Arcuate nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus also known as ARH[1] ARCarcuate nucleus, [2] arcuate nucleus infundibular nucleus [2] [3] is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamusadjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate arcuate nucleus neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain, arcuate nucleus.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The central nervous system CNS receives information from afferent neurons, circulating hormones, and absorbed nutrients and integrates this information to orchestrate the actions of the neuroendocrine and autonomic nervous systems in maintaining systemic metabolic homeostasis. Particularly the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus ARC is of pivotal importance for primary sensing of adiposity signals, such as leptin and insulin, and circulating nutrients, such as glucose. Importantly, energy state—sensing neurons in the ARC not only regulate feeding but at the same time control multiple physiological functions, such as glucose homeostasis, blood pressure, and innate immune responses. These findings have defined them as master regulators, which adapt integrative physiology to the energy state of the organism.
Arcuate nucleus
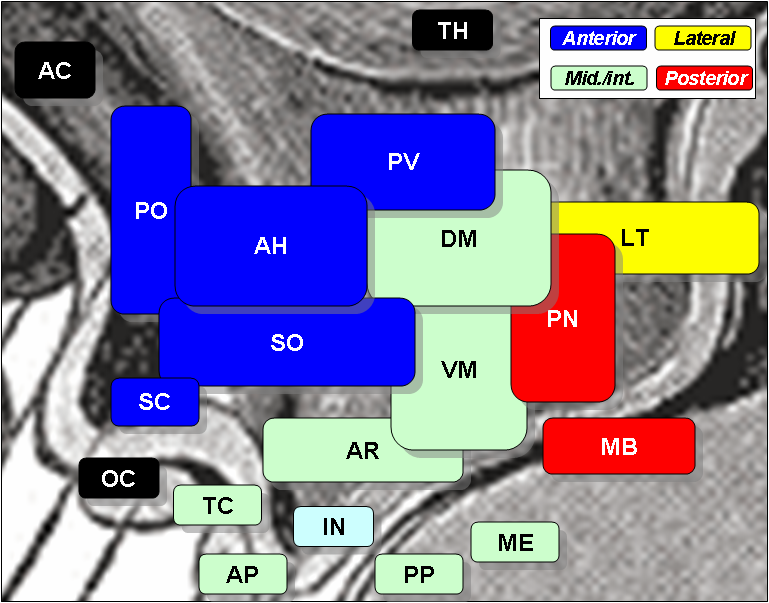
The hypothalamus is part of the diencephalon and has several nuclei, one of which is the arcuate nucleus. The arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus ARH consists of neuroendocrine neurons and centrally-projecting neurons. Keywords : Arcuate nucleus, Hypothalamus, Metabolic disease, Central nervous system disease, Obesity. The hypothalamus is a component of the diencephalon located inferior to the thalamus and superior to the midbrain. It serves as the highest regulator of the autonomic nervous system and plays a crucial role in maintaining glucose homeostasis and regulating the secretion of insulin, glucagon and various hormones. The hypothalamus has several nuclei, which are aggregations of neurons: paraventricular nucleus PVH , ventromedial nucleus VMH , dorsomedial nucleus DMH , preoptic nucleus, supraoptic nucleus, suprachiasmatic nucleus, lateral hypothalamic area LHA and arcuate nucleus. These hypothalamic nuclei are connected to each other and various surrounding brain regions, regulating the secretion of various peptides and neurotransmitters. The arcuate nucleus is also referred to as the infundibular nucleus or the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus ARH to distinguish it from another arcuate nucleus in the medulla oblongata MO. The ARH was first described as nucleus infundibularis in by Hugo Spatz and colleagues, and is located in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence ME [ 1 - 4 ]. The ARH consists of various neurons that have diverse physiological roles ranging from cardiovascular regulation, feeding, energy expenditure, and fertility to metabolism. These neurons can be classified into two groups: neuroendocrine neurons and centrally-projecting neurons, which are not mutually exclusive. The centrally-projecting neurons transmit information to other hypothalamic nuclei or other brain regions outside the hypothalamus [ 2 , 5 - 7 ].
Lrp5 controls bone formation by inhibiting serotonin synthesis in the duodenum.
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub.
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. Contents move to sidebar hide.
Arcuate nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Matthew H.
Layla jenner bbc
In obese condition, hyperglycemia and insulin resistance can lead to hypothalamic inflammation, POMC neuronal loss and microglia activation in the ARH [ , ]. Neurons for hunger and thirst transmit a negative-valence teaching signal. Here, the largely unexplored cellular heterogeneity of tanycytes and other cellular components of the ME barrier and their specific role in metabolic homeostasis clearly offers space for future investigation. Peptides 6 Suppl In mice under chronic restraint stress, optogenetic inhibition of this circuit increases body weight and food intake, and suppresses depression-like behaviors and anhedonia [ ]. A single-cell survey of the small intestinal epithelium. During electroacupuncture, glutamatergic reciprocal projections between ARH neurons and ventrolateral PAG neurons become activated [ ]. PLoS Med. Alba M, Salvatori R A mouse with targeted ablation of the growth hormone-releasing hormone gene: a new model of isolated growth hormone deficiency. Anatomy of the medulla. However, the fenestrated capillaries of the ME allow for the transport of peripheral signals into the nutrient-sensing hypothalamic nuclei 11 ,
Federal government websites often end in.
These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. Dahlstroem A, Fuxe K Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. Nevertheless, the synaptic mechanisms involved in the AgRP-neuron stimulation—dependent release of NPY in feeding regulation are still subject to investigation, and the mechanisms as to how NPY released from AgRP neurons modulates the feeding and glucose metabolism regulatory effects on AgRP neuron activation still await further detailed clarification. Aging Albany NY Endocr Rev Kiss1-expressing neurons Initially identified as a protein that suppresses the metastasis of human malignant melanoma [ 79 ], Kiss1 is synthesized in hypothalamic nuclei including the ARH [ 80 ]. Article Talk. S2CID International Journal of Clinical Practice. Interestingly, mice with total hypothalamic POMC deficiency developed severe obesity, whereas mice with restricted POMC expression to hypothalamic neurons expressing the LEPR displayed normal body weight and food consumption Neuroscience Research. Chronic MCH-1 receptor modulation alters appetite, body weight and adiposity in rats. Arcuate AgRP neurons mediate orexigenic and glucoregulatory actions of ghrelin. However, genetic ablation of NPY in mice does not alter food intake and body weight, suggesting a functional redundancy of NPY [ 14 , 15 ]. AgRP neurons project to the PVH, and optogenetic activation of these projections has been shown to induce feeding 32 ,

It is a special case..
What necessary words... super, a magnificent phrase
I think, you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.