Cross section of a leaf gcse
Ms Armit: The leaf is a major organ in plants in which photosynthesis occurs.
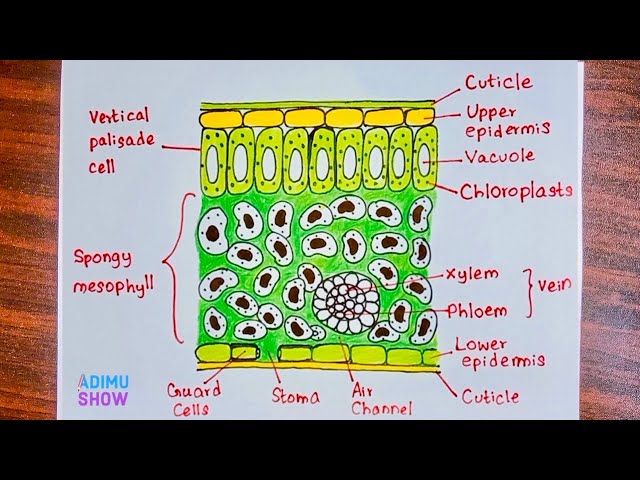
Learn Teach Quiz Login? The cuticle is transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. The epidermis is is also transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. These cells are located close to the leaf surface to maximise light absorption. They are upright, elongated and tightly packed together in order to increase the surface area for light absorption.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
The structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis close photosynthesis A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll close palisade mesophyll Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf. Palisade cells are column-shaped and packed with many chloroplasts close chloroplast Contains the green pigment chlorophyll; the site of photosynthesis. They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light energy can be absorbed. The stomata close stomata Tiny holes in the epidermis skin of a leaf. They control gas exchange by opening and closing and are involved in loss of water from leaves. Singular is stoma. Each stoma can be open or closed, depending on how turgid close turgid Enlarged and swollen with water. Having turgor. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis. Diffusion close diffusion The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In this guide.
Cal: I mean… Yeah, they're good, aren't they? They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light energy can be absorbed.
.
Plants are divided into flowers, stems, leaves and roots with root hairs. A generalised plant is shown in the illustration. The stem provides support for the leaves and flowers. It also allows water and food to travel both up and down the plant. The roots anchor the plant in the soil and take up water and salts mineral ions from the soil. The root hairs provide a large surface area for water and salt uptake. The flowers are reproductive organs.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
Teacher and Student Resources. For a typical leaf, we use that of the umbrella tree, which is commonly sold as a foliage plant throughout North America and Europe. It is actually a tree native to tropical rainforests of northern Australia; it is a good example because we can examine it at any time of the year. The structure of the umbrella tree leaf is typical of leaves in general Above left photo. It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating. The epidermis of the undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores stomata which control the loss of water vapor transpiration and the entry of carbon dioxide.
Tita sahara nude
The more we know about botany, the more we understand about life on Earth. It just seemed more applicable to life. Put some on the other side, like that. Label the leaf. Ms Armit: I'm so glad you've found a new passion. Biology: Exam-style questions Bitesize revision podcasts Personalise your Bitesize! Leaves have several adaptations which play an important role in photosynthesis. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis. Ecological sampling. Cal: Well, you inspired me. The role of stomata.
In angiosperm anatomy, a leaf can be identified by where it emerges from the node. In a node, a leaf emerges below the axillary bud.
They must also have extensive knowledge about trees, flowers, vegetables, nuts, bushes and fruits. They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light energy can be absorbed. Guard cells control the size of the stomata so that the leaf does not lose too much water in hot, windy or dry conditions. Leaves produce food for the plant through a process called photosynthesis. Watch the video to see how a horticulturist uses science in her job. Ms Armit: Precisely. Cal: Welcome back to the jungle! I work in the outside gardens. You know? A leaf needs:. Show answer Hide answer An expert who looks after plants, including feeding, watering, pruning and training. They all have the same basic setup. Ms Armit: This is something I can prove, though, with some nail varnish. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis. This plant is really well adapted to the Mediterranean climate where it doesn't rain very much, so it's got these leaf hairs which helps capture that water.

0 thoughts on “Cross section of a leaf gcse”