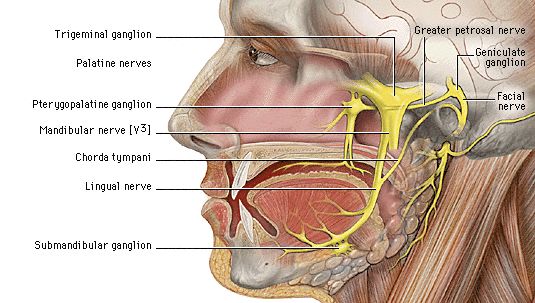
Chorda tympani
Damage can lead to loss of taste, burning mouth syndrome. The chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve and, along with other nerves, is important chorda tympani carrying information about taste and other sensations from your taste buds to your brain, chorda tympani.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ashnaa Rao ; Prasanna Tadi.
Chorda tympani
The Chorda Tympani Nerve is given off from the facial as it passes downward behind the tympanic cavity, about 6 mm. It then descends between the Pterygoideus externus and internus on the medial surface of the spina angularis of the sphenoid, which it sometimes grooves, and joins, at an acute angle, the posterior border of the lingual nerve. It receives a few efferent fibers from the motor root; these enter the submaxillary ganglion, and through it are distributed to the submaxillary and sublingual glands; the majority of its fibers are afferent, and are continued onward through the muscular substance of the tongue to the mucous membrane covering its anterior two-thirds; they constitute the nerve of taste for this portion of the tongue. Before uniting with the lingual nerve the chorda tympani is joined by a small branch from the otic ganglion. Human anatomy 1. Underlying structures: There are no anatomical children for this anatomical part. IMAIOS and selected third parties, use cookies or similar technologies, in particular for audience measurement. Cookies allow us to analyze and store information such as the characteristics of your device as well as certain personal data e. For more information, see our privacy policy. You can freely give, refuse or withdraw your consent at any time by accessing our cookie settings tool. If you do not consent to the use of these technologies, we will consider that you also object to any cookie storage based on legitimate interest.
Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. It innervates the muscles of facial expression while supplying parasympathetic innervation to the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, chorda tympani, hard and soft chorda tympani, and the lacrimal, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made. The chorda tympani is a nerve that arises from the mastoid segment of the facial nerve , carrying afferent special sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the lingual nerve , as well as efferent parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual glands. After branching off from the facial nerve, the chorda tympani courses through the temporal bone before joining the lingual nerve 2 :. The distance of ascent is variable, depending on the initial branching pattern from the mastoid segment of facial nerve. It then travels inferiorly to join the lingual nerve approximately 2 cm below the skull base.
In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the facial nerve — its anatomical course, functions and clinical correlations. The facial nerve is associated with the derivatives of the second pharyngeal arch :. The course of the facial nerve is very complex. There are many branches, which transmit a combination of sensory, motor and parasympathetic fibres. The nerve arises in the pons , an area of the brainstem.
Chorda tympani
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Sarah E. Fagan ; William Roy.
Do it yourself fleshlight
From there, it travels a relatively long and complex course with numerous branches performing many distinct functions. This nerve damage has also been demonstrated to result in taste disturbances. Figure 3: geniculate ganglion Figure 3: geniculate ganglion. The cranial nerves. The lingual branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve performs the same function for the back one-third of the tongue. The chorda tympani degenerates during chronic otitis media: an electron microscopy study. Its association with the ear is what gives the chorda tympani its name. The taste system involves a complicated feedback loop, with each nerve acting to inhibit the signals of other nerves. The cranial nerves pass through small holes in your skull base called foramen to exit and travel to various head and neck regions. Cholesteatomas are cysts that can be harmful and occur in the middle ear. Experts theorize that this kind of inhibition may help the brain accurately classify a broader range of tastes and other sensations.
The Chorda Tympani Nerve is given off from the facial as it passes downward behind the tympanic cavity, about 6 mm.
It passes behind the ear drum and between two tiny bones of the middle ear called the incus and malleus. OCLC The facial nerve exits the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus and enters the facial canal. Journal of Neurobiology. The website cannot function properly without these cookies, which is why they are not subject to your consent. Nucleus ambiguus Inferior salivatory nucleus Solitary nucleus. Taste damage, especially, can be long-lasting, most notably if it involves bitterness. Damage to the facial nerve can also impair the chorda tympani's function. Contact Us. The muscles of the face also derive from this arch. You can help by adding to it. Last revised:. Subsequently, a petrosal branch of the middle meningeal artery is thought to supply the nerve as it reaches the stylomastoid foramen.

Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also to me this idea is pleasant, I completely with you agree.
At me a similar situation. Is ready to help.