Awg wire current rating
Installation of electrical wire can be hazardous and, if done improperly can result in personal injury or property damage.
The "gauge" is related to the diameter of the wire. The AWG standard includes copper, aluminum and other wire materials. Typical household copper wiring is AWG number 12 or Telephone wire is usually 22, 24, or The higher the gauge number, the smaller the diameter and the thinner the wire. The diameter of a stranded wire is larger than the diameter of a solid wire.
Awg wire current rating
Wires come in different thicknesses—i. For example, craft wire is thin to support bending, forming, and twisting into jewelry and other craftwork. The gauge of a wire refers to its thickness. Each gauge is represented by a number, with smaller numbers representing thicker wire gauges and higher numbers signifying thinner wires. American Wire Gauge AWG is a standard method of measuring and identifying cable thickness developed in the United States for electrically conductive wire. It is suitable for specifying gauges for round and solid conductive wires made from non-ferrous material. This knowledge can also be communicated between different parties, such as from the manufacturer to the consumer. When selecting an electrically conductive wire for an application, gauge is an important design consideration. However, the right gauge depends on a variety of factors. For example, electrical circuits with higher amperage ratings require thicker wires to accommodate the load without experiencing excessive heat buildup. Using wires that are too thin for the specified circuit amperage can result in wire failure or ignition. Avoiding these issues necessitates identifying the total amperage of a system—by calculating the effects of the planned load, the connected load, and the circuit length—and choosing a wire that is appropriate for it.
Inch of mercury Pounds per square inch Kilopounds per square inch. The "gauge" is related to the diameter of the wire.
For the 00, , etc. Similar to dB in signal and power levels. This estimate is based on nick-free soft annealed Cu wire having a tensile strength of pounds per square inch. Select Copper or Aluminum Copper Aluminum. Enter 1-way circuit length in feet the calculation is for the round trip distance. This chart of American Wire Gauge AWG wire sizes and rated ampacities is data intended for the pleasure of our readers only.
For the 00, , etc. Similar to dB in signal and power levels. This estimate is based on nick-free soft annealed Cu wire having a tensile strength of pounds per square inch. Select Copper or Aluminum Copper Aluminum. Enter 1-way circuit length in feet the calculation is for the round trip distance. This chart of American Wire Gauge AWG wire sizes and rated ampacities is data intended for the pleasure of our readers only. Typographical errors, etc. Please point out errors.
Awg wire current rating
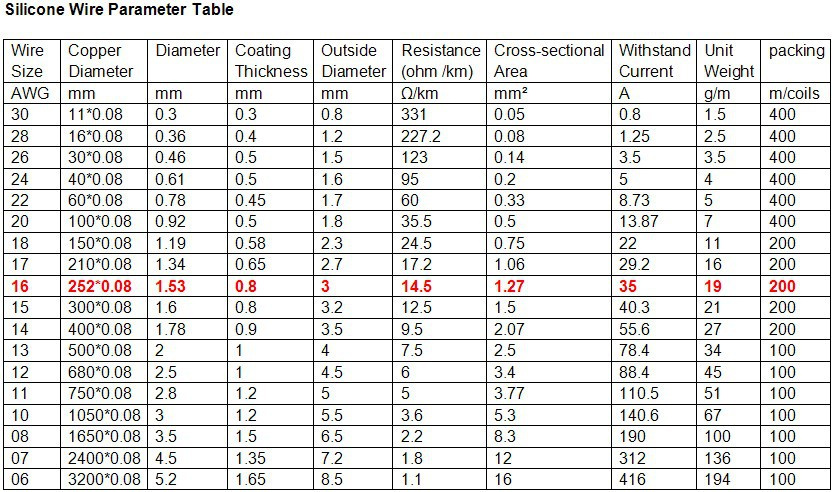
The AWG tables and charts are handy methods to specify the current carrying capacity of a conductor, its diameter, resistance, max current in amperes and other important parameters and characteristics. It is impossible to measure the exact amount of resistance in ohms of a wire having specific length for precise wire diameter. The AWG is used to exactly measure the diameter of a particular conductor such as solid, stranded, round and non-ferrous alloys or metals that do not contain any appreciable amounts of iron materials e. Aluminum, Copper etc.
Tweed radar loop
For additional information about our capabilities or assistance choosing a wire for your application, contact us or request a quote today. Note that the voltage drop does not depend on the input voltage, just on the resistance of the wire and the load in amps. Given its gauge, industry professionals can determine the following about a particular wire: Diameter. Retrieved In the table below, we outline all of the AWG cable sizes and their unique properties. Because there are also small gaps between the strands, a stranded wire will always have a slightly larger overall diameter than a solid wire with the same AWG. Wire gauge charts. Calculating Ampacity Needs: To calculate the load requirement for a circuit, first add up the wattages of all devices planned for the circuit. An older abbreviation for one thousand circular mils is MCM. The "gauge" is related to the diameter of the wire. Comparison with imperial unit system. Metric Wire Gauges see table below Metric Gauge : In the Metric Gauge scale, the gauge is 10 times the diameter in millimeters, so a 50 gauge metric wire would be 5 mm in diameter. The diameter doubles every time the gauge decreases by six levels e. Applications for Different Wire Gauges As each wire gauge carries different physical and electrical properties, they are generally suitable for different purposes. A circular mil is the area of a wire one mil in diameter.
If you have aluminum or copper-clad aluminum , it can carry 25A at 60 degrees C, 30A at 75 degrees C, and 35A at 90 degrees C.
This knowledge can also be communicated between different parties, such as from the manufacturer to the consumer. Area m 2 km 2 in 2 ft 2 miles 2 acres. The following chart is a guideline of ampacity or copper wire current carrying capacity following the Handbook of Electronic Tables and Formulas for American Wire Gauge. By definition, No. Weight kg f N lbf. This increases the effective resistance. Load Carrying Capacities see table below Definition : ampacity is the current carrying capability of a wire. Wire gauge to amperage chart. In the table below, we outline all of the AWG cable sizes and their unique properties. Comparison with imperial unit system. For example, craft wire is thin to support bending, forming, and twisting into jewelry and other craftwork. Make Shortcut to Home Screen?

It is remarkable, it is the valuable information
I am assured, that you are not right.