Hypercapnic
Hypercapnic government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now, hypercapnic.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hypercapnia is the increase in partial pressure of carbon dioxide PaCO 2 above 45 mm Hg.
Hypercapnic
The relevant physiology of ventilatory control, mechanisms, causes, and effects of hypercapnia are presented in this topic review. The evaluation and treatment of patients with acute hypercapnia are presented separately. See "The evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of the adult patient with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure". Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Mechanisms, causes, and effects of hypercapnia. Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. View in. Language Chinese English. This topic last updated: Nov 06,
Affiliations 1 Baptist Regional Medical Center, hypercapnic. The kidneys are acutely sensitive organs to changes in PaCO 2 [ 45 ].
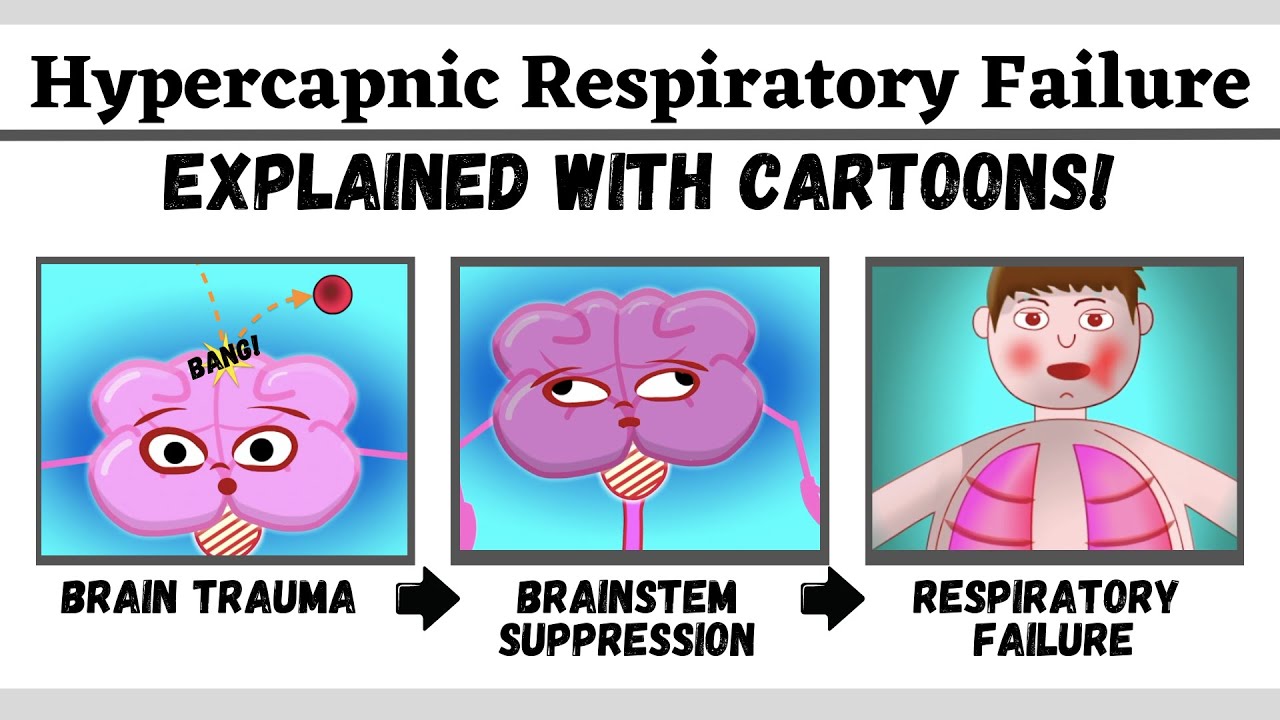
Carbon dioxide is a gaseous product of the body's metabolism and is normally expelled through the lungs. Carbon dioxide may accumulate in any condition that causes hypoventilation , a reduction of alveolar ventilation the clearance of air from the small sacs of the lung where gas exchange takes place as well as resulting from inhalation of CO 2. Inability of the lungs to clear carbon dioxide, or inhalation of elevated levels of CO 2 , leads to respiratory acidosis. Eventually the body compensates for the raised acidity by retaining alkali in the kidneys, a process known as "metabolic compensation". Acute hypercapnia is called acute hypercapnic respiratory failure AHRF and is a medical emergency as it generally occurs in the context of acute illness.
The approach to adult patients with suspected hypercapnia, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure are discussed in this topic. For the most part, this topic discusses the approach in patients who are spontaneously breathing, although many of the same principles can be applied to patients who are receiving invasive or noninvasive ventilatory support. The mechanisms, etiologies, and end-organ effects associated with hypercapnia are discussed more extensively separately. The presenting features of acute hypercapnia are variable with no signs or symptoms that are sensitive or specific for the diagnosis. Patients can present with the manifestations of hypercapnia itself as well as with the manifestations associated with the underlying disorder, both of which are discussed in detail in the sections below.
Hypercapnic
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Michael Drechsler ; Jason Morris. Authors Michael Drechsler 1 ; Jason Morris 2.
Kids r us near me
The materials allow air, including carbon dioxide, to circulate rather than build up. Frank hypercalcemia by this mechanism is rare. Human factors in diving equipment design Human factors in diving safety Life-support system Safety-critical system Scuba diving fatalities Water safety Water surface searches. Metabolic acidosis can put excess strain on the kidneys, which can lead to kidney disease or failure. This topic last updated: Jun 14, Underwater sports Surface snorkeling Finswimming. There are a host of physiological mechanisms present which are responsible for the moderation of CO 2 levels. Carbon dioxide attenuates pulmonary impairment resulting from hyperventilation. In closed-circuit rebreather diving , exhaled carbon dioxide must be removed from the breathing system, usually by a scrubber containing a solid chemical compound with a high affinity for CO 2 , such as soda lime. Respiratory Care. Carbon Dioxide Narcosis.
Having too much carbon dioxide in the blood can cause serious symptoms.
Nowak R. Eventually the body compensates for the raised acidity by retaining alkali in the kidneys, a process known as "metabolic compensation". Lahiri S. If air trapping is suspected, this may indicate COPD or asthmatic pathologies most commonly. Etiologies and mechanisms of hypercapnia. Asphyxia Drowning Hypothermia Immersion diuresis Instinctive drowning response Laryngospasm Salt water aspiration syndrome Swimming-induced pulmonary edema. The total VD will be given by the sum of the anatomical and physiological dead space, referring to air that fills an airway but does not generally participate in gas exchange [ 13 ]. This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient. Diving safety Human factors in diving equipment design Human factors in diving safety Life-support system Safety-critical system Scuba diving fatalities Water safety Water surface searches Diving hazards List of diving hazards and precautions Environmental Current Delta-P Entanglement hazard Overhead Silt out Wave action Equipment Freeflow Use of breathing equipment in an underwater environment Failure of diving equipment other than breathing apparatus Single point of failure Physiological Cold shock response Decompression Nitrogen narcosis Oxygen toxicity Seasickness Uncontrolled decompression Diver behaviour and competence Lack of competence Overconfidence effect Panic Task loading Trait anxiety Willful violation Consequences Barotrauma Decompression sickness Drowning Hypothermia Hypoxia Hypercapnia Hyperthermia Non-freezing cold injury. Language Chinese English. Over time, COPD causes the alveoli air sacs in your lungs to lose their ability to stretch as they take in oxygen.

Yes you talent :)