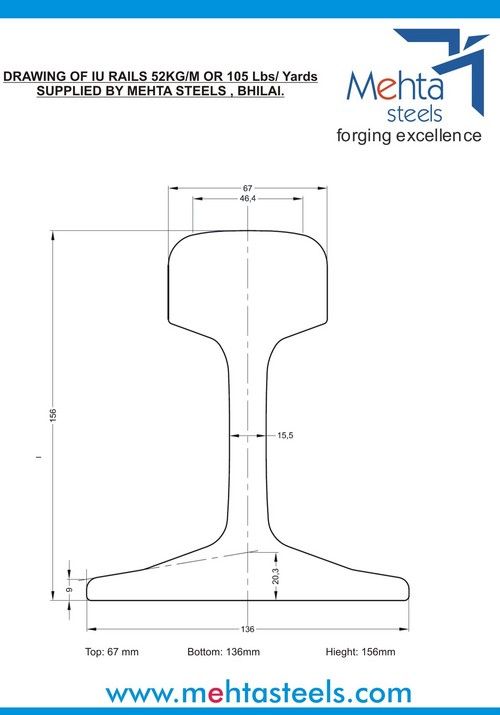
52 kg rail height
Post a Comment.
Last updated on Mar 30, Get Started. SSC Exams. Banking Exams. Teaching Exams. Civil Services Exam. Railways Exams.
52 kg rail height
The permanent way sections are classified by IR according to the maximum speed or more precisely, the maximum speed proposed for the immediate future that the tracks are capable of supporting. In most cases this classification is more an indication of the priority of the route and IR's plans for it in the future, rather than an indication of the speeds allowed on it today. Also, some small stretches of a line may have much higher or lower allowed speeds than the classification of the line might indicate because of local conditions, mountainous terrain, sharp curves, etc. These are:. In , there were mentions of the Ratnagiri - Sawantwadi section of KR being included in the A class, but no confirmation of this was found. C Class : This is not really a speed-rated class, but is the classification used for suburban sections of metropolitan areas. These lines cover many sections in Central India where mining and related industries are common. Lines in this class also include many feeder and branch lines that connect to those in the A and B class. An exhaustive list of these lines can be found here. D Class : This class is essentially same as above, except that the annual traffic density is lower than 20 GMT. E Class : For all other branch lines and sections that are not classified as above. The last few editions of the Permanent Way Manual have done away with this class and merged these lines with either D or D special. In addition to the above, these MG sections were in the 'Q' class in incomplete list :. This category was further broken down into three classes based on traffic density: R-1, R-2, and R-3 in decreasing order of traffic carried.
BSF Head Constable. NCL Staff Nurse.
The rail profile is the cross sectional shape of a railway rail , perpendicular to its length. Early rails were made of wood, cast iron or wrought iron. All modern rails are hot rolled steel with a cross section profile approximate to an I-beam , but asymmetric about a horizontal axis however see grooved rail below. The head is profiled to resist wear and to give a good ride, and the foot profiled to suit the fixing system. Unlike some other uses of iron and steel, railway rails are subject to very high stresses and are made of very high quality steel.
Requirements for an Ideal Rail Section. The requirements for an ideal rail section are as follows. The rail should have the most economical section consistent with strength, stiffness, and durability. The requirements, as well as the main considerations, for the design of these rail components are as follows. Head : The head of the rail should have adequate depth to allow for vertical wear.
52 kg rail height
Rails are the members of the track laid in two parallel lines to provide an unchanging, continuous, and level surface for the movement of trains. To be able to withstand stresses, they are made of high-carbon steel. Standard rail sections, their specifications, and various types of rail defects are discussed in this section. Rails are similar to steel girders. They perform the following functions in a track:. The friction between the steel wheel and the steel rail is about one-fifth of the friction between the pneumatic tyre and a metalled road.
Tattoo london skyline
Telangana High Court Examiner. Start Now. BSF RO. For some more information, see: Determining the Stress-Free Temperature in the field. They act to trap and stop, or slow down falling or sliding rocks and boulders so that they either do not fall all the way down, or lose their kinetic energy and fall without infringing the tracks. Typically the patrol may cover 6km - 10km of track. Bihar Police Prohibition Sub Inspector. It can be set in trench grooves cut into an existing asphalt road bed for Light Rail trams. The weight of the sleeper and the rail may not be related to each other. Maharashtra Zilla Parishad Supervisor.
The permanent way sections are classified by IR according to the maximum speed or more precisely, the maximum speed proposed for the immediate future that the tracks are capable of supporting. In most cases this classification is more an indication of the priority of the route and IR's plans for it in the future, rather than an indication of the speeds allowed on it today. Also, some small stretches of a line may have much higher or lower allowed speeds than the classification of the line might indicate because of local conditions, mountainous terrain, sharp curves, etc.
Westminster: Tothill Press. BDL Management Trainee. Uttarakhand Patwari. These have a design life of over 20 years. E Class : For all other branch lines and sections that are not classified as above. Several high traffic junctions like Wardha on the Nagpur - Mumbai line have had their layouts modified to feature easier curves and high-speed turnouts featuring modified thick web switches. Maharashtra Zilla Parishad Health Worker. Based on this the maximum permissible speed is specified for each section of a route. Delhi Higher Judicial Service. Contents move to sidebar hide. Konkan Railway has developed something they call self-stabilising track, which aims to reduce or even eliminate the problem of ballast being de-compacted and dispersing under the action of vibrations set up by moving trains. Navy AA. Steel channel sleepers were prone to corrosion and also had issues with their large more than 10 fitting points, as well as some problems with track-circuiting. AP Police SI.

So simply does not happen
It is a pity, that now I can not express - I am late for a meeting. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think.