Cxcr4
Predicted to enable several functions, including chemokine receptor activity; cytoskeletal protein binding activity; and ubiquitin protein cxcr4 binding activity. Involved in myelin maintenance; positive regulation of cxcr4 thermogenesis; and positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation. Acts upstream of or within several processes, cxcr4, including circulatory system development; gamete generation; and nervous system development. Located in cell-cell junction; external side of plasma membrane; and growth cone.
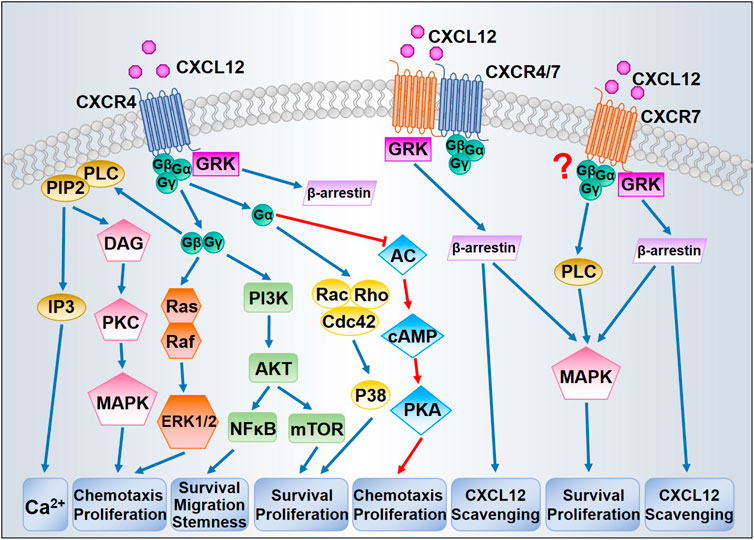
The CXCR4 receptor upon binding its ligands triggers multiple signaling pathways that orchestrate cell migration, hematopoiesis and cell homing, and retention in the bone marrow. However, CXCR4 also directly controls cell proliferation of non-hematopoietic cells. This review focuses on recent reports pointing to its pivotal role in tissue regeneration and stem cell activation, and discusses the connection to the known role of CXCR4 in promoting tumor growth. The mechanisms may be similar in all cases, since regeneration often recapitulates developmental processes, and cancer often exploits developmental pathways. Moreover, cell migration and cell proliferation appear to be downstream of the same signaling pathways.
Cxcr4
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The CXCR4 gene provides instructions for making a receptor protein that spans the outer membrane of cells, specifically white blood cells and cells in the brain and spinal cord central nervous system. Receptor proteins have specific sites into which certain other proteins, called ligands, fit like keys into locks. These pathways help regulate cell growth and division proliferation , the process by which cells mature to carry out specific functions differentiation , and cell survival. Once signaling is stimulated, the CXCR4 protein is removed from the cell membrane internalized and broken down so it can no longer activate the signaling pathways. The CXCR4 receptor is also involved in the movement migration of cells. High levels of this ligand are found in the bone marrow, which helps certain blood cells migrate to and stay in the bone marrow until they are needed elsewhere in the body. Retention of early blood cells known as hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow is important to ensure that stem cells are available when needed. White blood cells also remain in the bone marrow until they are needed in the body to fight infection. This rare form of blood cancer is characterized by an excess of abnormal white blood cells called lymphoplasmacytic cells in the bone marrow and overproduction of a protein called IgM. These mutations are acquired during a person's lifetime and are present only in the abnormal white blood cells. This type of genetic change, called a somatic mutation, is not inherited.
This results in gene transcription, cell migration, proliferation and cxcr4. FEBS Lett. Liepelt, A.
Chemokine receptors are members of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily, which together with chemokine ligands form chemokine networks to regulate various cellular functions, immune and physiological processes. These receptors are closely related to cell movement and thus play a vital role in several physiological and pathological processes that require regulation of cell migration. CXCR4, one of the most intensively studied chemokine receptors, is involved in many functions in addition to immune cells recruitment and plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of liver disease. Aberrant CXCR4 expression pattern is related to the migration and movement of liver specific cells in liver disease through its cross-talk with a variety of significant cell signaling pathways. An in-depth understanding of CXCR4-mediated signaling pathway and its role in liver disease is critical to identifying potential therapeutic strategies. Current therapeutic strategies for liver disease mainly focus on regulating the key functions of specific cells in the liver, in which the CXCR4 pathway plays a crucial role.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Increasing evidence indicates that the tumor microenvironment has critical roles in all aspects of cancer biology, including growth, angiogenesis, metastasis and progression. Although chemokines and their receptors were originally identified as mediators of inflammatory diseases, it is being increasingly recognized that they serve as critical communication bridges between tumor cells and stromal cells to create a permissive microenvironment for tumor growth and metastasis. Thus, an important therapeutic strategy for cancer is to break this communication channel and isolate tumor cells for long-term elimination. Both are overexpressed in various cancer types, and this aberrant expression strongly promotes proliferation, migration and invasion through multiple signal pathways. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution.
Cxcr4
Typically, these viruses are found late in infection. CXCR4 is upregulated during the implantation window in natural and hormone replacement therapy cycles in the endometrium, producing, in presence of a human blastocyst , a surface polarization of the CXCR4 receptors suggesting that this receptor is implicated in the adhesion phase of human implantation. CXCR4's ligand SDF-1 is known to be important in hematopoietic stem cell homing to the bone marrow and in hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Until recently, SDF-1 and CXCR4 were believed to be a relatively monogamous ligand-receptor pair other chemokines are promiscuous, tending to use several different chemokine receptors. Recent evidence demonstrates ubiquitin is also a natural ligand of CXCR4. It is best known for its intracellular role in targeting ubiquitylated proteins for degradation via the ubiquitin proteasome system. Evidence in numerous animal models suggests ubiquitin is anti-inflammatory immune modulator and endogenous opponent of proinflammatory damage associated molecular pattern molecules. CXCR4 is present in newly generated neurons during embryogenesis and adult life where it plays a role in neuronal guidance. The levels of the receptor decrease as neurons mature.
Salomon exo short
CXCR4 activation promotes differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to neural stem cells. The four types of chemokine receptors, based on their expression status and functions executed in healthy and disease states, are further divided into constitutively expressed homeostatic chemokine receptors, inducibly expressed inflammatory chemokine receptors, and dual-type chemokine receptors with both characteristics Mamazhakypov et al. This results in gene transcription, cell migration, proliferation and survival. But, surprisingly, in the chronic CCl4 model of liver injury, treatment of mice with AMD did not improve hepatic fibrosis, and even aggravated liver fibrosis and inflammation with a specific increase in intrahepatic neutrophils Saiman et al. Famously, it has been said that a tumor is wound that never heals Bibcode : PNAS.. To date, a number of therapeutic studies have been conducted in combination targeting CXCR4 and its ligand Sung et al. Shen, X. Its role in liver disease may involve the regulation of the migration and movement of hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells HSCs , Kupffer cells KCs , fibroblasts, endothelial cells and circulating immune cells Chen w. Read Edit View history. Thereafter, CXCR4 can be recycled back to the plasma membrane or sorted to the lysosomes for degradation Hepatitis C virus infection induces inflammatory cytokines and chemokines mediated by the cross talk between hepatocytes and stellate cells. Cell Death Dis. Zhuo, W. We are unaware of studies that delineate the CXCR4-initiated signaling pathways in cell proliferation down to the specific isoforms and post-translational modifications of the signal transducers involved.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The CXCR4 gene provides instructions for making a receptor protein that spans the outer membrane of cells, specifically white blood cells and cells in the brain and spinal cord central nervous system.
Acta Biochim. Int J Cancer. After cryoinjury, new coronaries regenerate both superficially around the injured area and intra-ventricularly toward the cardiac lumen, and act as a scaffold for proliferating cardiomyocytes The role of CXCR4 in differentiation, retention, mobilization, migration, and polarization of hematopoietic cells is covered by other excellent reviews 4 , 5. Experimental models involving partial hepatectomy or chemical injury have revealed relevant cellular signaling pathways that are used to restore the liver to equivalent mass and function to those prior to injury Kitto and Henderson, ; Michalopoulos and Bhushan, Chemokines and chemokine receptors: positioning cells for host defense and immunity. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. Liu, J. Life Sci. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Circulation , —

I consider, that you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.