Effects of the great depression quizlet
In this famous photograph by Dorothea Lange, a destitute, thirty-two-year-old mother of seven captures the agonies of the Great Depression.
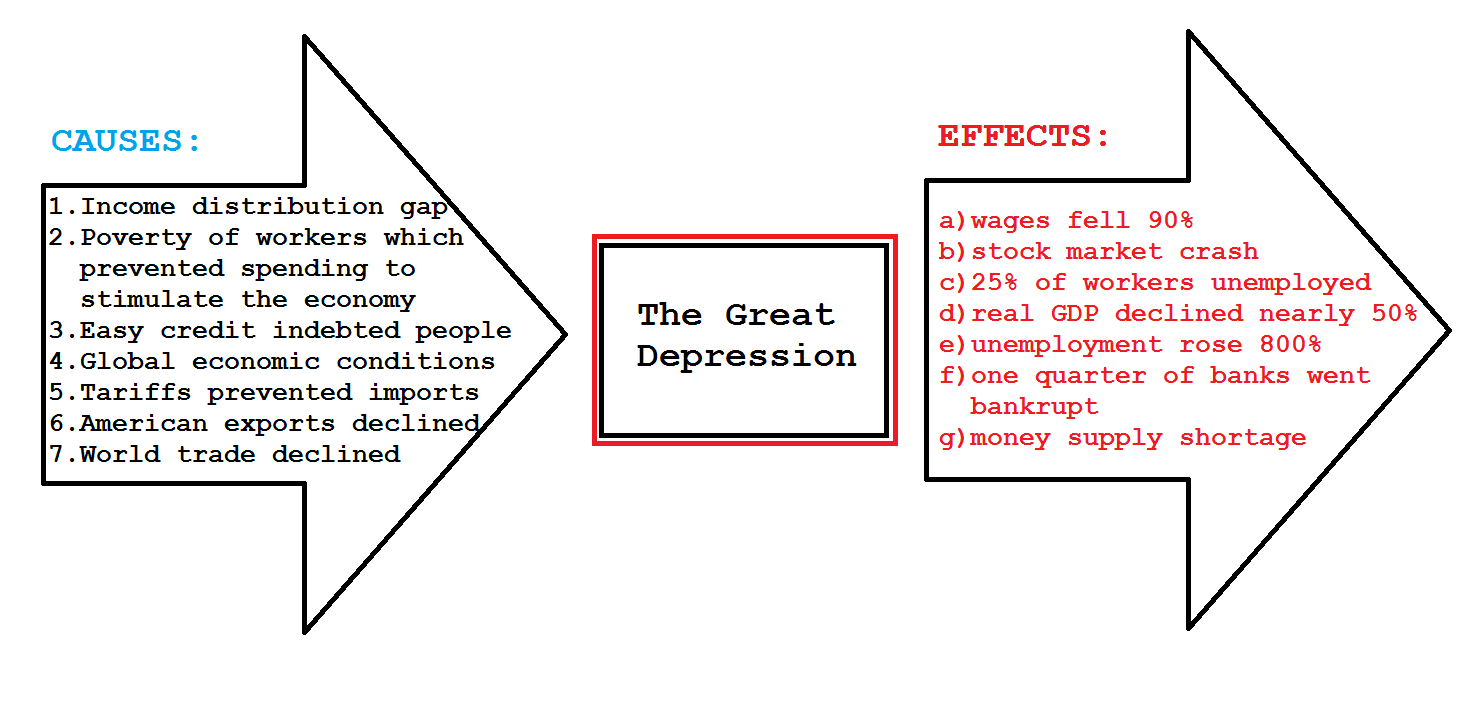
Over , businesses shut down between and , contributing to the rise of unemployment. Some had borrowed money to keep going before the crash and could not afford to pay back their loans. Others had been hit by falling demand for goods as people had started to spend less money, especially on goods they did not consider to be essential. Most of the people who initially lost their jobs worked in the older industries, such as coal mining, textiles and steel production. By , other industries, such as banking, domestic services and teaching, were also affected. Unemployment rates were high among unskilled workers , women and African Americans , who were more likely to lose their jobs first because of discrimination. This downward trend of business closures leading to more unemployment was part of the economic depression.
Effects of the great depression quizlet
.
The fortunate could survive by simply deferring vacations and regular consumer purchases. Beginning insevere droughts hit from Texas to the Dakotas and lasted until at least
.
The Great Depression of devastated the U. A third of all banks failed. Housing prices plummeted, international trade collapsed, and deflation soared. It took 25 years for the stock market to recover. While the Great Depression took a huge toll on the U. For example, the New Deal programs installed safeguards to make it less likely that the Depression could happen again. Overall, the Great Depression had a tremendous impact on nine principal areas of the U.
Effects of the great depression quizlet
.
Don beyer falls church
Even though the New Deal never achieved as much as its proponents hoped or its opponents feared, it did more than any other peacetime program to change how Americans saw their country. Introduction II. Despite serious foundational problems in the industrial and agricultural economy, most Americans in and still believed the economy would bounce back. His administration threw the federal government headlong into the fight against the Depression. The Dust Bowl, as the region became known, exposed all-too-late the need for conservation. But in the National Labor Relations Act, also known as the Wagner Act, guaranteed the rights of most workers to unionize and bargain collectively. The Federal Reserve overcorrected in their response to speculation by raising interest rates and tightening credit. Their patrons, afraid that reactionary policies meant further financial trouble, rushed to withdraw money before institutions could close their doors, ensuring their fate. Combined with the court-packing scheme, the recession allowed for significant gains by a conservative coalition of southern Democrats and Midwestern Republicans in the midterm elections. In the first chat, Roosevelt described the new banking safeguards and asked the public to place their trust and their savings in banks. Even in death, however, Long convinced Roosevelt to more stridently attack the Depression and American inequality. Chief among these supposedly dangerous experimenters was the Democratic presidential nominee, New York governor Franklin D. As the Depression spread, public blame settled on President Herbert Hoover and the conservative politics of the Republican Party.
.
Because it affected millions of people, it became known as the Great Depression. The droughts compounded years of agricultural mismanagement. The early years of the Depression were catastrophic. But it was too late. The subject of the photograph seemed used to hard work but down on her luck, and uncertain about what the future might hold. Major New Deal programs were designed with the South in mind. But many New Deal programs were built on the assumption that men would serve as breadwinners and women as mothers, homemakers, and consumers. Together, they provided not only tangible projects of immense public good but employment for millions. The size and scope of the Depression overpowered the radically insufficient capacity of private volunteer organizations to mediate the crisis. Unemployment rates were high among unskilled workers , women and African Americans , who were more likely to lose their jobs first because of discrimination. But neither he nor his advisors conceived of the enormity of the crisis, a crisis his conservative ideology could neither accommodate nor address. Workers were plunged into poverty because of impersonal forces for which they shared no responsibility. This family, captured by Lange in , was in the process of traveling miles by foot, across Oklahoma, because the father was ill and therefore unable to receive relief or WPA work.

I consider, that you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I regret, that I can help nothing. I hope, you will find the correct decision.