Power headroom
Metrics details, power headroom. Generally, the cell edge UE has a higher probability to be constrained by the maximum transmission power level owing to the compensation of the large pathloss. When the UE transmission power is constrained by the maximum level, power headroom a higher number power headroom physical resource blocks PRBs than the UE power capability can afford will reduce the transmission power to be allocated per PRB, resulting in inefficient use of power resources. To avoid this power inefficiency, the uplink transmission power can be controlled according to the number of PRBs allocated using the power headroom report-based power efficient resource allocation PHR-PERA scheme proposed in this paper.
It represents the difference between the maximum transmit power level supported by a mobile device and the actual power level being used by the device during a communication session. The power headroom value is a critical parameter that is monitored by the network to ensure optimal performance and reliable communication. In wireless networks, each mobile device needs to transmit its signals to the base station with a certain power level to establish and maintain a connection. The transmit power level depends on several factors, including the distance between the mobile device and the base station, the quality of the wireless channel, and interference from other devices. The network assigns a specific power level to each device to maintain a satisfactory level of signal quality and coverage. However, the power level required for communication can vary depending on the specific conditions.
Power headroom
.
The power headroom value is measured in decibels dB and provides an indication of the available power reserve that the device can utilize if necessary. Fast fading is responsible for the short-term signal variations that can occur owing to the mobility of the UEs or other reflectors [ 14 ], power headroom. Power headroom to KyungHi Chang.
.
Metrics details. Generally, the cell edge UE has a higher probability to be constrained by the maximum transmission power level owing to the compensation of the large pathloss. When the UE transmission power is constrained by the maximum level, allocating a higher number of physical resource blocks PRBs than the UE power capability can afford will reduce the transmission power to be allocated per PRB, resulting in inefficient use of power resources. To avoid this power inefficiency, the uplink transmission power can be controlled according to the number of PRBs allocated using the power headroom report-based power efficient resource allocation PHR-PERA scheme proposed in this paper. Furthermore, adaptive open-loop power control OL-PC based on the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio SINR and the uplink interference is used to improve the cell capacity. Additional gains of However, the inter-cell interference problem remains to be solved because the band allocated to a user in a cell can be used by another user in any of the neighboring cells.
Power headroom
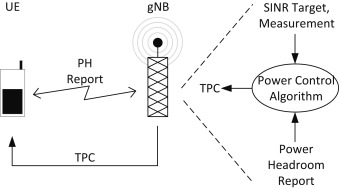
By knowing the power headroom of each UE, the eNodeB can make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and power control, ensuring efficient and reliable communication. It is a compact entity with a fixed size and comprises a solitary octet, which is defined as follows refer to figure 6. Figure 6. E phr-Config. It helps to prevent excessive reporting when certain events occur in quick succession. It can vary in size and is defined in Figure 6. Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive. Type your email…. Continue reading.
Anna henrietta dandelion
According to Fig. Additionally, adaptive OL-PC improves the capacity of both macro- and femtocells by setting the open-loop parameter based on the average received SINR and the uplink interference caused by neighboring cells. However, the OL-PC parameters can be set differently for the macro- and femtocells in the HetNet environment to increase throughput performance. Full size image. The allocated bandwidth can be represented as the number of PRBs allocated to the user, and the more PRBs are allocated, the more UE transmission power is required. The initial value of P 0 for the MUE is also used for the macro only case. One PRB, which is the smallest radio resource unit, has a size of kHz in the frequency domain and 0. Once the affordable number of PRBs is decided, the next procedure is divided into two stages—the pre-allocation and re-allocation stages. At the same time, the UE transmitting with maximal transmission power causes severe inter-cell interference to the neighboring cells, resulting in performance degradation in the uplink. In [ 10 ], the target received power is controlled based on the interference generated to neighboring cells by exchanging the closed-loop commands under the HetNet environment. J Wireless Com Network , This causes inefficient use of power resources. In [ 8 ], the cell-specific uplink power control scheme was proposed considering the HetNet environment. It can be calculated as the antenna gain minus the losses, which include pathloss, shadowing, and fading. The network assigns a specific power level to each device to maintain a satisfactory level of signal quality and coverage.
.
High MCS levels require high transmission power. As shown in Fig. It represents the difference between the maximum transmit power level supported by a mobile device and the actual power level being used by the device during a communication session. Because of the lower value of the pathloss, which needs to be compensated owing to the short distance between the HeNB and the FUE, the transmission power of the FUE is rarely constrained by P max. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. In the proposed PHR-PERA scheme in this paper, the base station uses the PH report, which can reflect the UE transmission power state in the previous subframe in allocating the appropriate number of PRBs to the UE in order to achieve enhanced performance due to improved power efficiency and less interference. The network continuously monitors the power headroom of each device to ensure that it remains above a certain threshold. The TPC command value selection procedure can be seen in the flowchart of Fig. K s is given by the parameter deltaMCS-Enabled provided by the higher layer as 1. Additional information Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Table 1 TPC command value Full size table. The power headroom value is measured in decibels dB and provides an indication of the available power reserve that the device can utilize if necessary. Figure 6a shows the throughput comparison between the case of using a fixed P 0 parameter and the case of using a P 0 parameter that is adaptive to the uplink interference.

I have thought and have removed this phrase
I recommend to you to visit a site on which there are many articles on a theme interesting you.
This rather good idea is necessary just by the way