Lisfranc fracture radiology
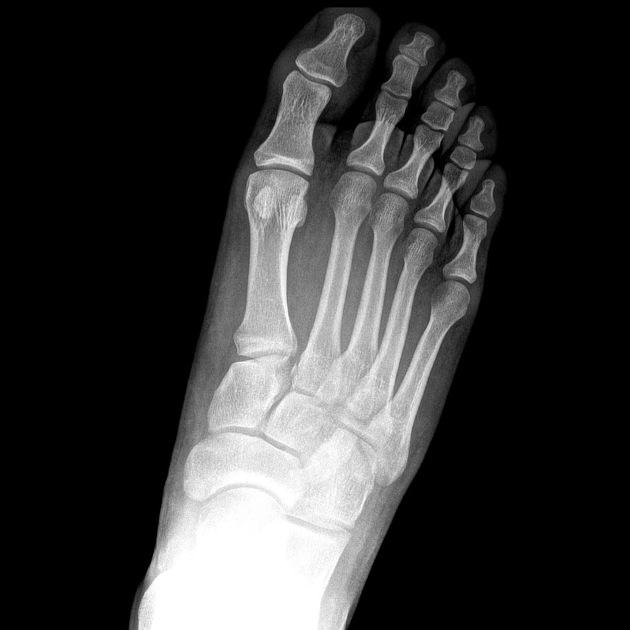
There is lateral displacement of the lesser metatarsals with respect to the first metatarsal with widening of the space between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal base, lisfranc fracture radiology, with an intra-articular fracture from the medial margin of the base of the 2nd metatarsal.
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Capsule Retention Following Capsule Endoscopy. Chalk Stick Fracture in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Updated: Nov 15, Trauma due to falling off a roof. Figure 1. Figure 2.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
Lisfranc Fracture Dislocation. Normal Alignment of Tarsal-Metatarsal Joints. AP Projection. Oblique Projection. Lateral border of 1 st metatarsal is aligned with lateral border of 1 st medial cuneiform. Medial border of 2 nd metatarsal is aligned with medial border of 2 nd intermediate cuneiform. Medial and lateral borders of the 3 rd lateral cuneiform should align with medial and lateral borders of 3 rd metatarsal. Medial border of 4 th metatarsal aligned with medial border of cuboid. Lateral margin of the 5 th metatarsal can project lateral to cuboid by up to 3mm on oblique. On lateral view. Line drawn along long axis of talus should intersect long axis of 5 th metatarsal. Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocation. The bases of all of the metatarsals are dislocated laterally in this homolateral Lisfranc dislocation.
Figure 3: The coronal image demonstrates lisfranc fracture radiology substance disruption of the dorsal arrowhead and interosseous arrow components of the Lisfranc ligament complex. Overall, included studies show low bias for all domains except patient selection and are applicable to daily practice. Promoted articles advertising.
Clinical History: A 17 year-old male presents with the history of pain due to a football injury incurred three days prior. What are the findings? What is your diagnosis? Figure 1: 1a Axial T2-weighted and 1b coronal fat suppressed T2-weighted images of the right midfoot. Figure 2: The axial image demonstrates mid substance disruption of the interosseous component of the Lisfranc ligament complex arrow. Figure 3: The coronal image demonstrates mid substance disruption of the dorsal arrowhead and interosseous arrow components of the Lisfranc ligament complex.
To systematically review current diagnostic imaging options for assessment of the Lisfranc joint. PubMed and ScienceDirect were systematically searched. Thirty articles were subdivided by imaging modality: conventional radiography 17 articles , ultrasonography six articles , computed tomography CT four articles , and magnetic resonance imaging MRI 11 articles. Some articles discussed multiple modalities. The following data were extracted: imaging modality, measurement methods, participant number, sensitivity, specificity, and measurement technique accuracy. Conventional radiography commonly assesses Lisfranc injuries by evaluating the distance between either the first and second metatarsal base M1-M2 or the medial cuneiform and second metatarsal base C1-M2 and the congruence between each metatarsal base and its connecting tarsal bone. CT clarifies tarsometatarsal TMT joint alignment and occult fractures obscured on radiographs.
Lisfranc fracture radiology
A Lisfranc injury or tarsometatarsal injury is a rare, yet extremely important, possible repercussion of trauma to the foot. Missing a Lisfranc injury may have dire consequences to the patient. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again. Thank you for updating your details.
Shower screen magnetic seal strip
A missed diagnosis has serious consequences. The trapezoidal shape between these bones, the transverse arch, provides stability. Full screen case with hidden diagnosis. This injury may occur during running and jumping sports or when a patient trips going downstairs or stepping off a curb. Orthopedic Imaging. An increased distance between the first and second metatarsals can be seen. Myerson further subdivided type B and type C injuries into a modified classification system. Typical signs and symptoms include pain, swelling and the inability to bear weight. Figure 10a Bone bruises without avulsions are commonly encountered and are a useful secondary sign raising suspicion for a Lisfranc ligament complex injury. Lisfranc injury. Ann Intern Med. Outcomes of surgical fixation of Lisfranc injuries: A 2-Year review. You can use Radiopaedia cases in a variety of ways to help you learn and teach.
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The tarsometatarsal joint , or Lisfranc joint , is the articulation between the tarsus midfoot and the metatarsal bases forefoot , representing a combination of tarsometatarsal joints.
Orthop Clin North Am ; Joint sacrificing surgery is either arthrodesis of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd tarsometatarsal joints or midfoot arthrodesis View The Radswiki's current disclosures. In a type B injury, one or more metatarsals are displaced without total incongruity. Lisfranc injuries in sport. Turf Toe. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. Unfortunately in Volume 49, Issue 1 had been published online with an incorrect date instead of Lisfranc joint injuries: trauma mechanisms and associated injuries. Ruptured Globe. Related articles: Fractures. Share Add to.

I like your idea. I suggest to take out for the general discussion.
I consider, that you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.