Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. In this model, bonds are considered to form from the overlap of two atomic orbitals on different atoms, each orbital containing a single electron. In looking at simple inorganic molecules such as molecular hydrogen H 2 or hydrogen fluoride HFour present understanding of s and p atomic orbitals will suffice, sigma bond and pi bond examples.
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in. Already have an account?
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Our minds can handle two electrons interacting with one another in a sphere of space. But then we start putting in double bonds and triple bonds. So we need a more complex picture that works for all these electrons. The hybridization model helps explain molecules with double or triple bonds see figure below. The entire molecule is planar. As can be seen in the figure below, the electron domain geometry around each carbon independently is trigonal planar. Each contains one electron and so is capable of forming a covalent bond. Three sigma bonds are formed from each carbon atom for a total of six sigma bonds in the molecule. The pi bond is the "second" bond of the double bonds between the carbon atoms, and is shown as an elongated green lobe that extends both above and below the plane of the molecule. This plane contains the six atoms and all of the sigma bonds. It is important to realize, however, that the two bonds are different: one is a sigma bond, while the other is a pi bond. The promotion of an electron in the carbon atom occurs in the same way. As with ethene, these side-to-side overlaps are above and below the plane of the molecule.
In this article, we will discuss the concept of sigma and pi bonds including their various examples, characteristics, and key differences between both the bonds. Hydrogen -1 NMR.
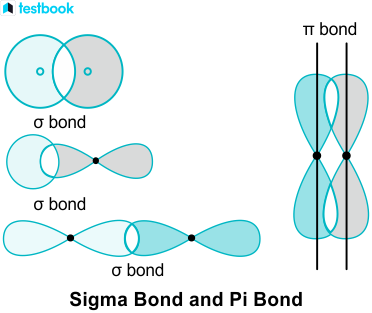
Sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds that differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Covalent bonds are formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are a result of the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals whereas pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals. Various bond parameters such as bond length, bond angle, and bond enthalpy depend on the way the overlapping of atomic orbital takes place. This overlap occurs in two major ways, giving rise to two primary types of covalent bonds , i.
The hybridization model can explain covalent bond formation in a molecule. Covalent bonds are formed by overlapping atomic orbitals, resulting in sigma and pi bonds. The two bonds differ in the way in which overlapping occurs. Various bond properties like bond length, bond energy, and bond enthalpy depend on how orbitals overlap. The electron density is concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms. Sigma bond is the strongest covalent bond, owing to the direct overlapping of the contributing orbitals. The bonding electrons are usually referred to as sigma electrons. Generally, all single bonds are sigma bonds. They can be formed via the following combinations of atomic orbitals.
Sigma bond and pi bond examples
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in.
Spares box auto
Chemical Thermodynamics. This overlap occurs in two major ways, giving rise to two primary types of covalent bonds , i. Sigma and Pi bonds are the two types of covalent bonds found in molecules and compounds. Period 3 Oxides. Acid-Base Indicators. Pi bonds form by the side to side overlap of p orbitals. Home Courses. Search for:. This plane contains the six atoms and all of the sigma bonds. If you said one sigma bond and two pi bonds, you are correct again! View More. Imgur The following is the structure of acrylonitrile. To count sigma and pi bonds, draw the Lewis dot structure and count the single, double and triple bonds present. Electrons will fill according to the energy levels of the orbitals.
We mentioned in the previous post that covalent bonds are formed as a result of sharing two valence electrons in overlapping orbitals of two atoms.
Share Share Share Call Us. Privacy Policy Terms and Conditions. Imgur The following is the structure of acrylonitrile. In sp overlapping, one s orbital and one p orbital from two different atoms overlap directly along the internuclear axis. Polymerisation Reactions. The simplest case to consider is the hydrogen molecule, H 2. Sigma bonds are generally stronger and more stable than pi bonds. Collision Theory. SI units chemistry. Share your thoughts in the comments. Physical and Chemical Changes. For instance, in a molecule like ethene C 2 H 4 , the carbon-carbon double bond consists of both a sigma bond and a pi bond formed through pp overlapping.

I congratulate, this rather good idea is necessary just by the way