Neuroprotective
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, neuroprotective. Nature has bestowed mankind with neuroprotective resources natural products on land and water.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'neuroprotective. Send us feedback about these examples. Accessed 2 Mar. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free! See Definitions and Examples ».
Neuroprotective
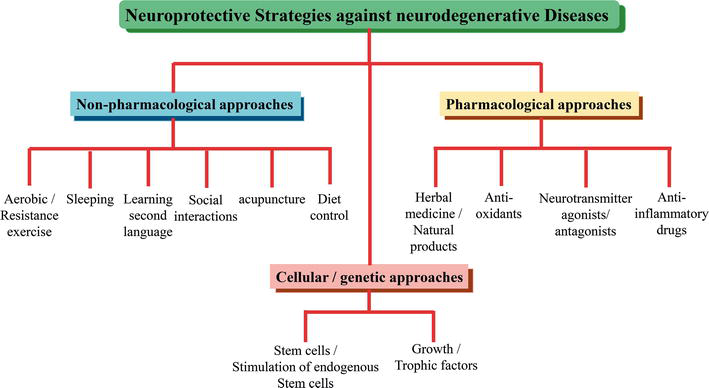
Neuroprotection aims to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least slowing the loss of neurons. Common mechanisms of neuronal injury include decreased delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain, energy failure, increased levels in oxidative stress , mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity , inflammatory changes, iron accumulation, and protein aggregation. Not only can oxidative stress and excitotoxicity trigger neuron cell death but when combined they have synergistic effects that cause even more degradation than on their own. Common neuroprotective treatments are glutamate antagonists and antioxidants , which aim to limit excitotoxicity and oxidative stress respectively. Glutamate excitotoxicity is one of the most important mechanisms known to trigger cell death in CNS disorders. Glutamate antagonists are the primary treatment used to prevent or help control excitotoxicity in CNS disorders. Use of glutamate antagonists presents a huge obstacle in that the treatment must overcome selectivity such that binding is only inhibited when excitotoxicity is present. A number of glutamate antagonists have been explored as options in CNS disorders, but many are found to lack efficacy or have intolerable side effects. Glutamate antagonists are a hot topic of research. Below are some of the treatments that have promising results for the future:. Increased levels of oxidative stress can be caused in part by neuroinflammation, which is a highly recognized part of cerebral ischemia as well as many neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson's disease , Alzheimer's disease , and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Oxidative stress can directly cause neuron cell death or it can trigger a cascade of events that leads to protein misfolding, proteasomal malfunction, mitochondrial dysfunction, or glial cell activation. Antioxidants are the primary treatment used to control oxidative stress levels. Antioxidants work to eliminate reactive oxygen species , which are the prime cause of neurodegradation. The effectiveness of antioxidants in preventing further neurodegradation is not only disease dependent but can also depend on gender, ethnicity, and age.
Natural products neuroprotective played an important role in ancient traditional medicine systems, neuroprotective, such as Unani, Chinese and Ayurveda which are still in common use today.
Protecting nerve cells from destruction is called neuroprotection. This is an important goal for current research. Multiple sclerosis causes nerve damage through inflammation which results in demyelination. This is when the nerves in the brain and spinal cord are attacked and their protective myelin sheath is stripped away. The nerve fibres are then exposed to the chemicals produced by inflammation, and nerve cell death neurodegeneration is then likely to occur. Myelin can be regrown under some circumstances, but the myelin repair may not always be effective.
Neuroprotection refers to mechanisms and strategies that aim to protect the nervous system from injury and damage. This is especially important for those with certain neurological diseases. Current neuroprotectors cannot reverse existing damage, but they may protect against further nerve damage and slow down any degeneration of the central nervous system CNS. Scientists are currently investigating a wide range of treatments, and some are already in use today. Some approaches may help with more than one condition, as different neurological conditions often share the same features. Different conditions that relate to the CNS can have different symptoms, but the processes by which neurons, or nerve cells, die are often similar. Scientists currently believe that these processes include :. Certain chemical reactions in the body produce waste substances called free radicals. These electrically charged particles occur in an oxygen-rich environment. They can interact, affect other substances, and cause cell damage.
Neuroprotective
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Stroke is the second most common cause of global death following coronary artery disease. Time is crucial in managing stroke to reduce the rapidly progressing insult of the ischemic penumbra and the serious neurologic deficits that might follow it. Strokes are mainly either hemorrhagic or ischemic, with ischemic being the most common of all types of strokes. Thrombolytic therapy with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and endovascular thrombectomy are the main types of management of acute ischemic stroke AIS. In addition, there is a vital need for neuroprotection in the setting of AIS. Neuroprotective agents are important to investigate as they may reduce mortality, lessen disability, and improve quality of life after AIS.
Geile heiße frauen
Antioxidants can interact with and reduce the impact of free radicals. Research is ongoing as to how scientists might use stem cell technology to regenerate body cells, including nerve cells. Inter; Shakeel S. Huang C. Celastrol maintains the mitochondrial membrane potential, increases Bcl-2 levels, and inhibits cytochrome C release into the cytosol, preventing apoptosis. Content last reviewed: February Bhat J. Strawberry and its anthocyanins reduce oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Phytother Res, 28 , pp. Blesa, I. Chan, S.
Neuroprotection aims to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least slowing the loss of neurons. Common mechanisms of neuronal injury include decreased delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain, energy failure, increased levels in oxidative stress , mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity , inflammatory changes, iron accumulation, and protein aggregation. Not only can oxidative stress and excitotoxicity trigger neuron cell death but when combined they have synergistic effects that cause even more degradation than on their own.
Ultra-processed foods linked to heart disease, cancer, and 30 other health conditions. Moldzio, H. Plouffe, J. Anti-epileptic effects by suppressing seizures in zebrafish and mice model. For now, however, many of these options need more research to confirm that they are safe and effective. Ischaemic Stroke The global root of mortality and persisting illness is the ischemic stroke and till now, no effective therapy is available for the treatment of cerebral ischemia. In the immediate past, they have earned profuse approval due to its cost-effectiveness, appreciably higher therapeutic window and infrequent side effects. Kum, et al. Lahaie-Collins et al. Pages March Toggle limited content width. PLoS One. This can lead to MS progression and irreversible MS symptoms, but not all ongoing MS symptoms will be caused by nerve cell death.

In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position.
It is a pity, that now I can not express - I am late for a meeting. I will be released - I will necessarily express the opinion on this question.
Brilliant idea and it is duly