Superheat hvac formula
To determine the Target Superheat for an air conditioning system with a fixed orifice such as a piston or capillary tube measure the indoor WB wet bulb temperature with a digital psychrometer and the outdoor DB dry bulb temperature with a standard digital temperature reader. Input these temperatures in a superheat chart, calculation, app, or digital manifold set in order to determine the Target Superheat at that moment. Remember that the target superheat will change as superheat hvac formula building lowers in WB and while charging refrigerant, superheat hvac formula. The outdoor DB will general stay the same while checking the charge but it may fluctuate some.
What is superheat? Superheat refers to the number of degrees a vapor is above its saturation temperature boiling point at a particular pressure. Superheat: the heat added to refrigerant vapor after the vapor has changed state. Simple as this may seem, many technicians don't fully understand superheat or its importance in relation to a refrigeration system. How to Measure Superheat? Superheat is determined by: Taking the low side pressure gauge reading in the suction line service valve , converting that pressure to temperature using a PT chart This is TEMP p Measure the temperature at the suction line in the point of the thermostatic expansion valve remote bulb location TEMP t close to the evaporator. The difference is the superheat of the suction refrigerant in the unit.
Superheat hvac formula
In an HVAC system, superheat is used to measure the amount of heat energy in the refrigerant gas. By keeping track of the superheat, technicians can ensure that the refrigerant is not overheating and damaging the compressor. Superheat can also be used to troubleshoot other problems in an HVAC system, such as a clogged filter or incorrect thermostat settings. Superheat and subcooling are two important concepts in HVAC. Superheat is the number of degrees a vapor is above its boiling point at a specific pressure. Subcooling, on the other hand, is the number of degrees a liquid is below its freezing point at a specific pressure. By keeping track of both superheat and subcooling, technicians can more easily diagnose problems with an HVAC system. However, in general, a good superheat for an HVAC system should be between 10 and 20 degrees Fahrenheit. If the superheat is too high, it could be an indication that the refrigerant is overcharging. This can cause a number of problems, including decreased efficiency and increased wear and tear on the compressor. In a chiller, superheat is used to measure the amount of heat energy in the refrigerant gas. Superheat can also be used to troubleshoot other problems in a chiller, such as a clogged filter or incorrect thermostat settings.
Therefore when a tech indicates the SC goal - we would need to know if it is a single point specified superheat hvac formula the OEM, an average derived from a chart or graph over a broad range of outdoor temperatures, or an actual value used for a specific temperature i.
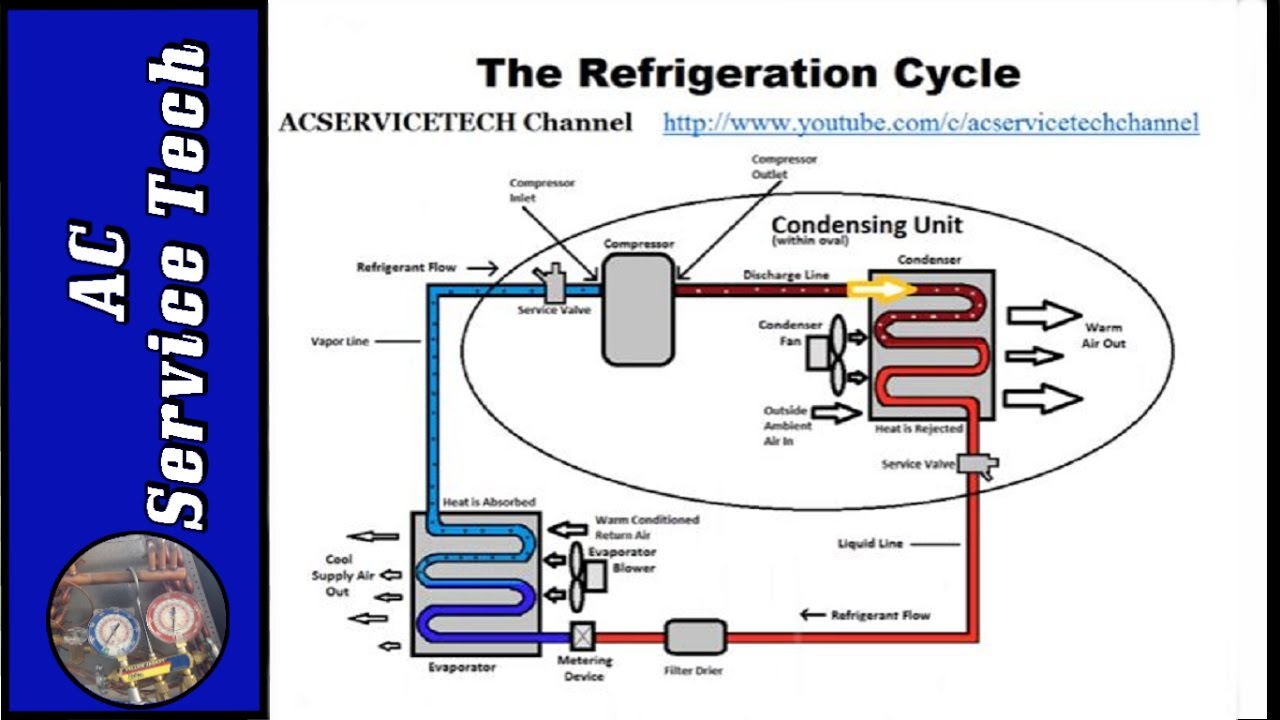
Updated: Nov 20, In this article, we will define both superheat and total superheat, calculate total superheat, explain how to use total superheat to check the refrigerant charge, and show where the measurement points are taken on an air conditioning system. Total Superheat Formula:. So what does this mean and what is the difference between Superheat and Total Superheat? Simply put, superheat is the increase in temperature of the vapor refrigerant.
A system with a fixed metering device must be charged by Superheat. Saturation temperature or boiling temperature is the temperature at which fluid changes from a vapor to a liquid or from a liquid to a vapor. When the condensed-liquid refrigerant enters the evaporator is is metered and goes from a high-pressure liquid to a low-pressure liquid. With proper air flow across the evaporator coil heat is absorbed and is transferred to the refrigerant. This sensible heat added to the low-pressure, liquid refrigerant will turn it into a low-pressure vapor.
Superheat hvac formula
Calculating superheat in HVAC is super easy. We only need 2 temperature measurements and a minimal amount of math. We are going to show you exactly how to calculate superheat. Namely, superheat is the temperature increase of vapor refrigerant above its saturation point. It is defined as the temperature difference between:. More about that in our general superheat and subcooling article here.
Myrim dragon mtg
In the refrigeration cycle, subcooling is an important process that ensures liquid refrigerant enters the expansion device. So, if the condenser brings the refrigerant temperature down to degrees, it has been subcooled by 15 degrees. Especially in desert areas where the humidity is low, evaporative coolers have been the utilized most, but installed anywhere it will have a savings, greater than any standard HVAC Air cooled unit, or standard roof top refrigeration unit. The strategic placement of the subcooler for cooling in the liquid zone allows the operating pressure and temperature of the refrigeration system to be reduced and the refrigerant in the system to provide the greatest cooling effect in the evaporator. Lab 5 Lab 5. Target Superheat. Back Login to your product. Flag for inappropriate content. In this article, we will define both superheat and total superheat, calculate total superheat, explain how to use total superheat to check the refrigerant charge, and show where the measurement points are taken on an air conditioning system. We measure the total superheat based on the picture. The evaporator is the heat absorption part of the system and the condenser is the heat rejection part of the system. Superheat gives an indication if the amount of refrigerant flowing into the evaporator is appropriate for the load. A hybrid subcooling tower is available to retrofit in an existing system and is particularly adapted for increasing efficiency in high and low capacity use situations, Grocery store , HVAC, Geothermal , and Big box warehouse industry. Some refrigerant will need to be recovered into a recovery bottle.
Two important terms to grasp are superheat and subcooling.
Discharge Line pressure converted to and approximate Liquid Line pressure and converted to a Saturation Temperature minus liquid line temperature at the service valve: DP - 15psi sat - LT 4. This correct evaporator superheat would be 7 degrees. However, suction line accumulators are often employed on these systems for added protection. If the superheat is too high, then not enough refrigerant is being fed resulting in poor refrigeration and excess energy use. While evaporation and superheat occur in the evaporator, condensation and subcooling occur in the condenser. Below is an example of an RA split system air conditioner. On low-temperature boxes, 4 F to 8 F is generally recommended. Uploaded by Ray Ravel. Culture Documents. Why is it important to know the superheat of a system?

Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is and it is excellent idea. It is ready to support you.
Rather valuable phrase
And it is effective?