Lipoprotein lipase liver
Immuno-Biological Laboratories Co. Hepatic lipase HL is a key enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of triglycerides TG and phospholipids PLs in several lipoproteins. It is generally recognized that HL is involved in the lipoprotein lipase liver of remnant, low-density lipoprotein LDLhigh-density lipoprotein HDL and the production of small, dense low-density lipoproteins sd-LDLs.
Lipoprotein metabolism involves two major steps Eisenberg The enzyme rapidly hydrolyzes triglycerides, which accomplishes two things Eckel : it enables the tissues to utilize fatty acids from the lipoproteins, and it transforms large TG-rich lipoproteins chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins, VLDL into cholesterol-rich remnant lipoproteins. This process is completed within the space of a few minutes to a few hours after the lipoproteins have entered circulation. Some of the remnants are rapidly removed from the circulation by receptor-mediated endocytosis, but some are transformed into low-density lipoproteins LDL and high-density lipoproteins HDL. Subjects with genetic deficiency of LPL demonstrate that the enzyme is indeed necessary for these reactions; there is massive accumulation of TG-rich lipoproteins in plasma and low levels of LDL and HDL Brunzell et al. These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors.
Lipoprotein lipase liver
The liver is the main organ that regulates lipid and glucose metabolism. Ectopic lipid accumulation in the liver impairs insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Lipoprotein lipase LPL , mainly expressed in the adipose tissue and muscle, is a key enzyme that regulates lipid metabolism via the hydrolysis of triglyceride in chylomicrons and very-low-density lipoproteins. Here, we aimed to investigate whether the suppression level of hepatic lipid accumulation via overexpression of LPL in mouse liver leads to improved metabolism. Lipid droplet formation in the liver decreased in Ad-LPL-treated mice relative to that in control Ad vector-treated mice. Glucose tolerance and insulin resistance were remarkably improved in Ad-LPL-treated mice compared to those in control Ad vector-treated mice. These results indicate that LPL overexpression in the livers of HFD-fed mice attenuates the accumulation of lipid droplets in the liver and improves glucose metabolism. These findings may enable the development of new drugs to treat metabolic syndromes such as type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files. Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. Body fat mass is determined by the balance between the storage and removal of adipose cell triglycerides TGs [ 1 ].
In: Borensztajn J ed Lipoprotein lipase. Hahn showed in that intravenous heparin stimulates TG hydrolytic activity in lipemic serum. Anal Biochem.
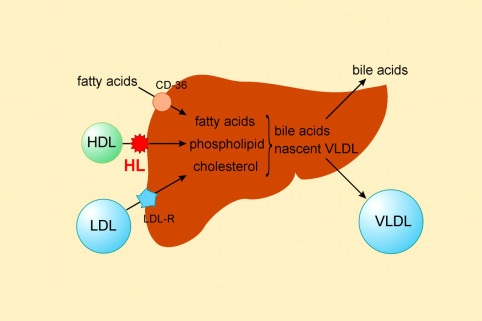
The hepatic lipase can either remain attached to the liver or can unbind from the liver endothelial cells and is free to enter the body's circulation system. This is because the triacylglycerides in HDL serve as a substrate, but the lipoprotein contains proteins around the triacylglycerides that can prevent the triacylglycerides from being broken down by HL. One of the principal functions of hepatic lipase is to convert intermediate-density lipoprotein IDL to low-density lipoprotein LDL. Hepatic lipase falls under a class of enzymes known as hydrolases. Its function is to hydrolyze triacylglycerol to diacylglycerol and carboxylate free fatty acids with the addition of water. It can also be sent to peripheral cells for its cholesterol and used in anabolic pathways to build molecules that the cell needs such as hormones that include a cholesterol backbone.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. This common disease can progress from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis, and eventually end-stage liver diseases. MAFLD is closely related to disturbances in systemic energy metabolism, including insulin resistance and atherogenic dyslipidemia. The liver is the central organ in lipid metabolism by secreting very low density lipoproteins VLDL and, on the other hand, by internalizing fatty acids and lipoproteins. This review article discusses recent research addressing hepatic lipid synthesis, VLDL production, and lipoprotein internalization as well as the lipid exchange between adipose tissue and the liver in the context of MAFLD.
Lipoprotein lipase liver
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Lipoprotein lipase LPL is an extracellular enzyme on the vascular endothelial surface that degrades circulating triglycerides in the bloodstream. These triglycerides are embedded in very low-density lipoproteins VLDL and chylomicrons traveling through the bloodstream. The role of lipoprotein lipase is significant in understanding the pathophysiology of type one familial dyslipidemias, or hyperchylomicronemia, and its clinical manifestations.
Hannahowo leaks
The liberation of HL by HDL from the cell surface therefore primes HL for its hydrolytic function by releasing the anchored enzyme and enabling HL to gain access to circulating substrate. Hum Gene Ther. PMC Acknowledgments We thank Dr. Mechanism of the hypertriglyceridemia induced by tumor necrosis factor administration to rats. The enzyme rapidly hydrolyzes triglycerides, which accomplishes two things Eckel : it enables the tissues to utilize fatty acids from the lipoproteins, and it transforms large TG-rich lipoproteins chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins, VLDL into cholesterol-rich remnant lipoproteins. Our study findings indicate that hepatic LPL overexpression can ameliorate HFD-induced lipid accumulation in the liver without altering the systemic levels of TG and free fatty acids, leading to improvement in glucose tolerance, fasting blood glucose, and insulin resistance, as assessed by HOMA-IR. J Lipid Res. Insulin resistance and insulin sensitizing agents. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. More reference expression data. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Nicotinic acid niacin receptor agonists: will they be useful therapeutic agents? Lipoprotein electrostatic properties regulate hepatic lipase association and activity. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Nature — They found that a build-up of triglyceride levels led to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. This process is completed within the space of a few minutes to a few hours after the lipoproteins have entered circulation. Doolittle M. Annu Rev Cell Biol 5: 1— Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. How important are carnitine and ketones for the newborn infant? Bengtsson-Olivecrona G, Olivecrona T Binding of active and inactive forms of lipoprotein lipase to heparin: effects of pH. The human body contains two inactive forms of HL. Hepatic LPL overexpression maintained mitochondrial content As mitochondria play a crucial role in fatty acid oxidation, we assessed the expression of the mRNA and proteins of mitochondrial genes using quantitative RT-PCR and western blot analysis, respectively, and the area of mitochondria using transmission electron microscopy.

Improbably!