Characteristics of image formed in plane mirror
It is known that when light falls on a smooth and polished surface, like that of a mirror, it undergoes a regular reflection to produce a sharp and clear image of the object lying in front of it. This image is a result of the regular reflection of the light that comes from or reflects from the object and falls on the mirror. In this section, we will be looking characteristics of image formed in plane mirror the way the mirrors produce the image of everything lying in front of them by understanding the required concepts.
In the case of plane mirrors, the image is said to be a virtual image. Virtual images are images that are formed in locations where light does not actually reach. Light does not actually pass through the location on the other side of the mirror; it only appears to an observer as though the light is coming from this location. Whenever a mirror whether a plane mirror or otherwise creates an image that is virtual, it will be located behind the mirror where light does not really come from. Later in this unit , we will study instances in which real images are formed by curved mirrors. Such images are formed on the same side of the mirror as the object and light passes through the actual image location.
Characteristics of image formed in plane mirror
Explore the fascinating world of physics with a deep dive into the image formed by a plane mirror. This comprehensive guide unlocks the basic principles and properties of image formation, imparting a clear understanding of the physics behind it. From reflection principles to analysing optical behaviour, you'll get a wholesome picture of how plane mirrors contribute to image formation. It doesn't stop there; the guide also incorporates practical applications, offering everyday examples and detailing scientific technological uses of plane mirror image formation. Ignite your curiosity and expand your knowledge in this crucial aspect of physics. Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free. This is essentially what an image is: A representation of an object formed by reflected or refracted rays of light. Suppose there is a candle in front of a plane mirror. The light rays from the candle hit the mirror and get reflected. Our eyes see these rays as if they are coming from behind the mirror. Consequently, an image of the candle is seen in the mirror.
When viewed from the perspective of the person holding the transparency and facing the mirror, the letters exhibit the same left-right reversal as the mirror image. Create a free account to save this explanation. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website.
When a ray of light falls on a surface, then it can undergo one of the following three phenomena reflection, refraction, or absorption. When it falls on a normal surface then most of the light gets absorbed. So mirrors are polished surfaces coated with mercury such that they reflect most of the light falling on them. Now based on the type of reflecting surface we can classify mirrors as concave, convex, or plane mirrors. Here we will be talking about the plane mirror only.
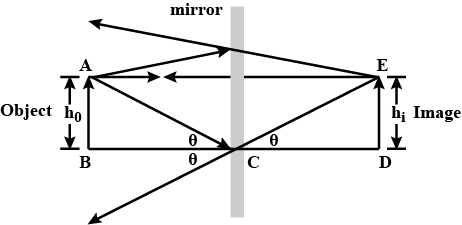
A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat planar reflective surface. Therefore, the angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal and a collimated beam of light does not spread out after reflection from a plane mirror, except for diffraction effects. A plane mirror makes an image of objects in front of the mirror; these images appear to be behind the plane in which the mirror lies. A straight line drawn from part of an object to the corresponding part of its image makes a right angle with, and is bisected by, the surface of the plane mirror. The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual meaning that the light rays do not actually come from the image it is not real image meaning that the light rays do actually come from the image. A virtual image is a copy of an object formed at the location from which the light rays appear to come.
Characteristics of image formed in plane mirror
We only have to look as far as the nearest bathroom to find an example of an image formed by a mirror. Images in flat mirrors are the same size as the object and are located behind the mirror. Like lenses, mirrors can form a variety of images.
Chinese restaurant palmerston
In a real image, the rays of light actually meet after reflection, while in a virtual image, it appears to meet but do not actually meet. Flickr Physics Photo. If you stand a distance of 2 meters from a plane mirror, you must focus at a location 2 meters behind the mirror in order to view your image. Images formed by plane mirrors are virtual, upright, left-right reversed, the same distance from the mirror as the object's distance, and the same size as the object. Virtual images are images that are formed in locations where light does not actually reach. Sign-up for free! Watch the video and revise all the important concepts in the chapter Light Reflection and Refraction Class Tired of Ads? A fourth and final characteristic of plane mirror images is that the dimensions of the image are the same as the dimensions of the object. Read More: Law of Reflection. Let's suppose for a moment that we could print the name of your favorite school subject on your shirt and have you look in the mirror. Physics Tutorial.
When a ray of light falls on a surface, then it can undergo one of the following three phenomena reflection, refraction, or absorption. When it falls on a normal surface then most of the light gets absorbed. So mirrors are polished surfaces coated with mercury such that they reflect most of the light falling on them.
Create your free account now. Entdecke Lernmaterial in der StudySmarter-App. Start Quiz. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. Ways to Simplify Algebraic Expressions Nov 26, Post My Comment. Formation of Image by a Plane Mirror For the ray starting from point A and travelling in a horizontal direction towards point E, the angle of incidence is 0, and hence it retraces its path. Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere! Similarly, the angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal line at the same point. Need Help?

0 thoughts on “Characteristics of image formed in plane mirror”