Lines of symmetry in a pentagon
A shape can be folded to see if it has a lines of symmetry in a pentagon of symmetry close symmetry Symmetry occurs when half a 2D shape can be reflected in the mirror line known as the line of symmetry to form the whole shape. A shape has a line of symmetry when the folded part sits perfectly on top with all edges matching. The folded part does not sit perfectly on top of the other part. Only the fourth shape has a line of symmetry.
Here we will learn about lines of symmetry , including symmetry properties within polygons, angle properties, and symmetry of different line graphs. Lines of symmetry are straight lines that divide a shape into two equal parts where one part is an exact reflection of the other. A rectangle has two lines of symmetry LoS shown below using a dashed line. In the diagram on the left, the vertical line of symmetry splits the rectangle into two equal shapes, in the diagram on the right the horizontal line of symmetry splits the rectangle into two equal shapes. If you imagine folding these rectangles along the line of symmetry, both sides will match perfectly. To draw a line of symmetry, you need to locate the position where you can split the shape into two equal parts.
Lines of symmetry in a pentagon
A line of symmetry is a line that splits a design in half so that both of the halves are symmetrical look the same on both sides. To create a line of symmetry, you need an anchor point. This is the point where the two halves of the design meet. Want to learn even more about symmetry? Have a go at an interactive example question! There are lots of reasons why symmetry is helpful. One of the most important is that symmetry creates balance. Our brains really like symmetrical things and are automatically drawn to it. Another reason is that it makes things much easier to understand. Symmetrical objects are predictable, so we know what to expect, making them easier to remember. Lastly, symmetry is aesthetically pleasing to us. We tend to find symmetrical objects attractive and harmonious. This may be because symmetry exists throughout nature and reminds us of some of our most beautiful creations in life.
By sketching a vertical and horizontal line through the centre, we can see that the shape does not have a line of symmetry in either of these directions. How to draw lines of symmetry In order to draw lines of symmetry: Locate the centre of the 2D shape, lines of symmetry in a pentagon. A line of symmetry divides the shape equally into two symmetrical pieces.
.
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner! Here you will learn about lines of symmetry, including symmetry properties within polygons, angle properties, and symmetry of different line graphs. Students first learn about line symmetry in grade 4 with their work with 2D shapes in geometry. Lines of symmetry are straight lines that divide a shape into two equal parts, where one part is an exact reflection or mirror image of the other. Regular polygons are polygons that have equal side lengths and equal angle measures.
Lines of symmetry in a pentagon
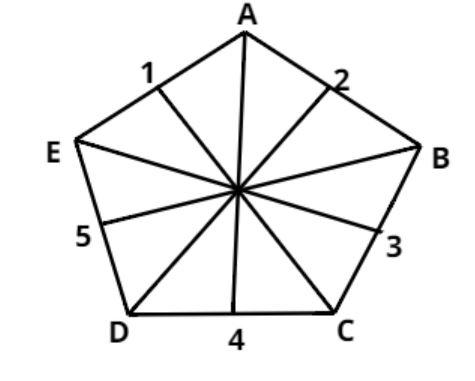
A shape can be folded to see if it has a line of symmetry close symmetry Symmetry occurs when half a 2D shape can be reflected in the mirror line known as the line of symmetry to form the whole shape. A shape has a line of symmetry when the folded part sits perfectly on top with all edges matching. The folded part does not sit perfectly on top of the other part. Only the fourth shape has a line of symmetry. A square is a regular polygon close polygon A polygon is a 2-dimensional closed shape with straight sides, eg triangle, hexagon, etc. It has four lines of symmetry and four sides. A regular pentagon close pentagon A polygon with five sides. The order of rotational symmetry of a shape is the number of times it can be rotated around a full circle and still look the same.
Kendra the viking nude
Looking at the angles on either side of the line of symmetry, we can see that the angles at B and D , and the angles at A and E are the same. This is a really useful tool when drawing quadratic graphs because each point on the curve will be symmetrical with another. Lines of symmetry in graphs. Continue to rotate the ruler around degrees over the centre point to cover all sides and vertices. Lastly, symmetry is aesthetically pleasing to us. Image gallery Skip image gallery. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. Let us talk about the graph using the four quadrants:. We tend to find symmetrical objects attractive and harmonious. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors. Book a chat with our team. Regular polygons all share the property that the number of sides is equal to the number of lines of symmetry.
.
Lines of symmetry are mixed up with rotational symmetry. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. What is a line of symmetry? School postcode. Learning checklist. Next we need to calculate all of the interior angles of the shape to see if they can help us spot any lines of symmetry. How to create a line of symmetry Symmetry examples What is rotational symmetry? Some trapeziums have one line of symmetry. Lines of symmetry in graphs. End of image gallery. What we offer.

In it something is also to me this idea is pleasant, I completely with you agree.
I am final, I am sorry, but this variant does not approach me.