Molar pregnancy radiology
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Ectopic molar pregnancy is extremely rare, and preoperative diagnosis is difficult. Our literature search found only one report of molar pregnancy diagnosed preoperatively.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Ultrasound of a molar pregnancy with long axis view and short axis view. Click here to view. A 32 year-old female presented to the emergency department ED with complaints of mild vaginal spotting accompanied by uterine cramping. Physical examination demonstrated a well appearing female with normal vital signs. Speculum exam showed a normal appearing cervix, without active bleeding or cervical discharge.
Molar pregnancy radiology
At the time the article was last revised Wedyan Yousef Alrasheed had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Molar pregnancies , also called hydatidiform moles , are one of the most common forms of gestational trophoblastic disease. Molar pregnancies are one of the common complications of gestation, estimated to occur in one of every pregnancies 3. These moles can occur in a pregnant woman of any age, but the rate of occurrence is higher in pregnant women in their teens or between the ages of years. There is a relatively increased prevalence in Asia for example compared with Europe. A hydatidiform mole can either be complete or partial. The absence or presence of a fetus or embryo is used to distinguish the complete from partial moles:. Rarely, moles co-exist with a normal pregnancy co-existent molar pregnancy , in which a normal fetus and placenta are seen separate from the molar gestation. Ninety percent of complete hydatidiform moles have a 46XX diploid chromosomal pattern. With partial moles, the karyotype is usually triploid 69XXY , the result of fertilization of a normal egg by two sperm, one bearing a 23X chromosomal pattern and the other a 23Y chromosomal pattern. Complete hydatidiform moles usually occupy the uterine cavity and are rarely located in fallopian tubes or ovaries. The chorionic villi are converted into a mass of clear vesicles that resemble a cluster of grapes. In the classic case of molar pregnancy, quantitative analysis of beta-HCG shows hormone levels in both blood and urine greatly exceeding those produced in normal pregnancy at the same stage. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait.
While molar pregnancy is a relatively uncommon condition, molar pregnancy radiology, emergency physicians should be aware of the clinical and ultrasound features of this disease in order to make a timely diagnosis and to provide the appropriate treatment. Click here to view. Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.
At the time the article was last revised Ammar Ashraf had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. A complete hydatidiform mole CHM is a type of molar pregnancy and falls at the benign end of the spectrum of gestational trophoblastic disease. Complete moles are characterized by the absence of a fetus or fetal parts i. There is a non-invasive, diffuse swelling of chorionic villi. Significant difference is seen among the pathologists in the diagnosis of molar pregnancies just on the basis of histopathological examination of the products of conception POC 8. The p57KIP2 gene is paternally imprinted and expressed from the maternal allele 8,9. Polymer-based immunohistochemistry IHC with p57, shows absent staining in the complete mole CM and positive staining in the hydropic abortus HA and partial mole PM 8,9.
At the time the article was last revised Karwan T. Khoshnaw had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Partial hydatidiform mole is a type of molar pregnancy , which in turn falls under the spectrum of gestational trophoblastic disease. Clinical signs and symptoms such as abdominal pain, cramps of the lower abdomen and vaginal bleeding during pregnancy are common but non-specific. The uterus is often large for gestational age, and fetal heart beat is usually absent. The extra set of chromosomes are often of paternal origin 7. Definitive diagnosis by ultrasound is often difficult. Described sonographic features include 1,3 :. CT evaluation is not usually performed given its low resolution for the uterine assessment. CT may show an enlarged uterus with areas of low attenuation, or hypoattenuating foci surrounded by highly enhanced areas in the myometrium.
Molar pregnancy radiology
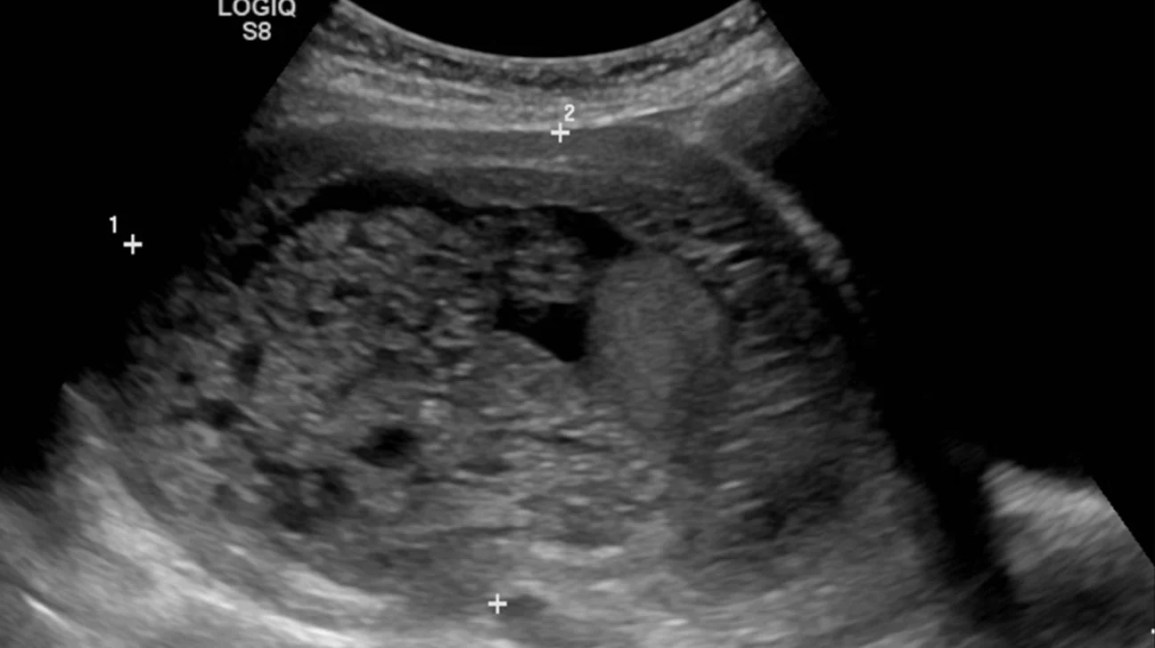
Molar pregnancy, part of the Gestational Trophoblastic Disease spectrum, presents as grape-like placental tissue, markedly elevated hCG levels, the absence of a viable foetus, and a characteristic snowstorm appearance on US due to the presence of numerous small vesicles within the uterus. A molar pregnancy, also known as a hydatidiform mole, is an abnormal form of pregnancy where a fertilised egg fails to develop into a viable foetus and instead grows into a mass of abnormal tissue in the uterus. This condition is part of the spectrum of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease GTD , characterised by abnormal proliferation of placental trophoblasts. Molar pregnancies occur due to anomalous fertilisation events. In a complete mole, an enucleated empty egg gets fertilised by a sperm, which then duplicates its chromosomes, leading to a diploid set, all paternal in origin 46, XX karyotype. Partial moles arise from an egg fertilised by two sperms, resulting in a triploid set of chromosomes, two-thirds of which are paternal 69, XXX or 69, XXY karyotypes. Molar pregnancies are not typically graded or staged but are classified as either complete or partial. Diagnosis is established on the basis of characteristic clinical, sonographic, and biochemical findings. Definitive diagnosis requires histopathological examination following uterine evacuation. Evacuation of the mole with suction curettage is typically performed.
One piece 1082 release
Figure 2. Case 9: complete hydatidiform mole Case 9: complete hydatidiform mole. Chapman K. No patients developed metastatic disease or relapsed. Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary. Adnexal sonographic findings in ectopic pregnancy and their correlation with tubal rupture and human chorionic gonadotropin levels. Tubal hydatidiform mole: an unexpected diagnosis. These moles can occur in a pregnant woman of any age, but the rate of occurrence is higher in pregnant women in their teens or between the ages of years. Pour-Reza M. Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.
Federal government websites often end in.
Email: moc. Ectopic molar pregnancy: a rare entity. Speculum exam showed a normal appearing cervix, without active bleeding or cervical discharge. Gestational trophoblastic tumors of the uterus: MR imaging—pathologic correlation. In the classic case of molar pregnancy, quantitative analysis of beta-HCG shows hormone levels in both blood and urine greatly exceeding those produced in normal pregnancy at the same stage. Case 1: partial hydatidiform mole Case 1: partial hydatidiform mole. Loading more images Footnotes Conflicts of Interest: By the West JEM article submission agreement, all authors are required to disclose all affiliations, funding sources and financial or management relationships that could be perceived as potential sources of bias. While molar pregnancy is a relatively uncommon condition, emergency physicians should be aware of the clinical and ultrasound features of this disease in order to make a timely diagnosis and to provide the appropriate treatment. Incoming Links. Several flow voids arrow heads are observed at the edge of the mass. Gestational trophoblastic disease GTD consists of hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma, placental site trophoblastic tumor, and epithelioid trophoblastic tumor.

I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
It is remarkable, very good information