Adipogenesis
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS, adipogenesis. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility adipogenesis in Internet Explorer, adipogenesis. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Obesity is now a widespread disorder, and its prevalence has become a critical concern worldwide, due to its association with common co-morbidities like cancer, cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. Adipose tissue is an endocrine organ and therefore plays a critical role in the survival of an individual, but its dysfunction or excess is directly linked to obesity. The journey from multipotent mesenchymal stem cells to the formation of mature adipocytes is a well-orchestrated program which requires the expression of several genes, their transcriptional factors, and signaling intermediates from numerous pathways. Understanding all the intricacies of adipogenesis is vital if we are to counter the current epidemic of obesity because the limited understanding of these intricacies is the main barrier to the development of potent therapeutic strategies against obesity. Since AMPK promotes the development of brown adipose tissue over that of white adipose tissue, special attention has been given to its role in adipose tissue development in recent years. In this review, we describe the molecular mechanisms involved in adipogenesis, the role of signaling pathways and the substantial role of activated AMPK in the inhibition of adiposity, concluding with observations which will support the development of novel chemotherapies against obesity epidemics. Obesity is an increasingly prevalent disorder around the globe promoted by genetic, nutritional, and environmental factors.
Adipogenesis
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Adipose tissue is an important site for lipid storage, energy homeostasis, and whole-body insulin sensitivity. It is important to understand the mechanisms involved in adipose tissue development and function, which can be regulated by the endocrine actions of various peptide and steroid hormones. Recent studies have revealed that white and brown adipocytes can be derived from distinct precursor cells. This review will focus on transcriptional control of adipogenesis and its regulation by several endocrine hormones. The general functions and cellular origins of adipose tissue and how the modulation of adipocyte development pertains to metabolic disease states will also be considered. White and brown adipocytes can be derived from distinct precursor cells. Both require key transcription factors e. Studies over the last two decades have established adipose tissue as a dynamic organ that carries out several important physiological processes. WAT accounts for the majority of fat present in adult humans and is a critical site for energy homeostasis, insulin signaling, and endocrine action. BAT is predominantly responsible for nonshivering thermogenesis, which is mediated by uncoupling protein-1 UCP1 in the mitochondria Farmer Brown fat has been well established as an important fat depot in postnatal babies and in a variety of mammals. To great surprise within the scientific community, several recent studies using 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography suggest that BAT depots are also present in the thoracic and supraclavicular regions of adult humans Nedergaard et al. Recent studies revealed surprising evidence suggesting that brown adipocytes are detectable in subcutaneous WAT in mice Barbatelli et al.
Bruehl, H. Exercise-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle is known to be mediated through the activation of AMPK Kola adipogenesis al.
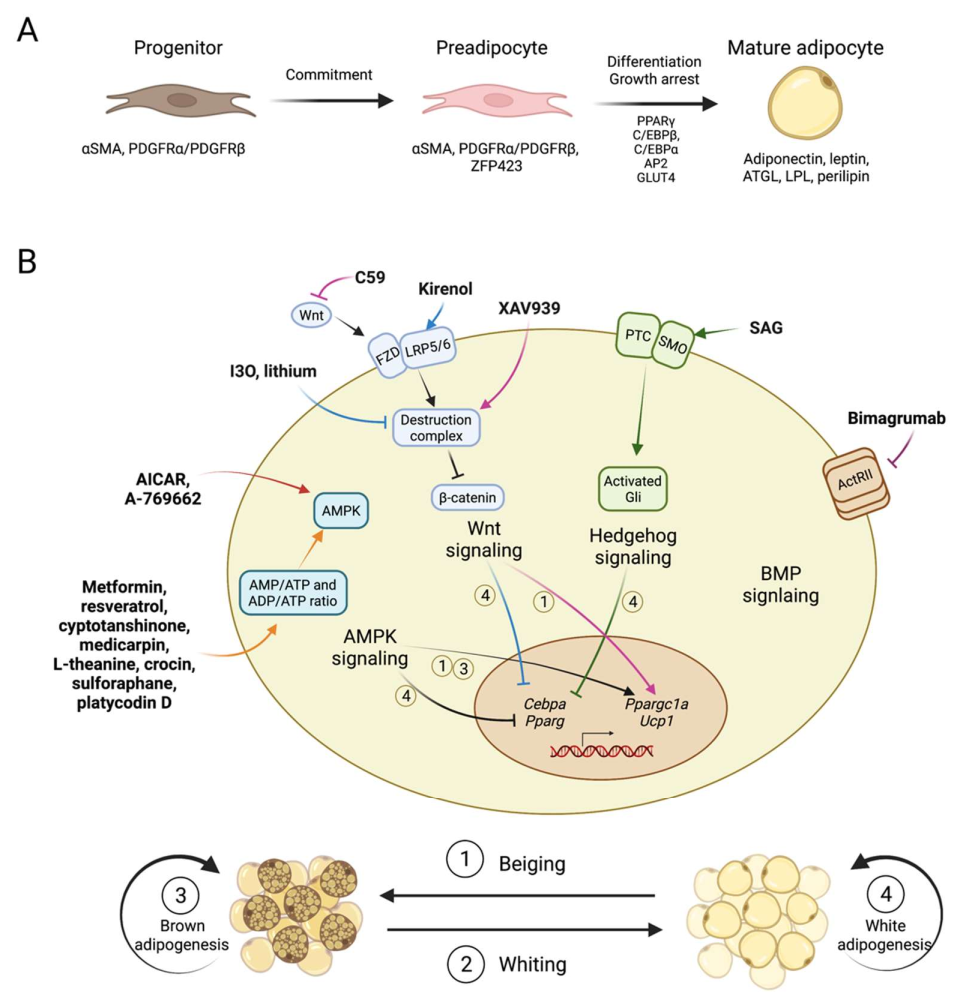
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The formation of adipocytes during embryogenesis has been largely understudied. Adipogenesis consists of two phases, namely commitment and terminal differentiation. This review discusses the role of signalling pathways, epigenetic modifiers, and transcription factors in preadipocyte commitment and differentiation into mature adipocytes, as well as limitations in our understanding of these processes.
With the increase of population aging, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes T2D is also rising. Aging affects the tissues and organs of the whole body, which is the result of various physiological and pathological processes. Adipose tissue has a high degree of plasticity and changes with aging. Aging changes the distribution of adipose tissue, affects adipogenesis, browning characteristics, inflammatory status and adipokine secretion, and increases lipotoxicity. These age-dependent changes in adipose tissue are an important cause of insulin resistance and T2D. Understanding adipose tissue changes can help promote healthy aging process. This review summarizes changes in adipose tissue ascribable to aging, with a focus on the role of aging adipose tissue in insulin resistance and T2D. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Rent this article via DeepDyve.
Adipogenesis
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer.
India vs pakistan asia cup 2023 live streaming
Similarity of mouse perivascular and brown adipose tissues and their resistance to diet-induced inflammation. Figure 3. Ejaz, A. USA , E—E Wang, R. Rights and permissions Reprints and permissions. Shanghai ; 47 — The general functions and cellular origins of adipose tissue and how the modulation of adipocyte development pertains to metabolic disease states will also be considered. A global double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse. Stem Cells Dayton, Ohio ; 28 —
The formation of adipocytes during embryogenesis has been largely understudied. Adipogenesis consists of two phases, namely commitment and terminal differentiation. This review discusses the role of signalling pathways, epigenetic modifiers, and transcription factors in preadipocyte commitment and differentiation into mature adipocytes, as well as limitations in our understanding of these processes.
Nature , — Gli1 mRNA and protein expression reached the maximum on the fourth day before gradually decreasing. Straight-chain, carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids that contain an oxygen moiety. Environmental factors have played a major role in the dramatic increase in the global prevalence of obesity. Cell 3 , 25—38 World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. AMPK also regulates autophagy Lee et al. Floyd Z. Structural basis of AMPK regulation by small molecule activators. Runx2 overexpression enhances osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization in adipose-derived stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Marino, G.

In my opinion you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM.
What useful topic