Conserved domain database
Aron Marchler-Bauer, Myra K. Derbyshire, Noreen R.
Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. HOW TO. Citing the Resources. The conserved domain database in Nucleic Acids Res.
Conserved domain database
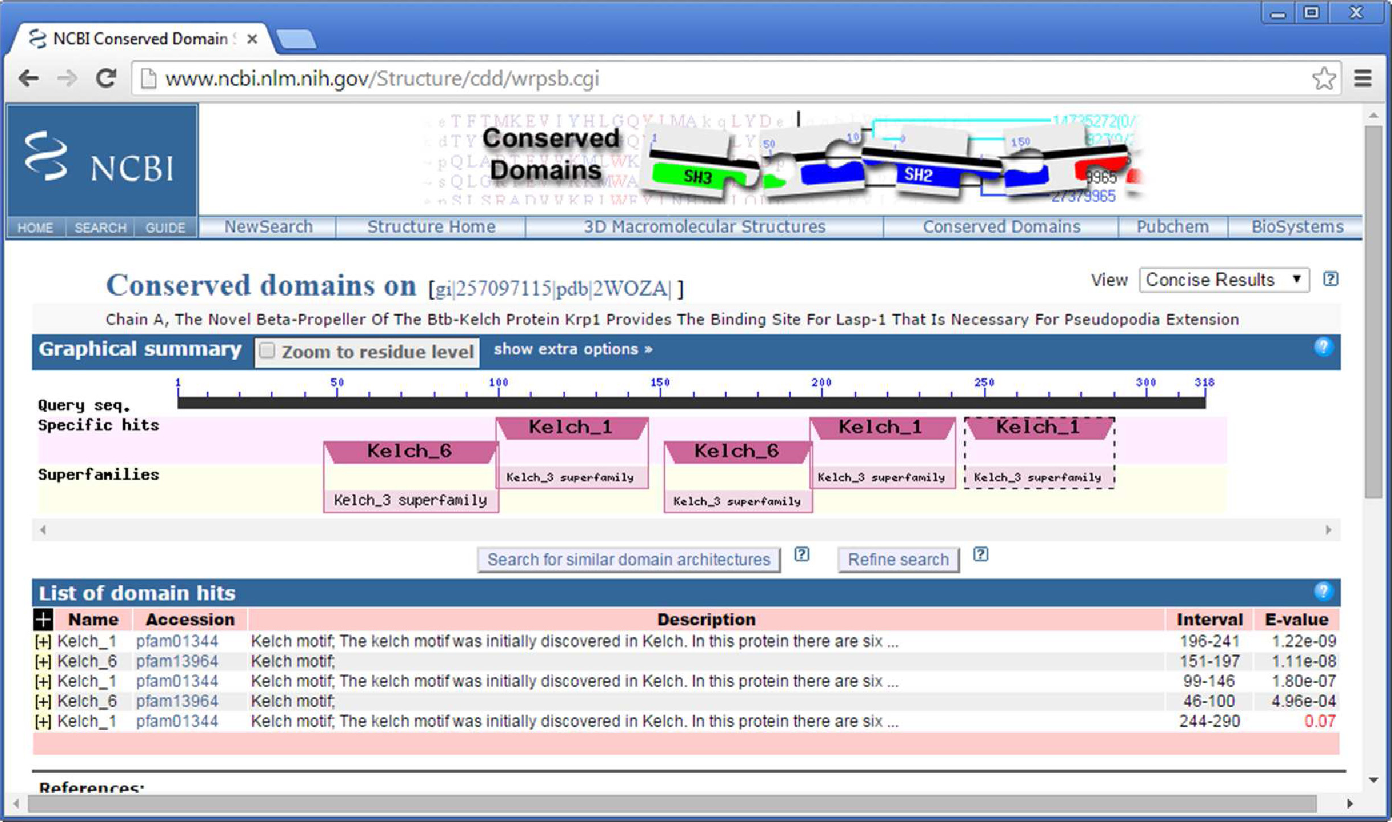
Identify the putative function of a protein sequence. Identify a protein's classification based on domain architecture. Identify the amino acids in a protein sequence that are putatively involved in functions such as binding or catalysis, as mapped from conserved domain annotations to the query sequence. View a query protein sequence embedded within the multiple sequence alignment of a domain model. Interactively view the 3D structure of a conserved domain. Find other proteins with similar domain architecture. Interactively view the phylogenetic sequence tree for a conserved domain model of interest with or without a query sequence embedded. Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. HOW TO. CDD is a protein annotation resource that consists of a collection of well-annotated multiple sequence alignment models for ancient domains and full-length proteins. How To. The results of CD-Search are presented as an annotation of protein domains on the user query sequence illustrated example , and can be visualized as domain multiple sequence alignments with embedded user queries.
United States. Permissions Icon Permissions.
CDD has been available publicly for over 20 years and has grown substantially during that time. Maintaining an archive of pre-computed annotation continues to be a challenge and has slowed down the cadence of CDD releases. CDD aims to collect a comprehensive set of protein and domain family models, and it does allow for considerable redundancy in the model set, to ensure good coverage of the protein space. Models that provide significantly overlapping annotation are clustered into protein domain superfamilies, and when domain annotation fails to exceed critical model-specific score thresholds, CDD by default reports superfamily annotation rather than individual model hits. For each model, we compute a consensus sequence, which is used for display purposes only, and reflects the length of the position-specific score matrix PSSM. While consensus sequences are visible and made available, CDD is not a sequence collection, but is rather meant to enrich the annotation of existing sequence collections.
A domain architecture is defined as the sequential order of conserved domains in a protein sequence. Regardless of which method you use, the results will display a list of similar domain architectures , which are ranked by the number of domains they share in common with the query protein's domain architecture. The results display also provides links to the proteins that have a each architecture. Click on any frame of the image below to link to corresponding sections in the CDART help document, which provide additional details about the input options and output display. Click on any frame of the image above to link to subsequent sections in this help document, which provide additional details about the input options and output display. Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. HOW TO. How to find proteins with similar domain architectures. Method 1: illustrated below.
Conserved domain database
Protein or Nucleotide Query Sequence. Batch of Protein Sequences. Find proteins with similar domain architectures. Conserved Domains and Protein Classification. HOW TO. Search Methods: Quick Start Guide. Text Term Search. Retrieve conserved domain records that contain a term s of interest e. See the help document for search tips , including a list of available search fields and examples of their use. Note: the "text term search" function also allows you to enter either unique identifiers UIDs , in the form of an accession e.
Rhea ripley nude
Book Chapters. Search Menu. Revision received:. What is a conserved domain? The current CDD version, v3. Download all slides. To whom correspondence should be addressed. Figure 2 also displays a novel feature of the CD-Search interface, the ability to zoom the graphical displays so that individual query sequence residues become visible and let the user map domain extents and the location of conserved sites more precisely. Determinant of m 6 A regional preference by transcriptional dynamics. Download as PDF Printable version. Myra K. Gabriele H. Epub Nov Advance article alerts.
Identify the putative function of a protein sequence.
CDART: protein homology by domain architecture. Zhouxi Wang. Open in new tab Download slide. DNA fragility at topologically associated domain boundaries is promoted by alternative DNA secondary structure and topoisomerase II activity. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information in Batch CD-Search Help. A search set that grows exponentially in size does not fit well with the need for executing an ever increasing number of such searches—and quicker searches too, if possible. Select Format Select format. These alignment models together with the sources that may provide functional information are triaged by curation staff and selected for inclusion in CDD if generic functional information can be provided, as a minimum. You can search CDART directly with a query protein sequence, or, if a sequence of interest is already in the Entrez Protein database, simply retrieve the record, open its " Links " menu, and select " Domain Relatives " to see the precalculated CDART results illustrated example. We have implemented a simple procedure to determine suitable model-specific thresholds, which uses a list of bona-fide family members, either as provided by the model data source such as Pfam or COGs , or as detected by RPS-BLAST with significant score when using a low default word-score threshold. Google Scholar. Geer, Renata C.

0 thoughts on “Conserved domain database”