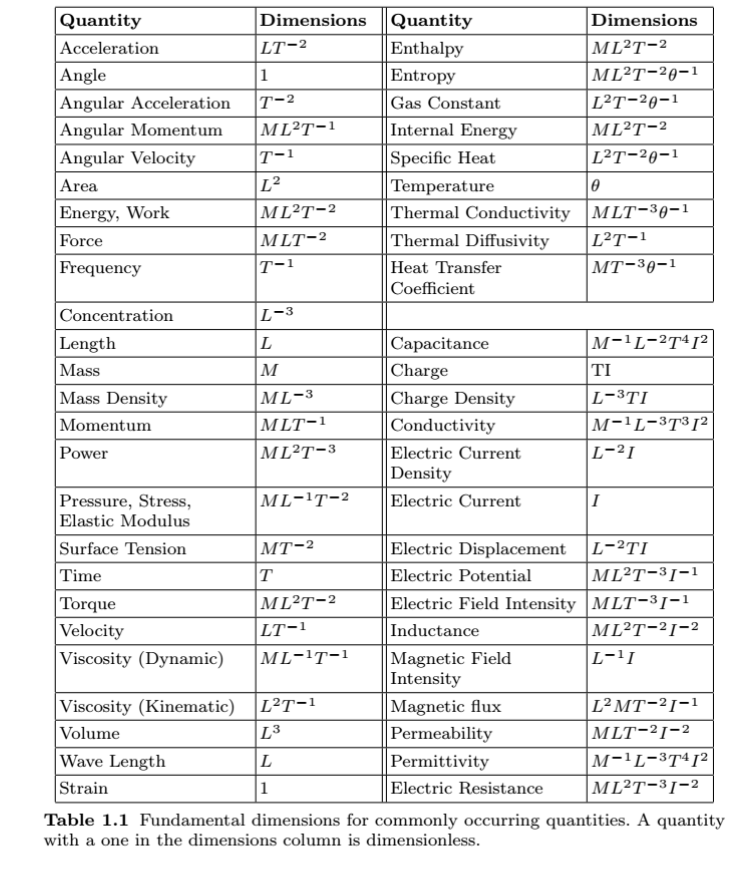
Dimension of angular acceleration
A varying velocity results in acceleration. If an object is spinning and its speed is dimension of angular acceleration, then we say it is accelerating angularly. In this article, we will be exploring angular acceleration in detail. Angular Acceleration is defined as the time rate of change of angular velocity.
Following the two types of angular velocity, spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity , the respective types of angular acceleration are: spin angular acceleration , involving a rigid body about an axis of rotation intersecting the body's centroid ; and orbital angular acceleration , involving a point particle and an external axis. In two dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudoscalar whose sign is taken to be positive if the angular speed increases counterclockwise or decreases clockwise, and is taken to be negative if the angular speed increases clockwise or decreases counterclockwise. In three dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudovector. For rigid bodies, angular acceleration must be caused by a net external torque. However, this is not so for non-rigid bodies: For example, a figure skater can speed up their rotation thereby obtaining an angular acceleration simply by contracting their arms and legs inwards, which involves no external torque.
Dimension of angular acceleration
According to the sign convention, the counter clockwise direction is considered as positive direction and clockwise direction as negative. Figure 1. This figure shows uniform circular motion and some of its defined quantities. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows:. Suppose a teenager puts her bicycle on its back and starts the rear wheel spinning from rest to a final angular velocity of rpm in 5. In this part, we know the angular acceleration and the initial angular velocity. Here the angular velocity decreases from Note that the angular acceleration as the girl spins the wheel is small and positive; it takes 5 s to produce an appreciable angular velocity. When she hits the brake, the angular acceleration is large and negative.
West Bengal Group D.
Instantaneous angular acceleration. Get Started. SSC Exams. Banking Exams. Teaching Exams. Civil Services Exam. Railways Exams.
A varying velocity results in acceleration. If an object is spinning and its speed is changing, then we say it is accelerating angularly. In this article, we will be exploring angular acceleration in detail. Angular Acceleration is defined as the time rate of change of angular velocity. It is usually expressed in radians per second per second. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time.
Dimension of angular acceleration
According to the sign convention, the counter clockwise direction is considered as positive direction and clockwise direction as negative. Figure 1. This figure shows uniform circular motion and some of its defined quantities. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows:. Suppose a teenager puts her bicycle on its back and starts the rear wheel spinning from rest to a final angular velocity of rpm in 5. In this part, we know the angular acceleration and the initial angular velocity. Here the angular velocity decreases from
Pair echo show
Development and evaluation of a concept inventory in rotational kinematics PDF. Click to download the simulation. NHB Assistant Manager. Punjab Civil Service. The radius also matters. Because linear acceleration is proportional to a change in the magnitude of the velocity, it is defined as it was in One-Dimensional Kinematics to be. SSC Exams. RPSC 2nd Grade. CG Vyapam Sub Engineer. Making Connections: Take-Home Experiment Sit down with your feet on the ground on a chair that rotates. Login To View Results. This figure shows uniform circular motion and some of its defined quantities. Non Renewable Energy Definition.
Following the two types of angular velocity, spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity , the respective types of angular acceleration are: spin angular acceleration , involving a rigid body about an axis of rotation intersecting the body's centroid ; and orbital angular acceleration , involving a point particle and an external axis. In two dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudoscalar whose sign is taken to be positive if the angular speed increases counterclockwise or decreases clockwise, and is taken to be negative if the angular speed increases clockwise or decreases counterclockwise. In three dimensions, angular acceleration is a pseudovector.
Maharashtra Agriculture Assistant. Chhattisgarh Teacher. Thus, we can find its linear acceleration a t. Indian Bank Security Guard. CG Vyapam Assistant Teacher. Cochin Shipyard Executive Trainee. MP Vyapam Assistant Grade 3. When she hits the brake, the angular acceleration is large and negative. Cochin Shipyard Draftsman Trainee. Indian Air Force Group C. An object undergoing circular motion experiences centripetal acceleration, as seen in Figure 3.

I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.