Ng108 15
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, ng108 15. Primary data not included in the primary or Supplemental Material are available upon request.
All cell cultures have the potential to carry as yet unidentified adventitious agents. It is the responsibility of the end user to ensure that their facilities comply with biosafety regulations for their own country. The Culture Collections represent deposits of cultures from world-wide sources. While every effort is made to ensure details distributed by Culture Collections are accurate, Culture Collections cannot be held responsible for any inaccuracies in the data supplied. References where quoted are mainly attributed to the establishment of the cell culture and not for any specific property of the cell line, therefore further references should be obtained regarding cell culture characteristics.
Ng108 15
Metrics details. The generation of action potential is required for stimulus-evoked neurotransmitter release in most neurons. But differentiation 21 days induced the action potential generation in Exploring cell molecular and electrophysiological properties such as expression and current of ion channels, and action potentials is very important for understanding the physiological and pathophysiological functions of the excitable cells including neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells. Although acute-isolated primary cell is the optimum choice for pursuing these measurements, cell lines are also served as an appropriate tool for the cell molecular and electrophysiological studies, because cell lines provide the advantage of enough homogeneous cells that can make the investigation under easily controlled conditions. After differentiation, this cell line presents neurite extension, forms synapses, and develops the ultimate neural property of acetylcholine release and specific activities of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase [ 2 — 4 ]. Therefore, many studies used NG cells as the cholinergic cells to investigating electrophysiological kinetics and cell functions of neurons [ 4 — 12 ]. Action potential is an important physiological feature of the excitable cells. In most vertebrate neurons, action potential production is required for neuronal excitation and stimulus-evoked neurotransmitter release, which are involved in neuron-to-neuron communication [ 13 , 14 ]. As a cholinergic neuron marker, choline acetyltransferase ChAT was detected in NG cells by immunofluorescence staining. Expression of choline acetyltransferase ChAT, a cholinergic neuronal marker in NG cells at undifferentiated state or after 21 days of differentiation, measured by immunofluorescence staining. Using whole-cell current-clamp recording method, the response of cell membrane to current injections was measured in undifferentiated and differentiated NG cells Figure 2 and Table 1. Alterations in membrane excitability of NG cells induced by differentiation. A : Representative traces show the membrane potential response to a depolarizing current injection pA, 1 sec under whole-cell current-clamp configuration.
All treatments but NS alone showed a significant increase in CREB, known to play an important role in driving differentiation [ 16,ng108 15, ] Figure 9 C.
The differentiated type of neuroblastomaxglioma hybrid cell line, NG, has widely been used in in vitro studies instead of primary-cultured neurons. Here we examined whether NG cells can be used as a model for studying the neuronal differentiation process. We compared the expression of neuronal proteins neurofilament NF , phosphorylated-NF p-NF , microtubule associated protein 2, synaptophysin, syntaxin 1, choline acetyltransferase, and acetylcholinesterase AChE and a glial protein vimentin between undifferentiated and differentiated NG cells by immunocytochemistry and immunoblot analysis. The expression of all neuronal proteins, with the exception of NF and p-NF, was positive in differentiated cells, but almost negative in undifferentiated cells. On the other hand, cytoskeletal intermediate filaments NF and p-NF for neurons and that vimentin for glia were present in both undifferentiated and differentiated cells. Our results showed that even though the expression of cytoskeletal filaments does not change during differentiation of NG cells, these cells during differentiation can serve as an appropriate tool for investigating and understanding the mechanisms involved in neuronal development and differentiation. Abstract The differentiated type of neuroblastomaxglioma hybrid cell line, NG, has widely been used in in vitro studies instead of primary-cultured neurons.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Primary data not included in the primary or Supplemental Material are available upon request. Glioblastoma is a rapidly progressing brain cancer that is very difficult to treat. Given that many aspects of cell and tissue behavior are controlled by electric signaling, we sought to test whether drugs that target ion channel proteins might be effective at controlling the spread and functionality of glioblastoma cells in culture. Testing aspects of cell growth and physiology, we show that several novel combinations of ion channel drugs, which are already approved in human patients for other purposes, are highly effective against two types of glioblastoma cells. This facilitates the development of new strategies to address cancer by repurposing the large class of ion channel drugs against cancer. Glioblastoma is a lethal brain cancer that commonly recurs after tumor resection and chemotherapy treatment.
Ng108 15
In the fundamental process of neuronal path-finding, a growth cone at the tip of every neurite detects and follows multiple guidance cues regulating outgrowth and initiating directional changes. Using fluorescence time lapse microscopy we could identify two distinct modes of growth cone collapse leading either to neurite retraction or to a controlled halt of neurite extension. In the latter case, lateral movement and folding of actin bundles filopodia confine microtubule extension and limit microtubule-based expansion processes without the necessity of a constantly engaged actin turnover machinery. We term this previously unreported second type fold collapse and suggest that it marks an intermediate-term mode of growth regulation closing the gap between full retraction and small scale fluctuations. Neuronal development during embryogenesis as well as regeneration after injury is a highly complex process that requires robust mechanisms on the single-cell level to produce reliable results. Therefore, a multitude of interacting and overlapping signaling and guidance mechanisms is necessary to regulate neuronal growth and steer neuronal processes towards their respective target areas. For this purpose, the highly complex and motile growth cone develops at the tip of outgrowing axons and, to a lesser extent, of dendrites.
Maxsold.maxsold.com
Hybridisation, fusion partner and virus studies: Sendai virus. Furthermore, ion channel transcripts have been shown to be upregulated in GSCs, including SCN8A , which encodes a sodium channel, KCNB1 , which encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel, and GRIA3 , which encodes an ionotropic glutamate receptor that is non-selective for monovalent cations [ 53 ]. The intermediate filament vimentin mediates microRNA miR function in cellular self-renewal by regulating the expression of the Sox2 transcription factor. Kamentsky L. Bioelectrical approaches to cancer as a problem of the scaling of the cellular self. Lobikin M. Using single-cell real-time PCR, we measured the Na v 1. This facilitates the development of new strategies to address cancer by repurposing the large class of ion channel drugs against cancer. Pillozzi S. The cells without action potential presented similar electrical characteristics to those cells with 9 days of differentiation Table 1. Current traces were sampled at 10 kHz and filtered at 5 kHz. Intuyod K. While every effort is made to ensure details distributed by Culture Collections are accurate, Culture Collections cannot be held responsible for any inaccuracies in the data supplied. The treatment with pantoprazole alone showed less differentiation and senescence when compared to pantoprazole in combination with retigabine, NS, TMZ, or rapamycin in U87 cells.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
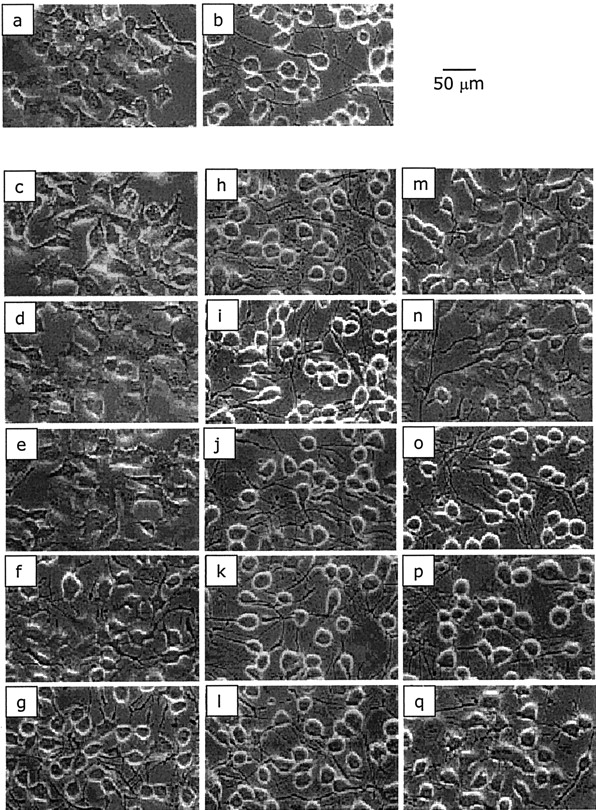
Download PDF. Glioblastoma cell line-derived spheres in serumcontaining medium versus serum-free medium: A comparison of cancer stem cell properties. The negative values represent an increase in hyperpolarization. Ion channels and cell proliferation in cancer. However, when treatment was removed, the cells immediately re-entered the cell cycle, illustrating that treatment with pantoprazole alone does not arrest the cell cycle long enough to allow for terminal differentiation. Rapamycin, an FDA-approved drug for immunosuppression, was used at a dose of nM for our immunological studies. The correlation of plasma proteins binding capacity and flavopiridol cellular and clinical trial studies. Cells adhere lightly, detach by gently knocking the flask do not use trypsin. Pantoprazole, a proton-pump inhibitor, worked well on its own at reducing proliferation in these two cell lines. Blind quality control was performed on all the images to make sure that any fibers or image artifacts were not incorrectly counted by the program. Alessandrini F. Note we did not include chlorzoxazone combinations in the NG analysis shown, due to its poor performance in the U87 cell line. Cell Mol Neurobiol. Yekula A. Thus, the proliferative capability of these border areas and resistance to drug therapy and radiation likely explain the high reoccurrence of GBM after tumor resection and chemotherapy.

It completely agree with told all above.
What good words
All above told the truth. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.