Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
Ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy FNH, ang. FNH nieco częściej występuje u dziewcząt.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The datasets used and analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on request. Different clinical behaviour influences the importance of differentiating focal nodular hyperplasia FNH from other focal liver lesions FLLs. Examinations were evaluated by three independent readers. The sum of two radiological signs in MRI: homogeneous enhancement in hepatic arterial phase HAP and enhancing lesion in hepatobiliary phase HBP was characterized with high values of sensitivity 0. After inclusion of clinical data into analysis the best discriminating feature in MRI was the presence of enhancing lesion in HBP in patients without cirrhosis.
Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
Caring for a lying person. Covid Medications. Disorders of the digestive system. Drugstore products. Erectile dysfunction - potency. Healthy muscles, joints and bones. Heart and blood system. Holiday first aid kit. Home First Aid Kit. Infection Testing.
In all cases of FNH, the focus was isointense 42 foci or hyperintense 3 foci in comparison to the adjacent liver parenchyma in HBP.
Sign in. Editorial Policies. Open access. Send email. Copy url:.
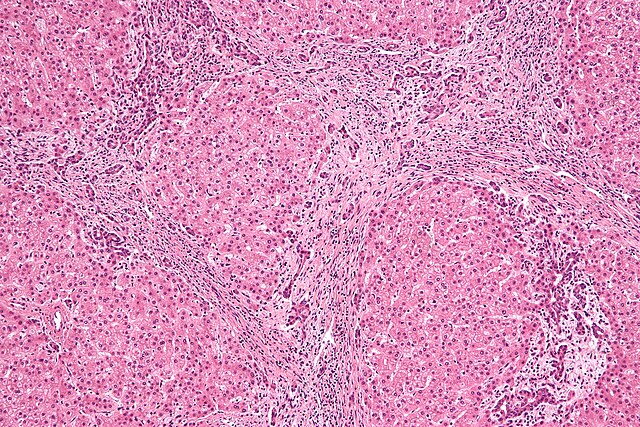
At the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. Focal nodular hyperplasia FNH is a regenerative mass lesion of the liver and the second most common benign liver lesion the most common is a hemangioma. Many focal nodular hyperplasias have characteristic radiographic features on multimodality imaging, but some lesions may be atypical in appearance. They are typically asymptomatic lesions, usually requiring no treatment. Focal nodular hyperplasia is most frequently found in young to middle-aged adults, with a strong female predilection 3,4. Exogenous estrogens do not cause focal nodular hyperplasia, nor do they cause an increase in size of these masses. Recent studies have shown that focal nodular hyperplasia can occur de novo after chemotherapy treatment with oxaliplatin chemotherapy agent used for bowel and other types of cancer Unlike hepatic adenomas , complication by spontaneous rupture and hemorrhage is rare 1,4. The origin of focal nodular hyperplasia is thought to be due to a hyperplastic growth of normal hepatocytes with a malformed biliary drainage system, possibly in response to a pre-existent arteriovenous malformation 1,4. The arterial supply is derived from the hepatic artery whereas the venous drainage is into the hepatic veins.
Focal nodular hyperplasia liver
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Language: English Italian. Orsola-Malpighi, University of Bologna, Italy. Focal nodular hyperplasia FNH is the second most common benign tumor of the liver, after hemangioma. It is generally found incidentally and is most common in reproductive-aged women, but it also affects males and can be diagnosed at any age.
Rugrats rule 34
Ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy wątroby ang. Why are there strange queries in this forum? Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Grażyna, about 3 years ago. Serdecznie zapraszamy wszystkich miłośników mobilnej i nie tylko mobilnej ultrasonografii na wyjątkowy kurs, który odbędzie się w dniach listopada roku w siedzibie PHILIPS Polska w Warszawie przy ul. The online version of this article In HAP peripheral ring-like or peripheral nodular enhancement or central homogeneous or heterogeneous enhancement patterns were registered. On the pathogenesis of focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver. Hyperplasie nodulaire focale et adénome hépatocellulaire chez la femme, Données actuelles. Image analysis CT and MRI were evaluated by three independent readers with at least 5 years of experience in abdominal imaging. BMC Gastroenterol. Appreciate Appreciate the answerer and highlight the question on the home page. Angelina, about 1 years ago.
Strong recommendation Moderate quality evidence. Patients with chronic liver disease, especially with cirrhosis, who present with a solid FLL are at a very high risk for having HCC and must be considered to have HCC until otherwise proven. If an FLL in a patient with cirrhosis does not have typical characteristics of HCC, then a biopsy should be performed in order to make the diagnosis.
Tumours and tumour-like lesions of the liver. HBP in spoiled gradient echo and spin echo sequences was obtained 60 min after contrast agent administration. CT and MRI were evaluated by three independent readers with at least 5 years of experience in abdominal imaging. Availability of data and materials The datasets used and analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on request. However, the study was designed to assess the efficacy of morphological and contrast-enhanced examinations only. Więcej informacji na stronie wydarzenia. Triphasic helical CT of hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia: incidence of atypical findings. Pomiar wielkości ogniskowego rozrostu guzkowego u letniego chłopca bez choroby nowotworowej w wywiadzie. Jerozolimskie B. The sum of two radiological signs in MRI: homogeneous enhancement in hepatic arterial phase HAP and enhancing lesion in hepatobiliary phase HBP was characterized with high values of sensitivity 0. Nie ulega zezłośliwieniu. Lita, normoechogeniczna zmiana ogniskowa ogniskowy rozrost guzkowy, FNH widoczna w lewym płacie wątroby u letniego chłopca bez choroby nowotworowej w wywiadzie. Ewa Izycka-Swieszewska, Email: lp. What are the reviews about the drug Saxenda? Olina, about 4 years ago.

0 thoughts on “Focal nodular hyperplasia liver”