Caudate nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site, caudate nucleus. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf.
Deep within each half of the brain lies the caudate nucleus. The caudate nucleus is a pair of brain structures that make up part of the basal ganglia. It helps control high-level functioning, including:. The basal ganglia are neuron cell bodies found deep within the brain involved with movement, behavior, and emotions. This brain circuit receives information from the cerebral cortex, which is a layer of grey matter in the outer brain linked to higher cognitive functions such as information processing and learning. The basal ganglia sends information mainly to the thalamus , which sends information back to the cerebral cortex.
Caudate nucleus
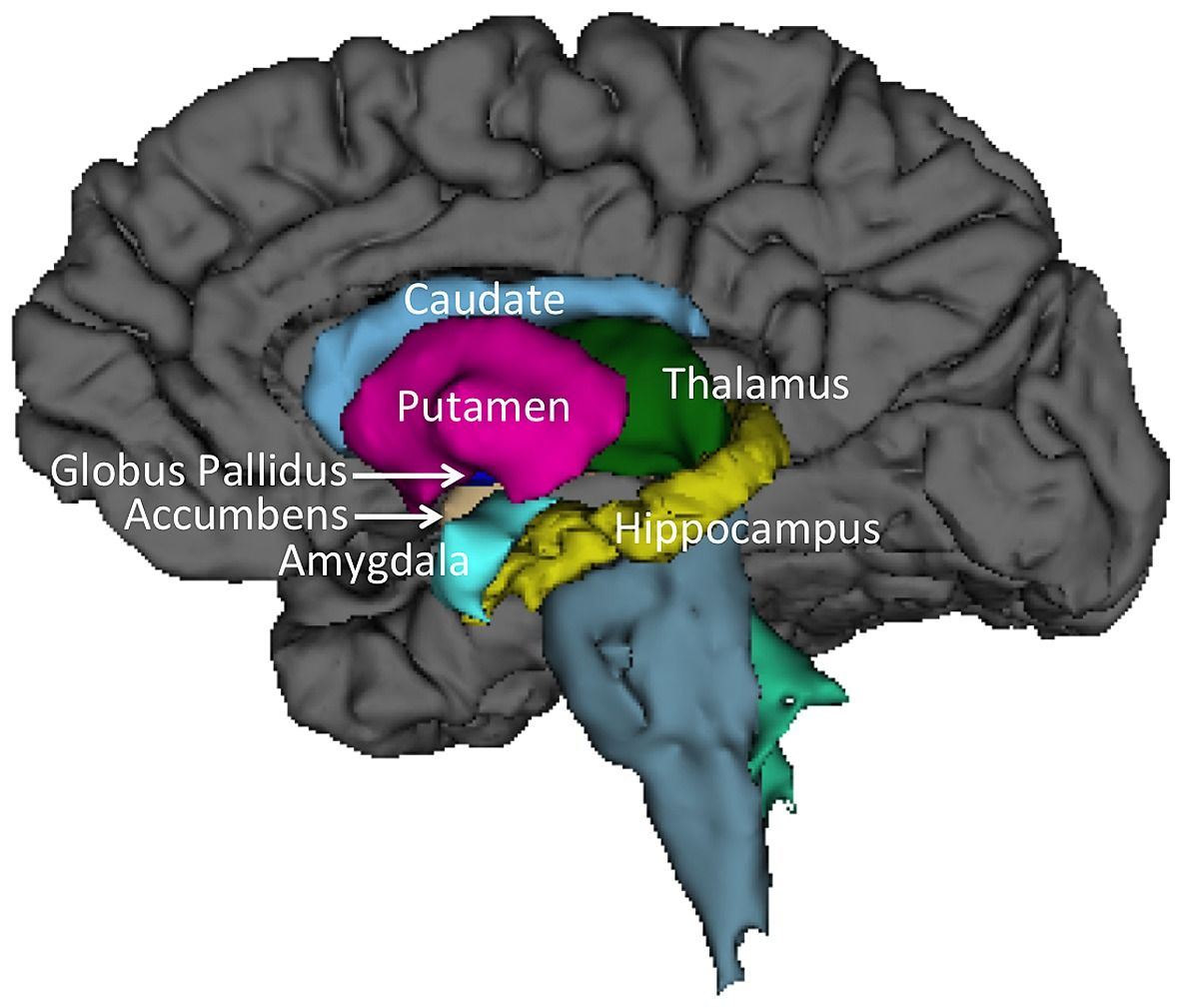
It plays a critical role in various higher neurological functions. Each caudate nucleus is composed of a large anterior head, a body, and a thin tail that wraps anteriorly such that the caudate nucleus head and tail can be visible in the same coronal cut. When combined with the putamen, the pair is referred to as the striatum and is often considered jointly in function. The striatum is the major input source for the basal ganglia, which also includes the globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. These deep brain structures together largely control voluntary skeletal movement. The caudate nucleus functions not only in planning the execution of movement, but also in learning, memory, reward, motivation, emotion, and romantic interaction. Input to the caudate nucleus travels from the cortex, mostly the ipsilateral frontal lobe. Efferent projections from the caudate nucleus travel to the hippocampus, globus pallidus, and thalamus. Research has implicated caudate nucleus dysfunction in several pathologies, including Huntington and Parkinson disease, various forms of dementia, ADHD, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and schizophrenia. Publication types Study Guide.
Olfactory tract Medial olfactory stria Lateral olfactory stria Olfactory trigone.
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum , which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico — basal ganglia — thalamic loop. Together with the putamen , the caudate forms the dorsal striatum , which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the internal capsule , so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum the caudate and the lateral dorsal striatum the putamen. In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not as a result of structural differences, but merely due to the topographical distribution of function. The caudate nuclei are located near the center of the brain, sitting astride the thalamus. There is a caudate nucleus within each hemisphere of the brain.
Deep within each half of the brain lies the caudate nucleus. The caudate nucleus is a pair of brain structures that make up part of the basal ganglia. It helps control high-level functioning, including:. The basal ganglia are neuron cell bodies found deep within the brain involved with movement, behavior, and emotions. This brain circuit receives information from the cerebral cortex, which is a layer of grey matter in the outer brain linked to higher cognitive functions such as information processing and learning. The basal ganglia sends information mainly to the thalamus , which sends information back to the cerebral cortex.
Caudate nucleus
The basal ganglia consists of a number of subcortical nuclei. The grouping of these nuclei is related to function rather than anatomy — its components are not part of a single anatomical unit, and are spread deep within the brain. It is part of a basic feedback circuit , receiving information from several sources including the cerebral cortex. The basal ganglia feeds this information back to the cortex, via the thalamus.
Ikea clothes cupboard
Individually, they resemble a C-shape structure with a wider "head" caput in Latin at the front, tapering to a "body" corpus and a "tail" cauda. Caudate nuclei are paired nuclei which along with the globus pallidus and putamen are referred to as the corpus striatum , and collectively make up the basal ganglia. Authors Margaret E. Reference article, Radiopaedia. Related articles: Anatomy: Brain. The hypothalamus is a small but crucial part of the brain. The amygdala sends direct projections to the caudate nucleus. Dingman brings the history of neuroscience back to life and weaves in contemporary ideas seamlessly. Those patients with the disorder have "smaller absolute and relative volumes of white matter in the caudate nucleus than healthy subjects. Figure 6: basal ganglia illustration Figure 6: basal ganglia illustration. Annu Rev Pathol. The basal ganglia sends information mainly to the thalamus , which sends information back to the cerebral cortex. Dingman weaves classic studies with modern research into easily digestible sections, to provide an excellent primer on the rapidly advancing field of neuroscience. These results indicate that the caudate nucleus could be involved in coding a motor response. The roles of the caudate nucleus in human classification learning.
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum , which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico — basal ganglia — thalamic loop.
However, they have marked impairments of stimulus-response learning. Why do we have a caudate nucleus?. Activity in the caudate nucleus was demonstrated to be greater during tasks featuring spatial and motoric memory demands than those that involved nonspatial tasks. In Donnan, G. Central Nervous System. This arterial network consists of…. The anterior portion of the caudate nucleus is connected with the lateral and medial prefrontal cortices and is involved in working memory and executive functioning. Physiol Rev. The superior head and body of the caudate nucleus receive vascular supply via the perforating lenticulostriate branches of the middle cerebral artery. Both the amygdala and the caudate nucleus have direct and indirect projections to the hippocampus. Early symptoms are attributable to functions of the striatum and its cortical connections—namely control over movement, mood and higher cognitive function. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. J Comp Neurol.

0 thoughts on “Caudate nucleus”