Cat5e vs cat6 vs cat7
Looking similar from the outside, but all of these Ethernet cable categories do have differences in transmission performance.
Although fiber optic cables are increasingly used today, twisted pair copper Ethernet cabling still can't be replaced in many application areas. In practice, most network faults are caused by poor or unsuitable cabling systems. Therefore, choosing a suitable Ethernet cable is vital for your business or home networks. Then you must know what are the differences between Cat 5e vs Cat 6 vs Cat 6A vs Cat 7 and be clear that when to choose the right one for specific applications. I hope this article will help.
Cat5e vs cat6 vs cat7
Ethernet represents the plumbing pipes of the Internet. Many network installers and system integrators are familiar with the ethernet types: Cat5e and Cat6 cables with RJ45 connectors. Each new iteration of Ethernet, or category, supports increasingly faster bandwidth speeds and improves upon noise cancelation. Cross sections of different category types of Ethernet reveal differing internal physical compositions. This guide will help you learn more about the subtle differences between each generation of twisted pair Ethernet cable. Ethernet cabling differences can be invisible to the casual observer. However, each new generation introduces copper pairs with tighter twists and more complex sheathing. Many earlier Ethernet generation cables have become obsolete. Cat3 cable is an earlier generation of Ethernet but can still be seen in older deployments. With the ability to support a maximum frequency of 16 MHz, this type of Ethernet can still be used for two-line telephone systems and 10BASE-T networks. CAT3 cable can also be used for alarm system installation or similar applications. CAT3 cable can have 2, 3, or 4 copper pairs though uncommon. Category 5e cable, however, has become the default Ethernet category of choice with the ability to support faster speeds and frequencies. Even though some older deployments still use CAT5 cable, it is now considered obsolete and has since been replaced by Cat5e. Crosstalk is interference that transfers from adjacent wires.
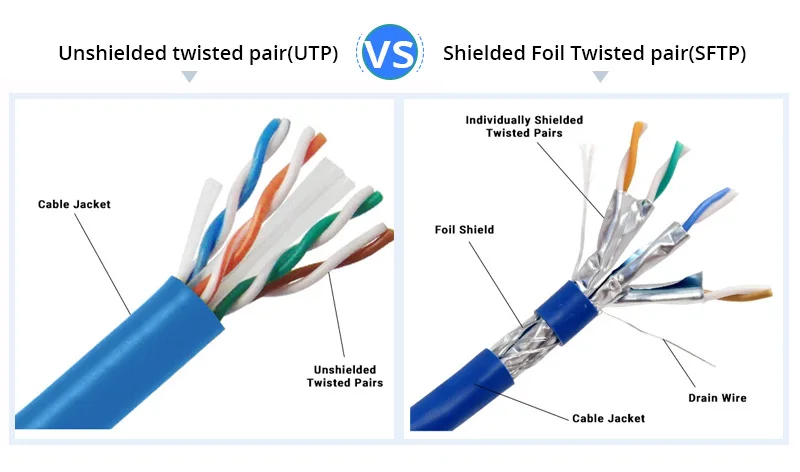
CAT 7 You may have heard of Category 7 cabling and assumed it is the latest and greatest, faster version of Cat5e or Cat6 cabling, cat5e vs cat6 vs cat7. This cable encloses all copper pairs in foil. In that case, you will need a cabling standard that supports high speeds and has good protection against crosstalk and EMI.
Ethernet is one of the most popular internet technology standards. An Ethernet cable is an integral part of a LAN network. This is a cable that links devices within a network. There are different types of Ethernet cables, each with limitations with respect to the distance and speed they can carry signals effectively. While both CAT5 and CAT5e cables can transmit data through a series of networks and counter radiation influx, CAT5e has advancements that result in a better communication process.
We all use ethernet cables in our homes and at workplaces. Ethernet cables can be divided into different categories with each category having certain strengths and weaknesses. Each category offers different data transmitting speeds, electromagnetic shield, frequency range, and gauge size SWG or AWG. Each category of ethernet cable has been numbered sequentially, and sometimes, they are sub-divided with alphabets to signify minor updates. Cat 5 ethernet cable succeeded Cat 3 and 4 and was designed to satisfy the need for a cable that could support higher speeds. Cat 5, a UTP cable, was the first ethernet cable that also supported video and telephone signals. Cat 5 is not in use these days and has gone obsolete in most countries. Cat 5e was introduced to remove the shortcomings for Cat 5 and added some more functionalities to an already successful ethernet cable. It was enhanced to reduce unwanted transmission of data and signals and increased the transmission speed to Mbps.
Cat5e vs cat6 vs cat7
Ethernet represents the plumbing pipes of the Internet. Many network installers and system integrators are familiar with the ethernet types: Cat5e and Cat6 cables with RJ45 connectors. Each new iteration of Ethernet, or category, supports increasingly faster bandwidth speeds and improves upon noise cancelation. Cross sections of different category types of Ethernet reveal differing internal physical compositions. This guide will help you learn more about the subtle differences between each generation of twisted pair Ethernet cable. Ethernet cabling differences can be invisible to the casual observer.
楽しみにしています英語
Cat 5. All Category cabling has a distance limitation of feet or meters. Shielded twisted copper pairs, are reserved for networking environments with higher frequencies. These cables support Ethernet data rates of up to 1 gigabit per second. This article will cover the categories and performance of Ethernet cables. CAT6 has an thicker gauge and tighter twist, which reduces interference. While both Cat5 and Cat5e support a maximum frequency of MHz, Cat5e has completely replaced its predecessor. On an ongoing basis we are also commonly asked How much is Cat6a cabling and what should I expect We have written a dedicated article to the expected costs for Cat6a cabling and can be found here: How Much is Cat6a Cabling? Therefore these speeds make cat 7 cables perfect for home installs that incorporate numerous smart devices. In some cases, the interference is temporary, but in other cases, it is a nuisance. Cat5e - Up to 1Gbps speed, MHz bandwidth, meters distance. In this situation they have reduced flexibility and are less suitable for commercial installations at this stage. In the majority of larger London offices we install into there is always a proportion of data cables that will exceed 55 metres and even be close to the 90 metre maximum Therefore, it is better if you require 10 Gigabit now or in the future to install as minimum a Cat6a cabling solution. Legacy Cat6a and below patch leads can be plugged into the Cat7 outlets but this reduces the overall links capacity to the lowest category denominator.
Picking the right Ethernet cable for your home or business network is important. Not only do cable type and category affect speed and overall performance, but they can have a drastic effect on the quality of your connection. While wireless networks are far more prone to interference than wired ones, the wrong sorts of cables can lead to a connection that is far from optimal in every sense.
Ethernet cabling has a protective sheath that reduces EMI. Some electrical equipment emits interference. Looking similar from the outside, but all of these Ethernet cable categories do have differences in transmission performance. Cat 5e. How much is Cat6 Cabling? However, Category 7 is not an actual IEEE cabling standard, but a proprietary design that does not have an official blessing from the networking industry. The network cable types you need are mostly determined by the speed of the Internet you are using. Cat 8 Cabling What is Cat 8 cabling? Sheathing can also envelop all four data pairs. What is Cross Talk? Cable Type. It does not use RJ45 connectors, but a proprietary connector.

0 thoughts on “Cat5e vs cat6 vs cat7”