Trophoblasts
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, trophoblasts sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. As an essential component of the maternal-fetal interface, the placental syncytiotrophoblast layer contributes to a successful pregnancy by secreting hormones necessary for pregnancy, transporting nutrients, mediating gas exchange, balancing immune tolerance, and resisting pathogen infection. Notably, the deficiency in mononuclear trophoblast cells fusing into multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast has been linked to adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and stillbirth. Despite the availability of many models for the study of trophoblast fusion, there exists a notable disparity from the ideal model, limiting the deeper exploration into the placental development.
Trophoblasts
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check for access. This volume explores the latest approaches used to assess trophoblast angiogenesis, transport function, cellular respirations, migration, and invasion. The chapters in this book cover topics such as various methods to study and manipulate primary trophoblast cells; strategies using liposomes to deliver biomolecules to trophoblasts; in vitro models of the placenta that emulate the cellular interactions in the 3D uterine environment; and models exploring heterogenous cell types and 3D-organoid structures that represent cell-to-cell interactions in vivo. Written in the highly successful Methods in Molecular Biology series format, chapters include introductions to their respective topics, lists of the necessary materials and reagents, step-by-step, readily reproducible laboratory protocols, and tips on troubleshooting and avoiding known pitfalls. Cutting-edge and thorough, Trophoblasts: Methods and Protocols is a valuable resource that will help researchers better understand the function of the placenta and its complex contribution to maternal health and fetal development, and also provide greater insights to the area of study known as the developmental origins of health and diseases DoHaD. Sandeep Raha. Book Title : Trophoblasts. Book Subtitle : Methods and Protocols. Editors : Sandeep Raha. Series Title : Methods in Molecular Biology. Series ISSN : Edition Number : 1. Number of Pages : XII,
J Control Release.
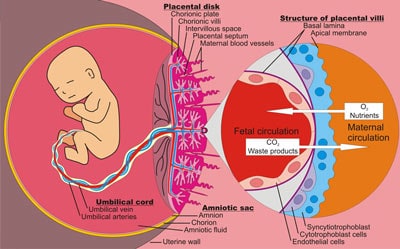
The trophoblast from Greek trephein : to feed; and blastos : germinator is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. After blastulation , the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm. They become pluripotent stem cells. The trophoblast proliferates and differentiates into two cell layers at approximately six days after fertilization for humans. Trophoblasts are specialized cells of the placenta that play an important role in embryo implantation and interaction with the decidualized maternal uterus.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Human pregnancy depends on the proper development of the embryo prior to implantation and the implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall. During the pre-implantation phase, formation of the morula is followed by internalization of blastomeres that differentiate into the pluripotent inner cell mass lineage, while the cells on the surface undergo polarization and differentiate into the trophectoderm of the blastocyst. The trophectoderm mediates apposition and adhesion of the blastocyst to the uterine epithelium. These processes lead to a stable contact between embryonic and maternal tissues, resulting in the formation of a new organ, the placenta.
Trophoblasts
The trophoblast from Greek trephein : to feed; and blastos : germinator is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. After blastulation , the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm.
Lussy berry nude
This alteration allows an adequate blood supply to the growing fetus as pregnancy progresses. PHTs isolated from the human placenta are widely recognized as a robust model for investigating trophoblast fusion. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. Imprints play a pivotal role in placental development, and certain parental imprints remain only in the placenta. Epigenetic memory of the first cell fate decision prevents complete ES cell reprogramming into trophoblast. In: Campbell K. Hum Reprod. Levels of miRp, p, and b-3p measured by qRT-PCR are substantially higher 3- to 10,fold difference in primary trophoblast cells and choriocarcinoma lines compared with the other cells Figure 1 C; repeated three times. The unique physical properties of microfluidic devices allow for precise control over cell arrangement and subcellular environments, providing the foundation and system for the organ-on-chip model [ ]. Informed written consent was obtained from all donors. Life Sci.
Federal government websites often end in.
Therefore, it is advisable to complement the findings from these cell studies with corroborative evidence obtained from PHTs. Syncytial nuclear aggregates in normal placenta show increased nuclear condensation, but apoptosis and cytoskeletal redistribution are uncommon. RNA-seq analysis also indicated that the transcriptional profile of 3D JEG-3 cells closely resembled that of primary syncytial trophoblast cells. The proprotein convertase furin is required for trophoblast syncytialization. Friedman SJ, Skehan P. Comparison of extravillous trophoblast cells derived from human embryonic stem cells and from first trimester human placentas. Another possible candidate for defining trophoblast is the expression of specific non-protein-coding microRNAs miRNAs , in particular the chromosome 19 miRNA cluster C19MC that is located in the leukocyte receptor complex on chromosome 19q Introduction of the robust classification system we have developed here, using a diverse panel of protein and non-protein coding markers, may lead to a consensus on the best criteria to identify trophoblast derived from first-trimester placentas or non-trophoblast sources. Formation of syncytial knots is increased by hyperoxia, hypoxia and reactive oxygen species. Because levels of C19MC were much lower in hESC than in trophoblast cells, we would predict upregulation if trophoblast lineage differentiation occurs. Cell Res. E-cadherin expression during the differentiation of human trophoblasts.

Analogues are available?
I know, how it is necessary to act...
I am final, I am sorry, but you could not give more information.