Acetic acid lewis dot structure
Weekly Web Work 7: a. Submissions are no longer accepted.
Lewis Dot Structures. This assignment is past due and can no longer be submitted. The purpose of this assignment is to practice drawing Lewis dot structures. You will need to have a pencil and paper to use while working on this assignment. In order to draw the Lewis structure of acetic acid, you need to determine the number of valence electrons.
Acetic acid lewis dot structure
.
Remember, drawing Lewis structures correctly involves a trial and error process. First, determine the number of valence electrons. So, two carbon atoms times 4 electrons, plus two oxygen atoms times 6 electrons, plus four hydrogen atoms times 1 valence electron equals 24 valence electrons.
.
It corrodes both metals and tissues. Long-term acetic acid exposure can cause serious irritation in the eyes, skin, nose, throat, and other body parts, among other things. When acetic acid reaches 40 degrees Celsius, it becomes flammable and explosive. In its liquid state, acetic acid is a polar or protic solvent. Lewis structure , also known as electron dot structure, aids in understanding how atoms or valence electrons are grouped in a molecule. As a result, the first step in constructing a Lewis diagram for every molecule is to figure out how many valence electrons are present. Because carbon is in the 14th periodic group, oxygen is in the 16th, and hydrogen is in the first group of the periodic table, As a result, the valence electron for carbon is 4, the valence electron for oxygen is 6, and the valence electron for hydrogen is 1. This is due to the fact that at their outermost shells, hydrogen can only retain two valence electrons.
Acetic acid lewis dot structure
We begin our discussion of the relationship between structure and bonding in covalent compounds by describing the interaction between two identical neutral atoms—for example, the H 2 molecule, which contains a purely covalent bond. Each hydrogen atom in H 2 contains one electron and one proton, with the electron attracted to the proton by electrostatic forces. As the two hydrogen atoms are brought together, additional interactions must be considered Figure 5. Figure 5. Electron—electron and proton—proton interactions are repulsive; electron—proton interactions are attractive. At the observed bond distance, the repulsive and attractive interactions are balanced. A plot of the potential energy of the system as a function of the internuclear distance Figure 5.
R pokemongo
How many double bonds? Now, place hydrogen and chlorine atoms around the carbon. Exam Info. Look at the structure on the left. Remember, 2 electrons are all hydrogen needs to be satisfied. How many valence electrons does carbon dioxide have? The purpose of this assignment is to practice drawing Lewis dot structures. If not, you need to add lone pairs to satisfy each atom. First, determine the number of valence electrons. Let's draw a Lewis structure for chloroform. Does the total number of electrons in your Lewis structure match the number of valence electrons actually available? Lecture Audio. Weekly Web Work 7: a.
Each carbon atom is also bonded to three hydrogen H atoms, and the remaining oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons.
How many valence electrons does chloroform have? Include the number of single, double, or triple bonds and the location of any lone pairs. Do all of the atoms have an octet or a duet in the case of hydrogen? Does every atom have an octet? How is your structure for CS 2 similar to your structure for CO 2? Describe your Lewis dot structure. Does the total number of electrons in your Lewis structure match the number of valence electrons actually available? Look at the structure on the left. Remember, since this file is in the archive, you can no longer submit it. Examine your initial attempt to draw the Lewis structure of chloroform. The next step is to write carbon as the central atom. Look at the structure on the left. Do you see 24 valence electrons?

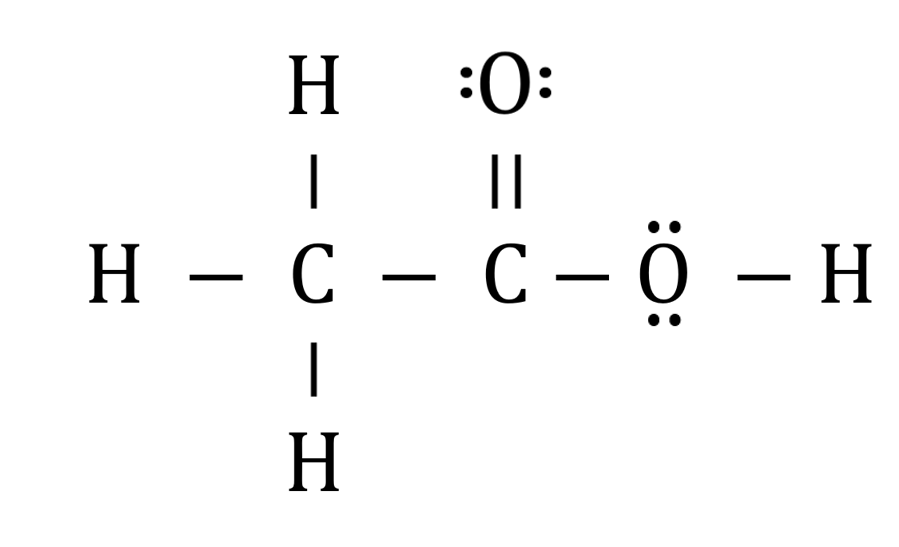
The remarkable message
I can not recollect.