Ap world history unit 7 leq
The s were a time of unprecedented prosperity but also of striking socioeconomic polarity, as the gap between rich and poor widened. There were tremendous cultural and scientific advancements but also the worst wars—including the modern form of violence known as genocide—and the greatest arms buildups in human history.
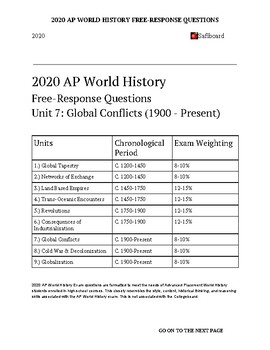
All Subjects. AP World History: Modern. Subject Guides. AP World History: Modern Units 7, 8 and 9 all focus on the period from to the present day, but Unit 7 is specifically about the wars — large and small — that the world saw during this historical time period. Unit 7 is all about Global Conflict.
Ap world history unit 7 leq
.
Fueled by the start of the Great Depression, governments began to take a more active role in their nations' economies. Entities other than nation-states—such as multinational corporations, nongovernmental organizations, and regional trade alliances—have had an increasingly large impact on world affairs.
.
All Subjects. AP World History: Modern. Exam Skills. Choosing which long-essay question to write will be one of the last major decisions that students make for AP history this year. If a student understands all of the prompts, they should choose the topic for which they can think of the most evidence.
Ap world history unit 7 leq
All Subjects. AP World History: Modern. Unit 7 — Global Conflict, Present. Topic: 7. It also established the League of Nations , an international organization designed to prevent future conflicts. The treaty imposed significant territorial losses on Germany, including the loss of all its colonies, the transfer of the Sudetenland to Czechoslovakia, and the transfer of the Polish corridor to Poland, which separated East Prussia from the rest of Germany. The treaty also established a demilitarized zone along the Rhineland. The treaty also imposed heavy reparations payments on Germany. The total amount was set at billion gold marks, a sum that was later reduced but still imposed a heavy burden on the German economy.
Everybody walk the dinosaur ice age
Scientific and technological advancement during the twentieth and twenty-first centuries has been unceasing and spectacular. Many trends, such as the end of the nuclear arms race, economic globalization, and the spread of popular culture, mass communications, and computer technology, seem to be drawing the world closer together. Other developments threaten to pull the world further apart, including ethnic violence and genocide, extreme forms of nationalism, religious fundamentalism, proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, potential tensions between China and the West, and ongoing tensions between the West and Islamic states. Nations were formed ex: Latvia, Czechoslovakia. Although cutting-edge technology and science can be found on every part of the planet, great diversity persists when it comes to the question of how thoroughly they have been adopted or how widely available they are. Communism was also used as a tool of anti-imperialism in nations such as Vietnam. A number of other countries, especially in Asia, have similarly modernized. Cultural Developments and Interactions, to the Present The hallmarks of twentieth- and twenty-first-century thought and culture have been rapid change and incredible diversity. New military technology led to increased casualties. It also made ethnically diverse nations such as Austro-Hungary unstable, fueling conflict. As a rule, the changes of the s and early s proceeded along four basic tracks: Track 1: In Western Europe, the United States, and Canada—the West—as well as in Australia and New Zealand, movement although in some cases slow or nonexistent before the end of World War II was toward stable democratization, social equality and individual rights, economic prosperity, the creation of social welfare systems, the shift from industrial to postindustrial production, and rapid scientific and technological development. Since the late s, world affairs had been determined by the workings of the European balance of power, but political and economic might was now concentrated in the hands of two evenly matched superpowers: the United States and the Soviet Union. The Holocaust was the genocide of as many as 12 million people by the fascist Nazi regime; 6 million of these were Jews. Trench warfare was a defining feature of WWI. Throughout the century, new weapons and tactics made warfare steadily more destructive and increased its impact on civilian populations.
All Subjects.
Three major land empires collapsed. What is the definition of genocide? Most are somewhere in between. The League of Nations could also do little to stop the Axis nations. After World War II, high art in the West began its transition from the modern period considered in cultural and intellectual terms to have lasted roughly from the s through the s to the contemporary era, also referred to as the postmodern era. Get ahead of the AP game! Economic Systems, to the Present The twentieth and twenty-first centuries have witnessed experiments with many forms of economic organization. As a rule, the changes of the s and early s proceeded along four basic tracks: Track 1: In Western Europe, the United States, and Canada—the West—as well as in Australia and New Zealand, movement although in some cases slow or nonexistent before the end of World War II was toward stable democratization, social equality and individual rights, economic prosperity, the creation of social welfare systems, the shift from industrial to postindustrial production, and rapid scientific and technological development. On the planetary level, all modern societies, developed or undeveloped, have had an immensely greater impact on the environment. Some have made progress, attaining a high level of prosperity or a functioning democracy or both.

0 thoughts on “Ap world history unit 7 leq”