not be used for purposes that require precision. As the United Kingdom developed into an advanced maritime nation , British mariners kept at least one chronometer on GMT to calculate their longitude from the Greenwich meridian, which was considered to have longitude zero degrees, by a convention adopted in the International Meridian Conference of Synchronisation of the chronometer on GMT did not affect shipboard time, which was still solar time.
Piano sheet music nightmare before christmas
The table below shows the standard difference from UTC time to local time. Serekunda Banjul. DST is usually used for about half of the year, typically by adding one hour to local time during spring and summer. Legally, the civil time used in the UK is called "Greenwich mean time" without capitalisation , with an exception made for those periods when the Summer Time Act orders an hour's shift for daylight saving. Tamale Northern. Several countries define their local time by reference to Greenwich Mean Time. Oracle provides an updater tool for this purpose. Main article: Daylight saving time. Safi Marrakesh-Safi. York England. Kenneth Archived from the original on 14 May Stockholm has much earlier sunrises, though.
.
St Helens England. What does GMT stand for? El Jadid Casablanca-Settat. Italian mathematician Quirico Filopanti introduced the idea of a worldwide system of time zones in his book Miranda! Article Talk. For the global time standard, see Universal Time. Originally, astronomers considered a GMT day to start at noon, [d] while for almost everyone else it started at midnight. It was the first clock ever to show Greenwich Mean Time directly to the public. Bobo-Dioulasso Hauts-Bassins. Myers, J.

0 thoughts on “Whats the time now gmt”