Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference ». A tumor- inducing hence the acronym plasmid found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens q. It is these hormones that cause gall formation. Only a small part of the plasmid actually enters the plant; the rest stays in the bacterium, where it has other functions. The wild-type plasmid produces tumor cells, but it can be modified so that it can carry foreign genes into cells without making the recipient cells tumorous.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
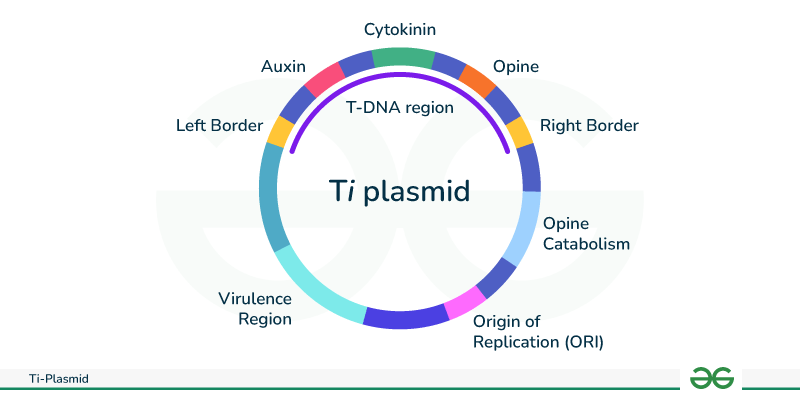
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium. The Ti-plasmid in the bacteria is known to induce crown gall disease in plants by transferring crucial regions from the plasmid. These crucial regions were seen to modify the plant cells into a tumour to produce synthetic plant hormones and cause crown gall. This led the scientists to believe that there is a scope for bioengineering techniques to modify the plants using Ti-plasmid for our own use. Ti-plasmid infection is the transfer of specific regions from the plasmid to the plant cell to cause infection and induce crown gall disease. Ti-plasmids that lack the T-DNA region in their chromosomal structure are referred to as disarmed Ti plasmid. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Post My Comment. Frequently Asked Questions Q1. What is Ti plasmid infection? What is disarmed Ti plasmid?
The Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Crown gall caused by Agrobacterium is one of the predominant diseases encountered in rose cultures. However, our current knowledge of the bacterial strains that invade rose plants and the way in which they spread is limited. Here, we describe the integrated physiological and molecular analyses of 30 Agrobacterium isolates obtained from crown gall tumors and of several reference strains. This study led to the classification of rose isolates into seven groups with common chromosome characteristics and seven groups with common Ti plasmid characteristics. Altogether, the rose isolates formed 14 independent groups, with no specific association of plasmid- and chromosome-encoded traits.
Ti-Plasmid is also known as an extrachromosomal genetic material found in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The crown ball disease that affects dicot plants is caused by this phytopathogen. The size of the Ti Plasmid is kb. These are large plasmids that typically have a size between kbp and 2 Mbp. Ti Plasmid is an extrachromosomal genetic material found in the dicot plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. This phytopathogen causes crown ball disease, which is a problem for dicot plants. A useful tool for transferring desired genes to different plant species, the Ti Plasmid was initially discovered in These Plasmids can range in size from Kbps to 2 Mbps, which is often rather large.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The trb operon from pTiC58 is one of three loci that are required for conjugal transfer of this Ti plasmid. The operon, which probably codes for the mating bridge responsible for pair formation and DNA transfer, contains 12 genes, 11 of which are related to genes from other members of the type IV secretion system family. Insertion mutations were constructed in each of the 12 genes, contained on a full-length clone of the trb region, using antibiotic resistance cassettes or a newly constructed transposon. This transposon, called mini-Tn 5 P trb , was designed to express genes downstream of the insertion site from a promoter regulated by TraR and AAI. Each mutation could trans complement downstream Tn 3 HoHo1 insertions in the trb operon of full-sized Ti plasmids.
Steohen hilton
Hirsch, P. For the T-DNA, a nick will be created at the T-DNA's border sequence, and the nicked T-strand will be transported to the cell membrane, where the rest of the transfer machinery is present. RiM26 II Succ. Rif r mutant of pathogenic strain C58 carrying pTiC Young, J. Suzuki, and K. Independent of the opine type, tmr was also amplified from the A. Nucleic acids in the environment. RepB ParB , P The only A. A similarity analysis with equal weights of Ti plasmid characteristics confirmed the homogeneity among the isolates that clustered in defined plasmid groups Fig. Supplementary Material [Supplemental material] Click here to view.
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria.
An improved suicide vector for construction of chromosomal insertion mutations in bacteria. This led the scientists to believe that there is a scope for bioengineering techniques to modify the plants using Ti-plasmid for our own use. Variation of 16SS internally transcribed spacer sequence and intervening sequence in rDNA among the three major Agrobacterium species. Quorum sensing but not autoinduction of Ti plasmid conjugal transfer requires control by the opine regulon and the antiactivator TraM. The site is secure. Movement of Agrobacterium within the plants would account for the identification of the same isolates in cuttings and roots RiM10 and RiM10r; RiM As the modified plasmid delivery system was simple and efficient, conversion of strains to the disarmed type was easy and should be applicable in studies to screen for useful strains. The transfer requires both the products of other genes located in the nontransferred virulence vir region of the Ti plasmid and proteins that are encoded by the chromosome 4. Plant-Microbe Interact. EMBO J. Kato, and K. Dafny-Yelin, S. Authentic nopaline, octopine, and mannopine standards were purchased from Sigma. Here, we present the establishment of a collection of Agrobacterium isolates that were obtained from diseased rose plants from France, Spain, and Morocco. This can then block the translational production of the RepC protein.

Between us speaking, in my opinion, it is obvious. I will refrain from comments.
To think only!