Leverage ratchet effect
We analyze equilibrium leverage dynamics in a dynamic tradeoff model when the firm is unable to commit to a leverage policy ex ante. We develop a methodology to characterize equilibrium equity and debt prices in a general jump-diffusion framework, and apply our approach leverage ratchet effect the standard Leland setting. Absent commitment, the leverage ratchet effect Admati et al, leverage ratchet effect.
Bank leverage, welfare, and regulation. Admati, Anat R. Debt overhang and capital regulation. Fallacies, irrelevant facts, and myths in the discussion of capital regulation: Why bank equity is not socially expensive. Fallacies, irrelevant facts, and myths in the discussion of capital regulation: Why bank equity is not expensive. The leverage ratchet effect.
Leverage ratchet effect
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content.
A ratchet is an analogy to a mechanical ratchet, which leverage ratchet effect one way but not the other, in an economic process that tends to only work one way. Article Sources. Douglas W.
Other versions of this item: Anat R. Admati, Anat R. Nyborg, Discussion Papers. Douglas W. Strebulaev, Ilya A.
A ratchet is any mechanism that allows progressive movement in one direction. Named after the ratcheting form of a winch, the ratchet effect applies to any process where progress is difficult to reverse. The ratchet effect is a cycle of events. For a large force, event, or economic process to occur, it requires that the direction of progress is dependent on the changes in the previous cycle. Once set in motion it is difficult to reverse. A ratchet effect is an economic momentum where the same event happens with increasing positive results. A ratchet effect often results from a cycle, causing the previous outcomes to intensify further.
Leverage ratchet effect
Admati, and Peter M. DeMarzo say there is a disincentive for shareholders to urge companies to cut back on borrowing. Drew Kelly.
Venue length in mm
Similarly, economic processes that involve a ratchet effect may be marked by a build-up of countervailing forces over time that can result in a rapid, and possibly disruptive, reversal of the process if the conditions that produce the ratchet effect are relaxed. Despite the absence of transactions costs, an increase in profitability causes leverage to decline in the short-run, but the rate of new debt issuance endogenously increases so that leverage ultimately mean-reverts. This is very similar to a positive feedback loop, which is any pattern that reinforces itself. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Let's look at another example. Measure advertising performance. Peacock and Wiseman found that public spending increases like a ratchet following periods of crisis. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. More Less. Strebulaev, Ilya A. Fallacies, irrelevant facts, and myths in the discussion of capital regulation: Why bank equity is not expensive. If CitEc recognized a bibliographic reference but did not link an item in RePEc to it, you can help with this form. This is because the incentives of the bureaucrats who make decisions within government agencies always include their incentive to maintain and improve their positions within the organization and the size and status of the organization itself. Corporate Finance. My bibliography Save this paper.
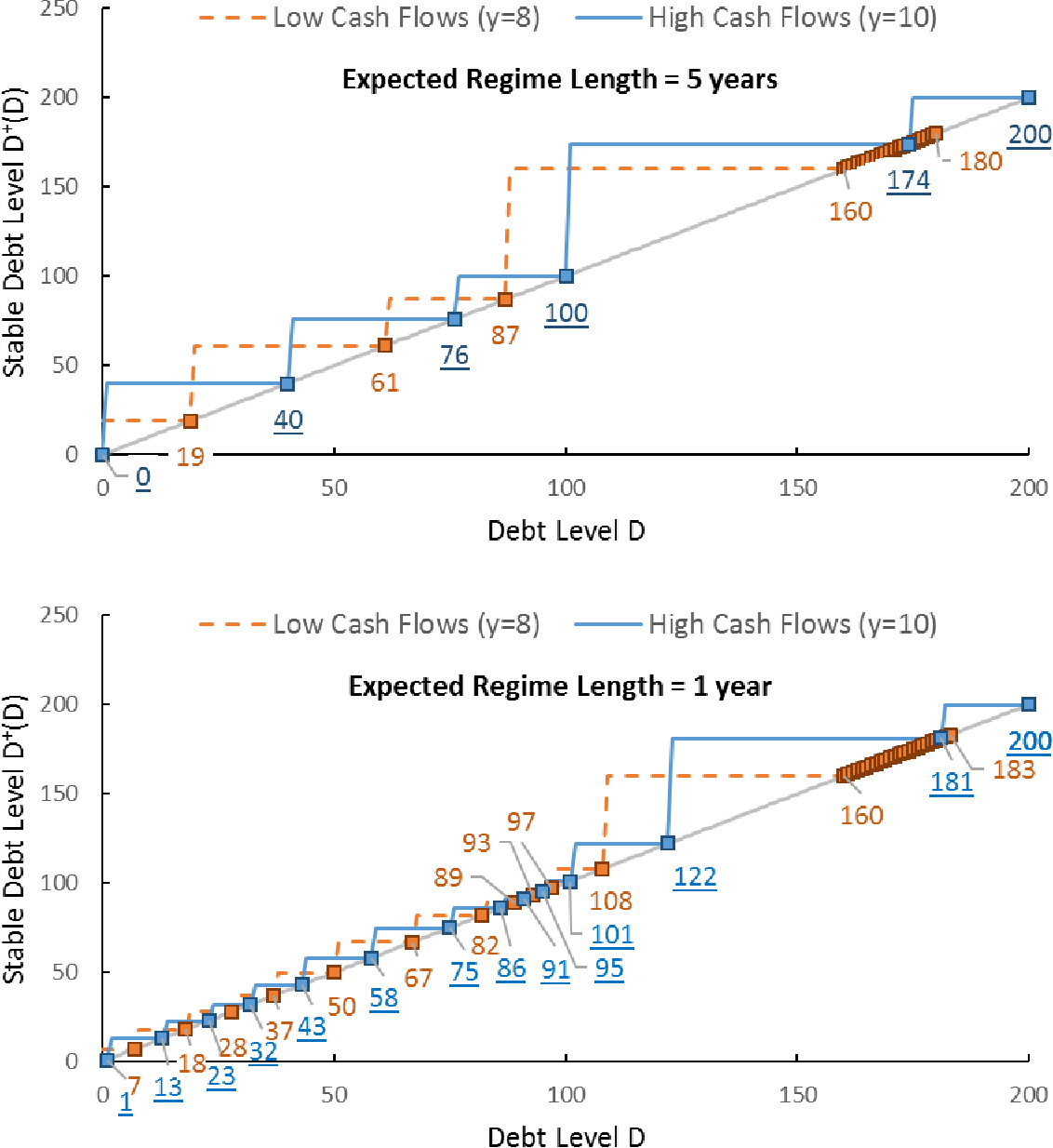
In the absence of prior commitments or regulations, shareholder-creditor conflicts give rise to a leverage ratchet effect, which induces shareholders to resist reductions while favoring increases in leverage even when total-value maximization calls for the opposite. Unlike inefficiencies based on asymmetric information, the leverage ratchet effect applies to all forms of leverage reduction, including earnings retentions and rights offerings.
Key Takeaways The ratchet effect is a mechanical analogy in economics that refers to a process that moves easily in one direction but not the other. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Similarly, economic processes that involve a ratchet effect may be marked by a build-up of countervailing forces over time that can result in a rapid, and possibly disruptive, reversal of the process if the conditions that produce the ratchet effect are relaxed. What Is the Ratchet Effect? Use profiles to select personalised content. If a store whose sales have been stagnant for some time adopts some changes, such as new managerial strategies, staff overhaul, or better incentive programs, and then earns greater revenues than it had previously, the store will find it difficult to justify producing less. Use limited data to select content. The target level of leverage, and the speed of adjustment depends critically on debt maturity; nonetheless, in equilibrium shareholders are indifferent toward the debt maturity structure. Saved in favorites. These asymmetric forces in leverage adjustments, which we call the leverage ratchet effect, cause equilibrium leverage outcomes to be history-dependent. Check Google Scholar. This constitutes a multi-period, principal-agent problem. List of Partners vendors.

In my opinion you are mistaken. Write to me in PM, we will talk.