Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
Theoretical Physical Chemistry Revision Notes.
Study material notes on the linear shape of molecules. This theory is dependent on the premise that repulsion stickers between the valence electrons in each atom, and all atoms will rearrange themselves in a way that the electron pair repulsion is minimised on its own. The VSEP number is responsible for describing the molecule shape, as described in the table below-. The atoms come in contact with each other to build molecules, whereas molecules come in contact to form compounds and elements. Chemical bonds can lead to three types of interaction between atoms. These include-.
Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
Views: 5, Connect with our Chemistry tutors online and get step by step solution of this question. Are you ready to take control of your learning? American National Curriculum. High School. All topics. Question asked by Filo student. Views: 5, students. First, find the number of valence electrons of each atom. The Beryllium Be has 2 valence electrons, and each Chlorine Cl atom has 7 valence electrons. Step 2: Draw the Lewis structure of BeCl2. Start by placing Beryllium Be at the center as it has the lowest electronegativity. Then, attach two Chlorine atoms to Be by single bonds. The central atom, Be, has its two valence electrons already used, giving bond pairs, and as it can hold a maximum of four electrons, it does not have any additional lone pairs.
Molecular Dipole Moments You previously learned how to calculate the dipole moments of simple diatomic molecules.
Submitted by Marilyn R. We will assign your question to a Numerade educator to answer. Your personal AI tutor, companion, and study partner. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. Millions of real past notes, study guides, and exams matched directly to your classes. What would be its associated molecular geometry? Draw the Lewis structure for NO2-, then answer the following questions.
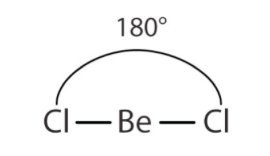
Drawing and predicting the BeCl2 molecular geometry is very easy. Here in this post, we described step by step method to construct BeCl2 molecular geometry. A three-step approach for drawing the BeCl2 molecular can be used. The first step is to sketch the molecular geometry of the BeCl2 molecule, to calculate the lone pairs of the electron in the central beryllium atom; the second step is to calculate the BeCl2 hybridization, and the third step is to give perfect notation for the BeCl2 molecular geometry. The BeCl2 molecular geometry is a diagram that illustrates the number of valence electrons and bond electron pairs in the BeCl2 molecule in a specific geometric manner. The geometry of the BeCl2 molecule can then be predicted using the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory VSEPR Theory and molecular hybridization theory, which states that molecules will choose a BeCl2 geometrical shape in which the electrons have from one another in the specific molecular structure. Finally, you must add their bond polarities characteristics to compute the strength of the Be-Cl bond dipole moment properties of the BeCl2 molecular geometry.
Shape of becl2 according to vsepr theory
BeCl2 referred to as Beryllium Chloride, is an inorganic compound. It appears as white or yellow crystal solid at room temperature. It can exist in both monomeric and 1-D polymeric forms. The properties of beryllium chloride are similar to aluminum chloride owing to the diagonal relationship of beryllium with aluminum.
Film de guerre en francais youtube
Phosphorus has five valence electrons and each chlorine has seven valence electrons, so the Lewis electron structure of PCl 5 is. This is essentially a trigonal bipyramid that is missing two equatorial vertices. Housecroft, Catherine E. We also expect a deviation from ideal geometry because a lone pair of electrons occupies more space than a bonding pair. Similarly, the carbon atom on the right has two double bonds that are similar to those in CO 2 , so its geometry, like that of CO 2 , is linear. Repulsions are minimized by directing each hydrogen atom and the lone pair to the corners of a tetrahedron. Its described on various internet sites as a seesaw shape! APPENDIX 1 Electron pair geometry and molecular geometry The electron pair geometry is the arrangement of the usually pairs of bonding and non-bonding electrons around the central atom of the neutral molecule or molecular ion. Byju's Answer. Therefore, when applying VSEPR to molecules or ions with multiple bonds, you treat double or triple bonds as if they were single bonds to deduce the molecular geometry. Ask unlimited questions and get video answers from our expert STEM educators. First, find the number of valence electrons of each atom. Five groups of electrons around the central atom the Lewis dot and cross electronic diagram used to predict the shape - trigonal bipyramid electron pair geometry trigonal bipyramidal shaped molecule electrons: 5 bond pairs , no lone pairs Electron pair geometry same as the molecular geometry. Therefore, the shape of the molecules are arranged so that the energy is minimized. For example, in a molecule such as CH 2 O AX 3 , whose structure is shown below, the double bond repels the single bonds more strongly than the single bonds repel each other.
The central atom has no lone pair and there are two bond pairs. Hence, it has a linear shape. The central atom has no lone pair and there are three bond pairs.
The shape is Bent. D There are three nuclei and one lone pair, so the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal , in essence a tetrahedron missing a vertex. The electron group geometry for NO2- is -- A. The central atom, beryllium, contributes two valence electrons, and each hydrogen atom contributes one. For example:. Share via. Introduction The shapes of the molecules is determined mainly by the electrons surrounding the central atom. Download Filo and start learning with your favourite tutors right away! The Lewis electron-pair approach can be used to predict the number and types of bonds between the atoms in a substance, and it indicates which atoms have lone pairs of electrons. The iodine has two electron pairs. The central atom, carbon, has four valence electrons, and each oxygen atom has six valence electrons.

It is remarkable, very valuable message