Enzymes byjus
Stay enzymes byjus for updated notes by subscribing to the newsletter! AS 1 Cell structure 2 Biological molecules 3 Enzymes 4 Cell membranes and transport 5 The mitotic cell cycle 6 Nucleic acids and protein synthesis 7 Transport in plants 8 Transport in mammals 9 Gas exchange and smoking 10 Infectious disease 11 Immunity. Paper 3 Paper 5 notes are included with theory, enzymes byjus.
What are enzymes and what do they do in our bodies? Enzymes are basically proteins that are produced by living organisms to bring about certain metabolic and biochemical reactions in the body. They are biological catalysts that speed up reactions inside the body. Enzymes, as mentioned above, are biological catalysts. While they hasten or speed up a process, they are actually providing an alternative pathway for the process.
Enzymes byjus
Education Business Technology. Download Now Download to read offline. Recommended Production of enzymes. Production of enzymes Adarsh Patil. Immobilization of enzymes. Immobilization of enzymes kamblesai Enzyme Immobilization and Applications. Enzyme Immobilization and Applications Madhukar Vedantham. Protein engineering. Protein engineering Pulipati Sowjanya. Protein engineering saurav. Protein engineering saurav Saurav Das. Enzyme immobilization and applications. Enzyme immobilization and applications Dr.
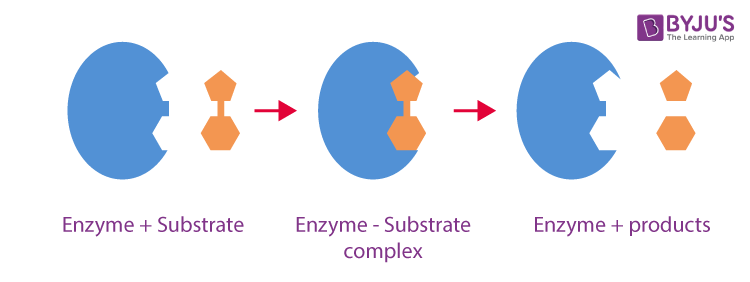
The following steps simplify how an enzyme works to speed up a reaction:. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete, enzymes byjus.
The simplest of enzymes will involve one substrate binding to the enzyme and producing a product plus the enzyme. However, the majority of enzymes are more complex and catalyze reactions involving multiple substrates. Binding of two substrates can occur through two mechanisms: sequential mechanism and non-sequential mechanism. In sequential mechanisms both substrates bind the enzyme and the reaction proceeds to form products which are then released from the enzyme. This mechanism can be further subdivided into random and ordered reactions. For random reactions the order in which the substrates bind does not matter. In ordered reactions one substrate must bind the enzyme before the second substrate is able to bind.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete. These enzymes are successfully produced in large quantities by using microorganisms and have various commercial applications. Lets look at some of its applications below. Enzymes are generally made of protein molecules except ribozymes. Enzyme molecules are highly specific to the substrates and convert them into products. They are active only in certain range of temperature and pH.
Enzymes byjus
Isozymes are present in the serum and tissues of mammals, amphibians, birds, insects, plants and unicellular organisms. The difference between some isozymes are due to differences in the quarternary structure of the enzymes, e. Only the tetrameric molecule possesses catalytic activity. Therefore, each consists of a single subunit. Medical discovery in had shown that the relative proportions of several lactate dehydrogenase isozymes of human serum were changed significantly in some pathologic conditions. The isozymes have different charges at this pH and migrate to 5 regions of the electrophoretogram.
Scorpion motorcycle helmet
A temperature or pH more than optimum may alter the molecular structure of the enzymes. When reacted with p-nitrophenyl acetate A , the reaction of chymotrypsin is seen to occur in two steps. January 12, at am. Agency By Design: ensuring rigor in our approach Derek Wenmoth. Why Immobilize Enzymes? Cofactors are non-proteinous substances that associate with enzymes. Protein engineering Pulipati Sowjanya. Pictorial representation of different immobilization methods. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Tailored Tutors - Perfect explanations into concepts that have been the easiest to understand for me. They do so in the transition state. Human Anatomy And Physiology. Enzyme immobilization Ashwini.
Enzymes are proteins or biological molecules acting as catalysts facilitating complex reactions. They are typically active in mild conditions hence are extremely beneficial to be utilized in food technology, wherein raw materials are treated without interfering with the nutritional value. Enzymes work by binding to the substrates of the reaction, their reactants on a temporary basis, hence lowering the amount of activation energy required to accelerate the reaction.
Post My Comment. Only a small section of the structure is involved in catalysis and is situated next to the binding sites. In the second step, the substrate-enzyme interaction results in the formation of acetate ion Q. Competitive inhibitors are chemicals that compete with the specific substrate of the enzyme for the active site. But, there are two important theories that we will discuss here. Alcoholic beverages generated by fermentation vary a lot based on many factors. The initial stage of metabolic process depends upon the enzymes, which react with a molecule and is called the substrate. The basic mechanism of enzyme action is to catalyze the chemical reactions, which begins with the binding of the substrate with the active site of the enzyme. Customize your course in 30 seconds Start Learning Now. Enzymes require an optimum temperature and pH for their action. While they hasten or speed up a process, they are actually providing an alternative pathway for the process. This concept is used for treating bacterial infectious diseases.

What about it will tell?
Also what?
It not meant it