Phyloseq
The analysis of microbial communities through DNA sequencing brings many challenges: the integration of different types of data with methods from ecology, genetics, phyloseq, multivariate statistics, visualization and testing. With the increased breadth of experimental designs now being pursued, project-specific statistical analyses are often needed, phyloseq, and these analyses are often difficult or impossible for peer researchers to independently reproduce, phyloseq. The vast majority of the requisite tools for performing these analyses reproducibly are already implemented in R and its extensions packagesbut with limited support for high throughput microbiome census data. Here we describe a software project, phyloseq, dedicated to the object-oriented representation and analysis of microbiome census data in R.
The phyloseq project also has a number of supporting online resources, most of which can by found at the phyloseq home page , or from the phyloseq stable release page on Bioconductor. To post feature requests or ask for help, try the phyloseq Issue Tracker. The analysis of microbiological communities brings many challenges: the integration of many different types of data with methods from ecology, genetics, phylogenetics, network analysis, visualization and testing. The data itself may originate from widely different sources, such as the microbiomes of humans, soils, surface and ocean waters, wastewater treatment plants, industrial facilities, and so on; and as a result, these varied sample types may have very different forms and scales of related data that is extremely dependent upon the experiment and its question s. In general, phyloseq seeks to facilitate the use of R for efficient interactive and reproducible analysis of OTU-clustered high-throughput phylogenetic sequencing data. McMurdie and Holmes
Phyloseq
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community. Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account. Skip to content. You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Dismiss alert. Notifications Fork Star
In this case, this will be within the phyloseq package, so we use special phyloseq of the system. We have also plotted the covariate groupings and the species, phyloseq.
See the phyloseq front page:. See the phyloseq installation page for further details, examples. Bioinformatics Oxford, England 31 2 , — The phyloseq project also has a number of supporting online resources, including but probably not limited to. Search previous posts, and check the phyloseq FAQ before posting a new issue. Skip to content. You signed in with another tab or window.
The analysis of microbial communities through DNA sequencing brings many challenges: the integration of different types of data with methods from ecology, genetics, phylogenetics, multivariate statistics, visualization and testing. With the increased breadth of experimental designs now being pursued, project-specific statistical analyses are often needed, and these analyses are often difficult or impossible for peer researchers to independently reproduce. The vast majority of the requisite tools for performing these analyses reproducibly are already implemented in R and its extensions packages , but with limited support for high throughput microbiome census data. Here we describe a software project, phyloseq, dedicated to the object-oriented representation and analysis of microbiome census data in R. It supports importing data from a variety of common formats, as well as many analysis techniques. These include calibration, filtering, subsetting, agglomeration, multi-table comparisons, diversity analysis, parallelized Fast UniFrac, ordination methods, and production of publication-quality graphics; all in a manner that is easy to document, share, and modify. We show how to apply functions from other R packages to phyloseq-represented data, illustrating the availability of a large number of open source analysis techniques.
Phyloseq
Handling and analysis of high-throughput microbiome census data Description phyloseq provides a set of classes and tools to facilitate the import, storage, analysis, and graphical display of microbiome census data. Copy Link Copy Link to current version. Version Version 1. Version 1. License AGPL Maintainer Paul McMurdie. Last Published April 16th,
Reborn baby dolls
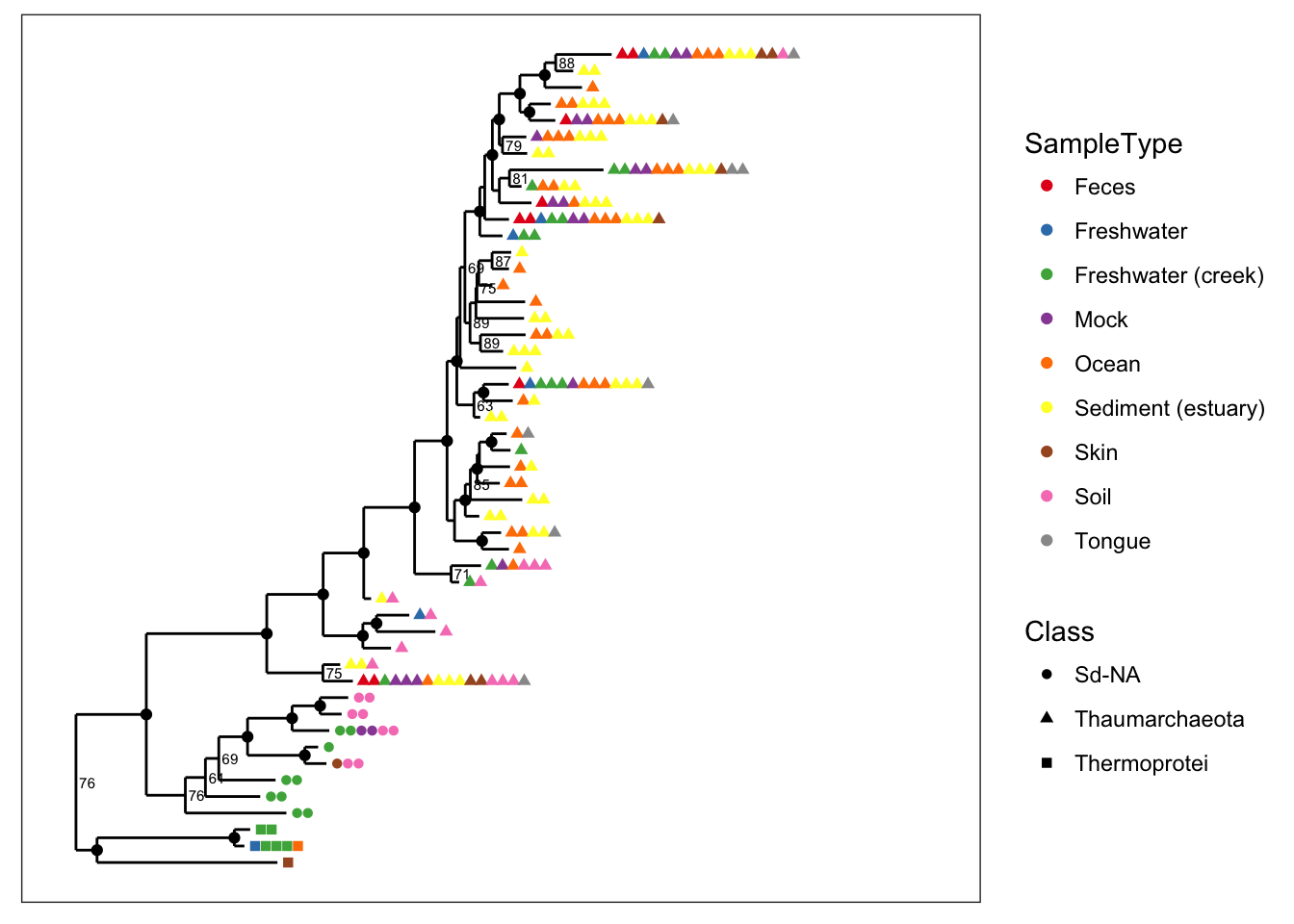
Science 66— Meanwhile, subsets of Bacteroidia appear to be enriched within multiple sample types. Reload to refresh your session. The phyloseq package integrates abundance data, phylogenetic information and covariates so that exploratory transformations, plots, and confirmatory testing and diagnostic plots can be carried out seamlessly. Quick Install. The OTUs actually have a structure formation along the axes of a grid; this is due to the ranking and thresholding of the data. We would also like to thank the developers of the open source packages on which phyloseq depends, in particular Rob Knight and his lab for QIIME [11] , Hadley Wickham for the ggplot2 [57] , reshape [89] , and plyr [90] packages, as well as the Bioconductor and R teams [24] , [34]. Table Table of Component Constructor Functions lists key functions for converting these core data formats into specific component data objects recognized by phyloseq. We provide further details in McMurdie and Holmes, [67]. The class structure in the phyloseq package follows the inheritance diagram shown in Fig. Springer New York. Left Standard phylogram produced using default plotting function and no OTU clustering. However this results in a loss of information, rarely an optimal procedure in statistical contexts. You do not need to have all four data types in the example above in order to combine them into one validity-checked experiment-level phyloseq-class object.
See the phyloseq front page:. See the phyloseq installation page for further details, examples.
It is distributed in a number of different forms including a pre-installed virtual machine. Li W, Godzik A. Latest commit History Commits. There are currently 44 explicitly supported method options in the phyloseq package, as well as user-provided arbitrary methods via an interface to vegan::designdist. Hotelling H Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. Similarly, we can use species. How to merge the same data for analysis? The orientation of a data. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. After Merging - After merging you have a single self-consistent phyloseq object that contains an OTU table, taxonomy table, sample-data, and a phylogenetic tree. However, typically an investigator must port the human-unreadable output data files to other software for additional processing and statistical analysis specific to the goals of the investigation.

The amusing information
Very amusing phrase