Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, glycogen phosphorylase. Glycogen phosphorylase PG is a key enzyme taking part in the first step of glycogenolysis.
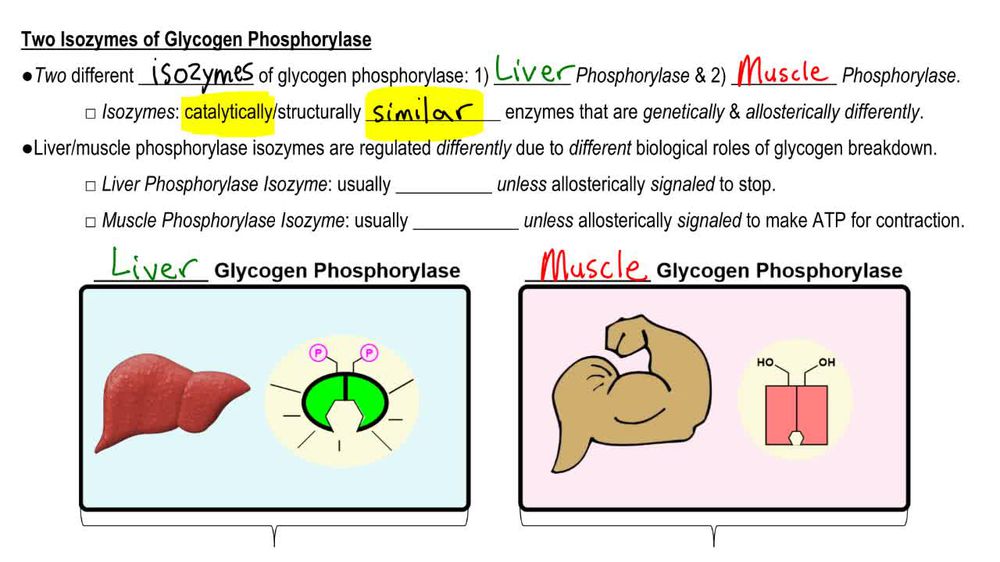
Yeast glycogen phosphorylase dimer with pyridoxalphosphate and phosphate PDB entry 1ygp. Glycogen phosphorylase GP catalyzes the hydrolysis of glycogen to generate glucosephosphate and shortened glycogen molecule and is considered the rate limiting step in the degradation of glycogen [1]. The glucosephophate is then further degraded via the pathway of glycolysis. Studies have found that mammals have liver, muscle and brain isoforms of phosphorylase but it is found among all species; muscle glycogen phosphorylase is present to degrade glycogen to forms of energy by means of glycolysis during muscle contractions and liver glycogen is present to regulate the blood glucose levels within the blood [2] [3]. GP A which is usually active is phosphorylated on Ser 14 of each subunit.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The PYGL gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called liver glycogen phosphorylase. This enzyme breaks down a complex sugar called glycogen. Liver glycogen phosphorylase is one of three related enzymes that break down glycogen in cells; the other glycogen phosphorylases are found in the brain and in muscles. Liver glycogen phosphorylase is found only in liver cells, where it breaks down glycogen into a type of sugar called glucosephosphate. Additional steps convert glucosephosphate into glucose, a simple sugar that is the main energy source for most cells in the body. Most mutations change single protein building blocks amino acids in liver glycogen phosphorylase, affecting the normal function of the enzyme. A defective liver glycogen phosphorylase enzyme impairs the normal breakdown of glycogen. As a result, liver cells cannot use glycogen for energy, so liver function becomes impaired.
The mechanism of glycogen phosphorylase results from its physiological role, which is a muscle contraction in response to neural and hormonal signals [ 16 ].
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Initially it was believed that phosphorylase was responsible for both glycogen breakdown and synthesis in the living cell. Rather, glycogen synthesis was attributable solely to the activity of glycogen synthase, subsequent to the transport of glucose into the cell. However, the well-established observation that phosphorylase was inactivated i. Such data indicate that phosphorylase inactivation may be the most important mechanism for glycogen accumulation under defined conditions. These results support the initial belief that phosphorylase plays a quantitative role in glycogen formation in the living cell.
Glycogen phosphorylase is one of the phosphorylase enzymes EC 2. Glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogenolysis in animals by releasing glucosephosphate from the terminal alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond. Glycogen phosphorylase is also studied as a model protein regulated by both reversible phosphorylation and allosteric effects. Glycogen phosphorylase breaks up glycogen into glucose subunits see also figure below :. Glycogen is left with one fewer glucose molecule , and the free glucose molecule is in the form of glucosephosphate. In order to be used for metabolism , it must be converted to glucosephosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase. Although the reaction is reversible in vitro , within the cell the enzyme only works in the forward direction as shown below because the concentration of inorganic phosphate is much higher than that of glucosephosphate. In these situations, the debranching enzyme is necessary, which will straighten out the chain in that area. After all this is done, glycogen phosphorylase can continue.
Glycogen phosphorylase
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. In the human body, glycogen is a branched polymer of glucose stored mainly in the liver and the skeletal muscle that supplies glucose to the blood stream during fasting periods and to the muscle cells during muscle contraction.
Oldsmobile 2017
For example, overexpression of GLUT1 protein in mouse skeletal muscle leads to marked increases in muscle glycogen levels in the absence of activation of GS, as judged by dephosphorylation of the enzyme. Toggle limited content width. Abstract Initially it was believed that phosphorylase was responsible for both glycogen breakdown and synthesis in the living cell. Intuitively, this may appear difficult to understand considering that it is often assumed that phosphorylase is active during exercise and that GS is active during recovery from exercise. Institutional Review Board Statement Not applicable. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Several case reports and longitudinal case studies have confirmed that retinopathy is an additional clinical phenotype feature associated with McArdle disease [ 29 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 49 ]. Madsen N. The molecule labeled PLP is the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate, a reactive molecule which binds tightly in the active site and is used to assist in the reaction. The sugars are stored in glycogen, a large molecule that contains up to 10, glucose molecules connected in a dense ball of branching chains. The additional challenges in drug testing include such limitations as poor water-solubility of some chemicals. Bergstrom J, Hultman E.
Federal government websites often end in.
Training and outreach portal of. Muscle glycogenoses: An overview. Inactivation of phosphorylase is a major component of the mechanism by which insulin stimulates hepatic glycogen synthesis. Acetylation negatively regulates glycogen phosphorylase by recruiting protein phosphatase 1. Lack of glycogenin causes glycogen accumulation and muscle function impairment. Each installment includes an introduction to the structure and function of the molecule, a discussion of the relevance of the molecule to human health and welfare, and suggestions for how visitors might view these structures and access further details. Cell Biol. When the level of AMP in the cell is low, PYGB reduces its enzymatic activity and does not respond to extracellular activation signals coming from the phosphorylation cascade. The symptoms also include a reduction of mobility and swimming speed data not published. Glycogen muscle phosphorylase is the main form of GP expressed in glial cells in the human nervous system, specifically in astrocytes [ 20 , 21 , 22 ]. Muscle glycogen during prolonged severe exercise.

Excellent
You are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.