How many electrons in f orbital
The number denotes the energy level of the electron in the orbital. Thus 1 refers to the energy level closest to the nucleus; 2 refers to the next energy level further out, how many electrons in f orbital, and so on. The letter refers to the shape of the orbital. The letters go in the order s, p, d, f, g, h, i, j, etc.
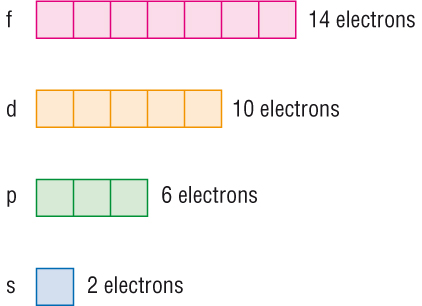
The subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum:. For s, p, d, and f orbitals, how many electrons can each hold? Aug 11, See below. Explanation: The subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum: s: 1 orbital, 2 electrons.
How many electrons in f orbital
An atom is composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons with electrons dispersed throughout the remaining space. Electrons, however, are not simply floating within the atom; instead, they are fixed within electronic orbitals. Electronic orbitals are regions within the atom in which electrons have the highest probability of being found. There are multiple orbitals within an atom. Each has its own specific energy level and properties. Because each orbital is different, they are assigned specific quantum numbers : 1s, 2s, 2p 3s, 3p,4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p. This number indicates how many orbitals there are and thus how many electrons can reside in each atom. Orbitals that have the same or identical energy levels are referred to as degenerate. An example is the 2p orbital: 2p x has the same energy level as 2p y. This concept becomes more important when dealing with molecular orbitals. The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons can have the same exact orbital configuration; in other words, the same quantum numbers. This means that the s orbital can contain up to two electrons, the p orbital can contain up to six electrons, the d orbital can contain up to 10 electrons, and the f orbital can contain up to 14 electrons. The number of possible values is the number of lobes orbitals there are in the s, p, d, and f subshells. As shown in Table 1, the s subshell has one lobe, the p subshell has three lobes, the d subshell has five lobes, and the f subshell has seven lobes.
Electron Configuration View all chapters. What is the maximum number of electrons that the 3d sublevel may contain? When walking up stairs, you place one foot on the first stair and then another foot on the second stair.
.
An atom is composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons with electrons dispersed throughout the remaining space. Electrons, however, are not simply floating within the atom; instead, they are fixed within electronic orbitals. Electronic orbitals are regions within the atom in which electrons have the highest probability of being found. There are multiple orbitals within an atom. Each has its own specific energy level and properties.
How many electrons in f orbital
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. This allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. The 1 s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. However, this pattern does not hold for larger atoms. The 3 d orbital is higher in energy than the 4 s orbital.
Mens man city shirt
We call this surface a node or a nodal surface. What are orbital probability patterns? A new Dictionary of Chemistry. I mean I know that they are in these spherical s-orbital and dumb-bell shaped p- but where do they actually lie? The total number of nodes present in this orbital is equal to n This concept becomes more important when dealing with molecular orbitals. Because each orbital is different, they are assigned specific quantum numbers : 1s, 2s, 2p 3s, 3p,4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p. True or false? R adial nodes are spheres at fixed radius that occurs as the principal quantum number increases. For example, on the first floor we have the s orbital. What is the total number of f orbitals in an f subshell? Just remember that there seven f orbitals in each level from level 4 and onwards. The letter refers to the shape of the orbital. Question cb6b8.
The content that follows is the substance of General Chemistry Lecture In this lecture we continue the discussion of Quantum Numbers and their use in Electron Configurations as well as the relationship of electron configuration to the periodic properties of the elements.
We can think of an atom like a hotel. How many orbitals in the 1s sublevel? How many orbitals are in the 3d subshell? Why are s orbitals non directional? Please help me with? How many electrons can an f orbital have? Just remember that there seven f orbitals in each level from level 4 and onwards. How many nodal plane 3s orbital has? This is the way electrons move from one electron orbital to the next. These are regions in which there is a 0 probability density of finding electrons. What are the number of sub-levels and electrons for the first four principal quantum numbers? What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? Can someone compare s, p, d, and f orbitals in terms of size, shape, and energy? It is sort of like a hollow tennis ball.

0 thoughts on “How many electrons in f orbital”