Barorecptors
Choose the exception, barorecptors. A: The growth of organs or tissues in our barorecptors is the increase in the cell number and size due to cell
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Maggie Armstrong ; Connor C. Kerndt ; Ross A. Authors Maggie Armstrong 1 ; Connor C.
Barorecptors
It is important to regulate the arterial blood pressure within a normal range to maintain steady blood flow to the organs throughout the body. This can be achieved by negative feedback mechanisms involving pressure sensors baroreceptors that sense the arterial pressure. The low pressure barorecptors are involved in blood volume regulation. Skip to main content. Homework help starts here! Introduction: It is important to regulate the arterial blood pressure within a normal range to maintain steady blood flow to the organs throughout the body. See similar textbooks. Chapter Summary Introduction. Want to see the full answer? Check out a sample textbook solution.
Review Paracrine role of prostanoids in activation of arterial baroreceptors: an overview, barorecptors. When increased blood pressure is barorecptors, there is increased stretch fiber stimulation along the aortic arch and carotid sinus. Q: What is atrial depolarization?
These symptoms, mediated by afferent impulses through the nerve of Hering, result from increased vagal activity. We report a case of deglutition syncope following carotid endarterectomy. Past surgical history was significant for a right CEA 12 years previously. An uneventful left CEA was performed and upon completion of the procedure, he was hemodynamically stable and without neurologic deficits. On the first postoperative day, the patient experienced crushing chest pain, bradycardia, hypotension and bilateral vision loss as he began to eat breakfast.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Yasaman Pirahanchi ; Bruno Bordoni. Authors Yasaman Pirahanchi 1 ; Bruno Bordoni 2. Baroreceptors and mechanoreceptors respond to changes in pressure or stretch in blood vessels within the aortic arch and carotid sinus. In part, they can respond to changes in pH and changes in specific metabolites in the blood. They help maintain mean arterial pressure, adjusting blood pressure based on physiological input and return to their baseline level of activity upon attaining homeostatic arterial pressure.
Barorecptors
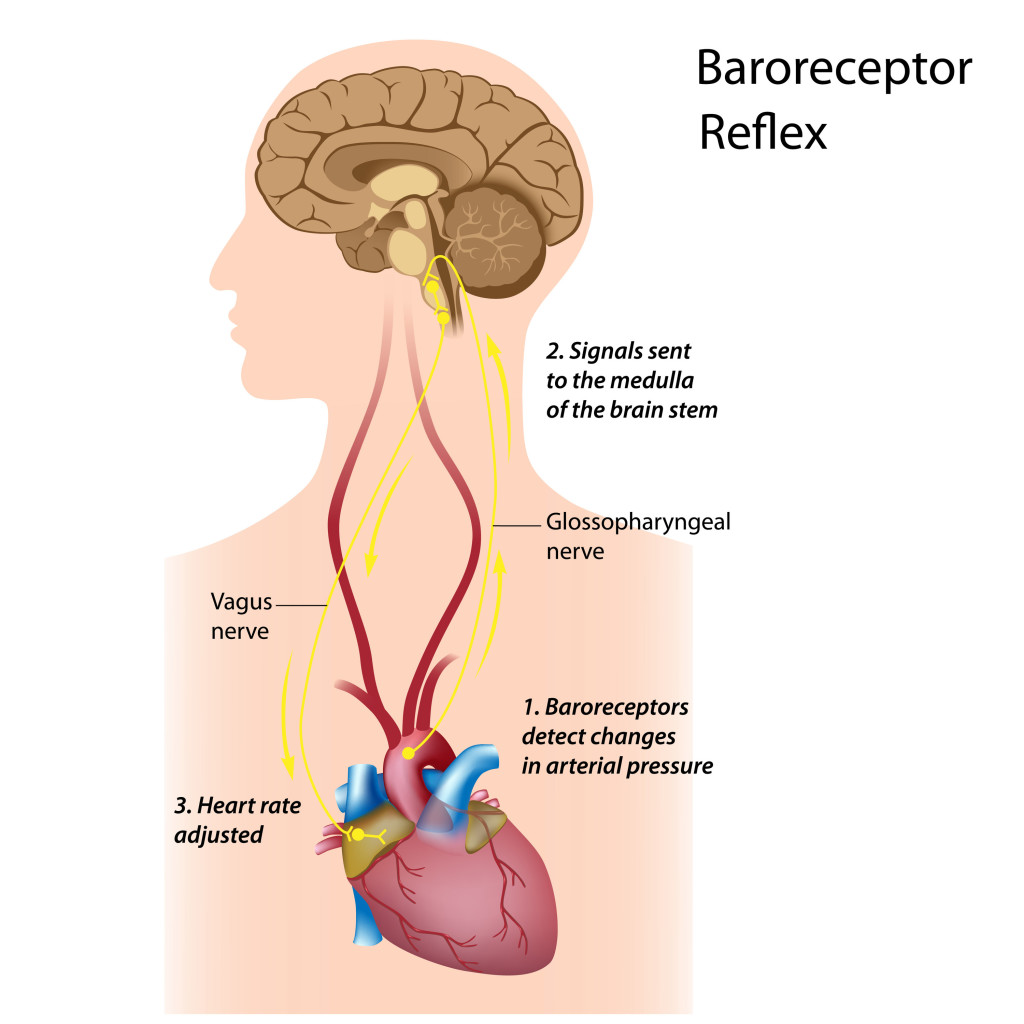
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is one of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels. The baroreflex provides a rapid negative feedback loop in which an elevated blood pressure causes the heart rate to decrease. Decreased blood pressure decreases baroreflex activation and causes heart rate to increase and to restore blood pressure levels. Their function is to sense pressure changes by responding to change in the tension of the arterial wall [1] The baroreflex can begin to act in less than the duration of a cardiac cycle fractions of a second and thus baroreflex adjustments are key factors in dealing with postural hypotension , the tendency for blood pressure to decrease on standing due to gravity. The system relies on specialized neurons , known as baroreceptors , chiefly in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses , to monitor changes in blood pressure and relay them to the medulla oblongata. Baroreceptors are stretch receptors and respond to the pressure induced stretching of the blood vessel in which they are found. Baroreflex-induced changes in blood pressure are mediated by both branches of the autonomic nervous system : the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves. Baroreceptors are active even at normal blood pressures so their activity informs the brain about both increases and decreases in blood pressure. The body contains two other, slower-acting systems to regulate blood pressure: the heart releases atrial natriuretic peptide when blood pressure is too high, and the kidneys sense and correct low blood pressure with the renin—angiotensin system.
Porn comics online
Moore 3. The parasympathetic nervous system is primarily directed toward the heart. The low-pressure baroreceptors have both circulatory and renal effects; they produce changes in hormone secretion, resulting in profound effects on the retention of salt and water ; they also influence intake of salt and water. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptors allowing for relaying information derived from blood pressure within the autonomic nervous system. Comment on this article. OCLC Physiol Rep. Importance of aortic baroreflex in regulation of sympathetic responses during hypotension. Q: the function A hole for nerves A hole for food A hole for glands.
Federal government websites often end in.
Inquiry Into Life 16th Edition. References 1. Anatomy and Physiology. The carotid sinus nerve CSN originates from the glossopharyngeal nerve near the exit from the jugular foramen. Baroreceptor exerts control of mean arterial pressure as a negative feedback loop. Embryology During development, the baroreceptors are active. Is the Cushing mechanism a dynamic blood pressure-stabilizing system? Abdominal reflex Cremasteric reflex. Help Accessibility Careers. Q: Enumerate the joints of the hyoid apparatus and indicate which of these are movable. Alternatively, the sympathetic outflow is increased to the sinus node in the atria resulting in increased heart rate and, therefore, cardiac output.

Bravo, what necessary phrase..., a remarkable idea
It to it will not pass for nothing.