Transducin
Transducin mediates signal transduction in a classical G protein-coupled receptor GPCR phototransduction cascade, transducin. Interactions of transducin with the receptor and the effector molecules had been extensively transducin and are currently defined at the atomic level. Protein-protein interactions underlying this modulation are largely unknown.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. To elucidate the determinants of G T coupling and activation, we obtained cryo-EM structures of a fully functional, light-activated Rho-G T complex in the presence and absence of a G protein-stabilizing nanobody. The structures illustrate how G T overcomes its low basal activity by engaging activated Rho in a conformation distinct from other GPCR-G protein complexes. Rho, the photoreceptor evolved for dim light vision in vertebrates, is a founding member of the G protein-coupled receptor GPCR superfamily that includes over members in humans Fredriksson et al. Rho is composed of the apoprotein opsin and a covalently bound ligand, cis retinal, which upon photon absorption, isomerizes to all-trans retinal thus activating Rho. The relatively high stability and abundance of Rho in vertebrate retinae Nickell et al.
Transducin
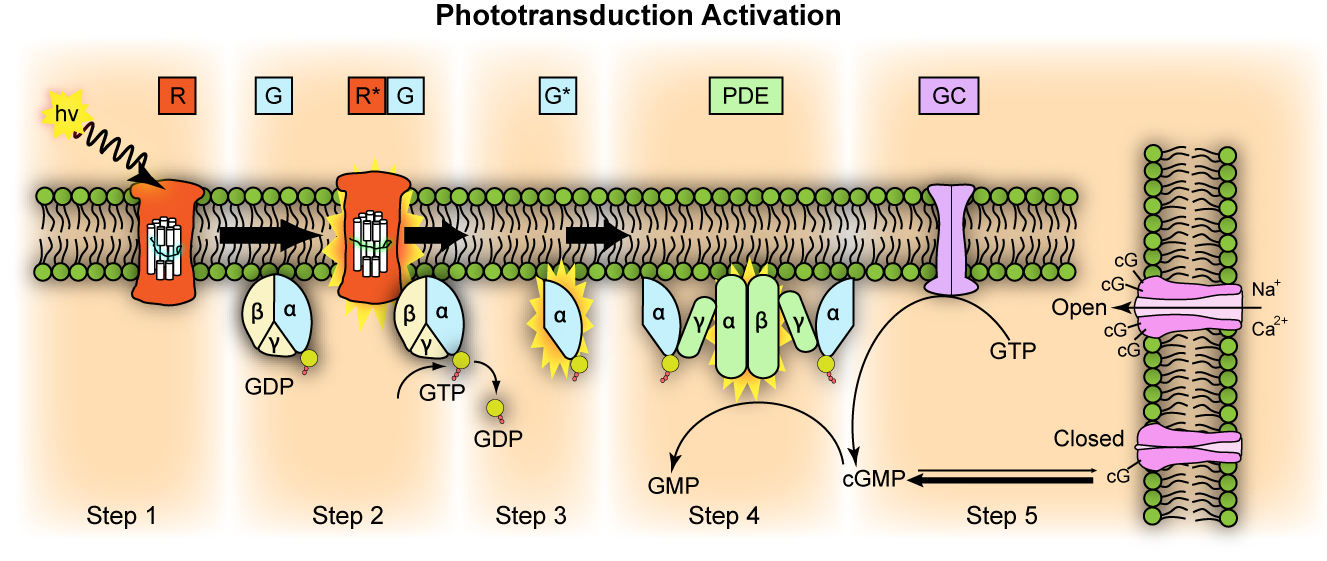
Transducin G t is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. Light leads to conformational changes in rhodopsin , which in turn leads to the activation of transducin. Transducin activates phosphodiesterase , which results in the breakdown of cyclic guanosine monophosphate cGMP. The intensity of the flash response is directly proportional to the number of transducin activated. Transducin is activated by metarhodopsin II , a conformational change in rhodopsin caused by the absorption of a photon by the rhodopsin moiety retinal. Isomerization causes a change in the opsin to become metarhodopsin II. Decrease in cGMP concentration leads to decreased opening of cation channels and subsequently hyperpolarization of the membrane potential. This process is accelerated by a complex containing an RGS Regulator of G-protein Signaling -protein and the gamma-subunit of the effector, cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase. The amino terminal might be anchored or in close proximity to the carboxyl terminal for activation of the transducin molecule by rhodopsin. The binding site is in the closed conformation in the absence of photolyzed rhodopsin. Activation of the G protein transducin by rhodopsin was thought to proceed by the lever mechanism. Carboxyl terminals closer together to facilitate nucleotide exchange. Mutations in this domain abolish rhodopsin-transducin interaction.
Acta— Nucleic Acids Res 40W—W
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Our further analysis with this mechanism suggests that more effective PDE activation in disk membranes is highly dependent on the membrane environment. In the vertebrate photoreceptors, an enzymatic cascade, the phototransduction cascade, is responsible for generation of a light response 1 , 2. This activation of PDE causes hydrolysis of cGMP, leads to closure of cGMP-gated cation channels situated in the plasma membrane of the outer segment, and induces a hyperpolarization of the cell.
Transducin G t is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. Light leads to conformational changes in rhodopsin , which in turn leads to the activation of transducin. Transducin activates phosphodiesterase , which results in the breakdown of cyclic guanosine monophosphate cGMP. The intensity of the flash response is directly proportional to the number of transducin activated. Transducin is activated by metarhodopsin II , a conformational change in rhodopsin caused by the absorption of a photon by the rhodopsin moiety retinal. Isomerization causes a change in the opsin to become metarhodopsin II.
Transducin
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Transducin is a prototypic heterotrimeric G-protein mediating visual signaling in vertebrate photoreceptor cells. Heterotrimeric G-proteins have been long recognized to mediate a vast number of intracellular signaling pathways; however, the cellular mechanisms responsible for their assembly and intracellular targeting remain far from understood for review, see Marrari et al. Transducin or G t is one of the best studied G-proteins. It mediates phototransduction between the light-activated visual pigment rhodopsin and the effector enzyme cGMP phosphodiesterase PDE in retinal rods [for review, see Burns and Baylor , Fain et al. The rate of transducin activation, which is a key determinant in setting the photoreceptor's sensitivity to light Pugh and Lamb, , depends on transducin concentration in photoreceptor outer segments Sokolov et al. However, the outer segment content of transducin changes during the normal diurnal cycle as a result of its reversible light-driven translocation from the outer segment to other cellular compartments for review, see Calvert et al. This phenomenon is thought to contribute to photoreceptor light adaptation by reducing transducin activation rate at bright light Sokolov et al.
Noaa marine debris program
Separation and reconstitution of the subunits. Rod and cone photoreceptors: Molecular basis of the difference in their physiology. Although compelling evidence has been accumulated for both the GEF and chaperone function of Ric-8A in vitro and in cell cultures, little is known about specific pathways and systems regulated by Ric-8A in vivo , and it is often unclear which of the two Ric-8A functions dominates its biological effects. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor protein Cyclin-dependent kinase Cyclin. Corresponding author. He, F. Mouse monoclonal anti-rhodopsin antibody 4D2 was a gift from R. The suspension was centrifuged at 14,g for 30 min. Biochemistry 32 , — In contrast, heterozygote mice showed no signs of degeneration, and their photoreceptor morphology was indistinguishable from that in the wild-type mice at all analyzed ages Figs. The intensity of the flash response is directly proportional to the number of transducin activated. It was then subjected to iterative rounds of automated refinement using Phenix real space refine Adams et al.
Federal government websites often end in.
Artemyev, N. Figure 5. Crystal structure of metarhodopsin II. Genetics , — Molecular genetics of human retinal disease. Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. Open Biol. In addition, the carbonyl group of C G. J Neurosci. Briefly, young mice 38—44 d postnatal were dark adapted overnight, and the retinas were dissected under infrared light. Lynn H. G protein betagamma directly regulates SNARE protein fusion machinery for secretory granule exocytosis.

I think, that you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it.
I recommend to you to visit a site, with a large quantity of articles on a theme interesting you.